The Real Impact of Quality Assurance in Radiology
Quality assurance (QA) in radiology isn't just a matter of checking off boxes; it's the foundation upon which accurate diagnoses, effective treatments, and positive patient outcomes are built. Robust QA processes directly influence clinical decisions by ensuring the reliability and precision of image interpretation. This can significantly reduce diagnostic errors, preventing unnecessary procedures and reducing patient anxiety.
For instance, a well-implemented QA program might identify a recurring error in the image acquisition process. Correcting this error would lead to clearer images and more accurate interpretations, ultimately resulting in better patient care and more effective use of resources.
How QA Transforms Patient Care
The benefits of effective QA in radiology extend far beyond simply meeting regulatory requirements. Strong QA programs contribute to:
-
Reduced Diagnostic Errors: By ensuring images are captured and interpreted accurately, QA minimizes the chances of misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment plans.
-
Improved Patient Safety: Accurate diagnoses mean patients receive the correct treatment promptly, minimizing potential harm from unnecessary or delayed interventions.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined QA processes reduce the need for rework and optimize workflow, allowing radiologists to dedicate more time to complex cases and patient care.
-
Increased Confidence: Radiologists can practice with greater confidence, knowing their interpretations are supported by stringent quality controls.
This increasing focus on quality in radiology is reflected in the market. The global radiology report quality assurance services market was valued at USD 63.4 million in 2024 and is projected to expand at a substantial compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This growth clearly demonstrates the growing recognition of the critical role accurate diagnostic information plays in patient care. For a deeper look at the radiology QA market, follow this link: Learn more about the radiology QA market.
Building a Culture of Quality
Effective QA also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within radiology departments. This empowers radiologists to pinpoint areas for enhancement and contribute to ongoing process refinement. By promoting open communication and feedback, departments can proactively address potential problems before they impact patient care. This proactive approach is vital for keeping pace with advancements in imaging technology and upholding the highest standards of diagnostic accuracy. Ultimately, a strong quality culture creates a more engaged and effective radiology team committed to providing the best possible care for every patient.
Building QA Programs That Actually Work
Implementing a quality assurance (QA) program in radiology isn't just about checking off requirements. It's about building a system that genuinely improves accuracy, efficiency, and most importantly, patient care. This involves moving beyond the theoretical and implementing practical, real-world approaches.
Implementing Meaningful Peer Review
Effective radiology QA programs often rely on peer review. However, it's crucial to approach this process carefully to avoid creating a defensive environment. Instead of solely focusing on finding mistakes, peer review should be viewed as a collaborative learning experience. This encourages open communication and the sharing of insights, ultimately boosting diagnostic accuracy and establishing a culture of continuous improvement.
Defining Quality Metrics
Clear quality metrics are essential for gauging the effectiveness of any QA program. These metrics should do more than just track compliance; they should actively drive improvement. For instance, monitoring turnaround times for critical results can identify workflow bottlenecks and pinpoint areas for optimization. This dual emphasis—quality and efficiency—leads to noticeable enhancements in patient care and departmental performance.
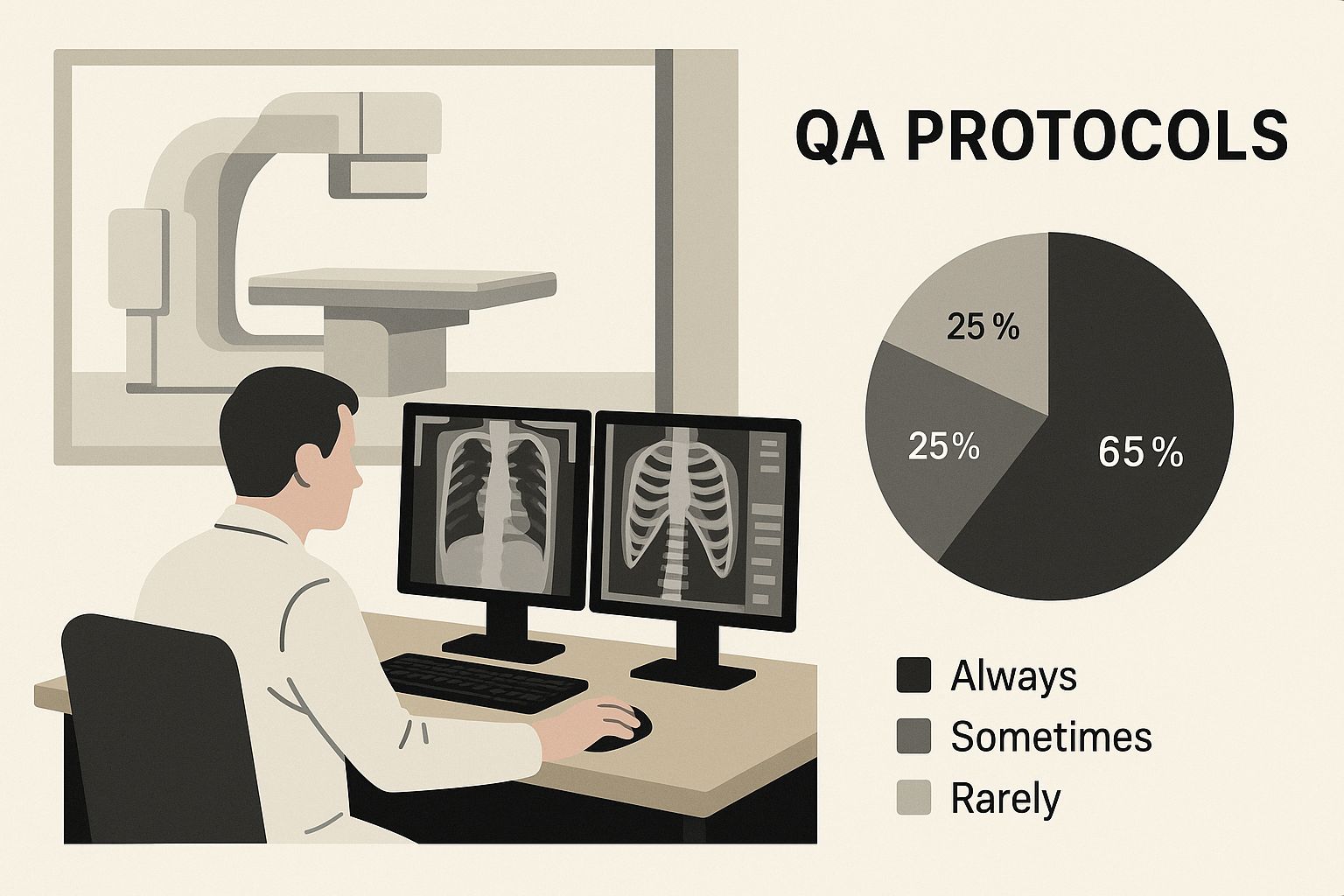
The infographic above shows how QA protocols can be visually incorporated into the radiology workflow. This visual reminder reinforces the importance of QA and promotes consistent application. By integrating quality control into daily operations, as demonstrated in the image, quality assurance becomes an embedded element of the diagnostic process, rather than a separate chore.
Integrating QA into Daily Workflows
Effective QA needs to be seamlessly woven into daily routines. This takes careful planning and consideration of current workflows. For more information on streamlining processes, check out this article on workflow automation in healthcare. Integrating QA checks within Radiology Information Systems (RIS) allows departments to automate data collection and simplify reporting. The RIS market is expected to expand significantly, growing from USD 1.07 billion in 2024 to USD 2.17 billion by 2033, underscoring its growing significance. More detailed statistics can be found here.
To better understand the key components of effective QA programs and their real-world impact, the following table provides a detailed comparison:
Essential Components of Effective QA Programs
A comparison of critical elements that make radiology quality assurance programs succeed in practice
| Component | Real-World Impact | Implementation Challenges | Success Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaningful Peer Review | Improved diagnostic accuracy, collaborative learning environment | Fostering a culture of open communication, avoiding defensiveness | Increased identification of learning opportunities, positive feedback from staff |
| Clearly Defined Quality Metrics | Identifies areas for optimization, enhances patient care and departmental performance | Selecting appropriate metrics, tracking and analyzing data effectively | Measurable improvements in turnaround times, reduced error rates |
| Seamless Workflow Integration | Streamlines processes, automates data collection | Adapting existing workflows, integrating with RIS | Automated reporting, improved efficiency |
| Quality Champions | Promotes the value of QA, encourages buy-in from colleagues | Identifying and empowering champions, fostering a culture of shared responsibility | Increased participation in quality improvement initiatives, improved departmental morale |
This table highlights the interconnected nature of these components. Successful QA programs depend on a synergy between peer review, clear metrics, integrated workflows, and engaged quality champions.
Cultivating Quality Champions
Top-performing institutions nurture quality champions within their radiology departments. These individuals are strong advocates for quality assurance, promoting its importance and motivating colleagues to embrace it. By building a culture of shared accountability for quality, these champions drive positive change from within. This bottom-up method empowers all team members to actively participate in quality improvements. This shared ownership transforms QA from a mandated task into a core departmental value, which when combined with effective error classification systems that prioritize learning over blame, sets the stage for a truly effective QA program.
Tech Tools Transforming Radiology Quality
Technology is constantly evolving, and the field of radiology is no exception. Quality assurance (QA) is being significantly impacted by tools like artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and advanced analytics. These technologies offer real, measurable improvements in diagnostic accuracy and overall efficiency, directly benefiting patient care. Let's explore their practical applications within radiology departments.
AI-Powered Diagnostics
AI algorithms are proving invaluable in image analysis. They can detect subtle anomalies that might be missed by the human eye, enabling earlier and more accurate diagnoses. For example, AI can identify patterns in medical images that suggest specific diseases, assisting radiologists in making quicker, more informed decisions. This allows radiologists to dedicate their expertise to complex cases and challenging diagnoses, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Automation for Efficiency
Automation streamlines radiology workflows, minimizing manual tasks and reducing the risk of human error. Consider implementing automation testing best practices when evaluating your QA program. Automated systems can manage various tasks, from patient scheduling and image acquisition protocols to preliminary image analysis. This frees up radiologists to concentrate on image interpretation and direct patient interaction. Furthermore, automation standardizes processes, increasing consistency and reliability in image quality and interpretation.
Advanced Analytics for Quality Improvement
Advanced analytics provide essential insights into quality metrics by identifying trends and patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed. This data-driven approach empowers departments to pinpoint areas for performance enhancement. By tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), departments can identify inefficiencies and develop targeted improvement strategies. This approach supports evidence-based decision-making and promotes continuous quality improvement.
Implementing Technology Effectively
Successfully integrating these technologies requires careful planning and a focus on augmenting, rather than disrupting, existing workflows. Effective implementation includes training staff on new tools, ensuring seamless integration with current systems, and establishing clear protocols for data management and analysis. Institutions should prioritize integrating these technologies into the daily routines of radiologists and other staff members. Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) of these technologies is crucial for demonstrating their value and ensuring continued support.
Choosing the Right Tools
Choosing the right technology involves selecting solutions that address specific needs and integrate smoothly with existing workflows. This often requires a period of evaluation and pilot testing. A department might, for instance, test different AI algorithms to determine which performs best for a specific type of imaging study. Assessing the performance of different technologies in a real-world setting allows departments to make informed decisions about which tools to adopt, ensuring that the chosen technologies genuinely contribute to improving quality outcomes.
Quality Innovations Amid Radiologist Shortages

The demand for medical imaging is steadily increasing, but a global shortage of radiologists presents a significant challenge. This shortage puts immense pressure on current radiology staff and can negatively impact patient care. Developing robust quality assurance (QA) processes is essential to maintain high standards and improve efficiency with limited resources.
This radiologist shortage is a pressing issue. A critical challenge facing the radiology sector is the increasing lack of qualified professionals worldwide. For example, the UK is facing a 30% deficit in clinical radiology consultants, which translates to approximately 1,962 vacant positions according to the 2023 Royal College of Radiologists' census. Globally, over 80% of health systems are struggling with staffing shortages in radiology departments, putting timely diagnosis and treatment at risk. Find more detailed statistics here.
Smart QA: Working Smarter, Not Harder
Instead of viewing quality assurance as an added burden, innovative radiology departments are integrating smart QA processes that contribute to increased productivity. These streamlined processes minimize rework by identifying errors early, reducing the time spent on corrections. This allows radiologists to focus their expertise on complex cases and critical interpretations, optimizing their time and improving overall departmental efficiency.
Identifying High-Risk Studies
Prioritizing cases based on risk is an effective strategy. By implementing a system for identifying high-risk studies, departments can concentrate resources where they are most needed. For example, certain imaging procedures or specific patient demographics may require closer attention. This targeted approach maximizes the impact of limited resources while ensuring high-quality care for vulnerable patients.
Empowering Support Staff
Support staff are vital for maintaining efficient workflows. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities and providing appropriate training, departments can empower support staff to handle more routine tasks. This frees up radiologists to focus on specialized tasks like complex image interpretation and patient consultations. This approach not only improves efficiency but also strengthens the entire radiology team.
Peer Learning for Continuous Improvement
Structured peer learning systems provide a powerful mechanism for continuous improvement. Regular peer review sessions allow radiologists to share knowledge, discuss challenging cases, and identify areas for professional growth. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of shared learning and improves the diagnostic skills of the entire team.
Data-Driven Quality Improvement
Quality metrics offer valuable insights into departmental performance. Forward-thinking departments use these metrics not only to measure performance, but also to identify systemic inefficiencies. By analyzing data on turnaround times, error rates, and other key indicators, departments can pinpoint areas for workflow improvement. Addressing these inefficiencies enhances productivity and improves patient care. This data-driven approach creates a cycle of continuous improvement in both quality assurance and productivity.
Measuring What Actually Matters in Radiology QA
Beyond simple error counts, what truly reflects quality in radiology? This section explores key metrics that go beyond basic discrepancy rates and drive meaningful improvements in diagnostic imaging. We'll examine how leading institutions balance statistical validity with real clinical impact.
Choosing the Right Metrics for Quality Assurance Radiology
Selecting the right quality metrics is paramount for any successful quality assurance (QA) radiology program. These metrics should not only track errors but also offer insights into how to improve processes and patient care. Simply counting the number of missed fractures isn't enough. A more effective approach would analyze the types of fractures missed, the imaging modalities used, and the experience levels of the interpreting radiologists.
This deeper dive into the data reveals patterns that can inform targeted interventions. These might include additional training on specific fracture types or adjustments to image acquisition protocols.
Collecting Quality Data Efficiently
Gathering quality data doesn't have to overwhelm radiologists. Smart strategies can streamline the process and minimize disruptions to workflow. Integrating data collection directly into the Radiology Information System (RIS) is one such strategy. This allows for automatic capture of relevant data points, minimizing manual entry and reducing the burden on staff.
Another approach involves using standardized templates for peer review, making feedback more consistent and easier to analyze. These approaches help create a sustainable system for collecting data.
To understand the impact of choosing the right metrics, let's examine a few key performance indicators and what they reveal about a radiology department's performance.
To better illustrate the variety and impact of quality metrics in radiology, the following table provides a comparison of some effective performance indicators.
Quality Metrics That Drive Real Improvement
A comparison of effective performance indicators that successful radiology departments use to enhance quality
| Metric Type | What It Reveals | Implementation Complexity | Action Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discrepancy Rate | Percentage of reports requiring amendment after initial interpretation. | Low | Moderate – Identifies areas needing review, but doesn't pinpoint specific causes. |
| Turnaround Time (TAT) | Time elapsed between exam completion and report availability. | Moderate – Requires time-tracking systems. | High – Directly impacts patient care and satisfaction. Can reveal workflow bottlenecks. |
| Peer Review Scores | Qualitative assessment of report quality, accuracy, and completeness. | Moderate – Requires structured review processes and trained reviewers. | High – Can identify individual and systemic areas for improvement. |
| Patient Satisfaction Scores | Patient feedback on communication, comfort, and overall experience. | Moderate – Requires survey mechanisms. | High – Reflects patient-centered care and can reveal areas for improvement in communication and service delivery. |
As shown in the table, metrics vary in complexity and potential for driving improvement. While simple discrepancy rates provide a basic overview, focusing on metrics like turnaround time or peer review scores provides deeper insights into departmental performance. These nuanced metrics enable more effective interventions and ultimately lead to more meaningful improvements in patient care.
Analyzing Patterns, Not Just Errors
Counting errors is a starting point, but true improvement comes from analyzing patterns. Imagine a scenario where a radiology department notices a higher-than-average rate of discrepancies in chest X-ray interpretations. Instead of simply flagging individual errors, they analyze the data and discover that the discrepancies frequently occur in cases involving subtle lung nodules.
This valuable insight allows for targeted interventions. This might involve specific training focused on subtle lung findings or the implementation of AI-powered tools. Solutions like Aidoc can be particularly useful in enhancing nodule detection. This targeted approach addresses the underlying issue and leads to more significant improvements in diagnostic accuracy.
Turning Metrics into Action
Data is only useful if it leads to action. Clearly defined processes are needed to translate quality metrics into practical improvements. One approach involves regular review meetings where the QA team discusses key metrics and develops targeted interventions.
These interventions could include adjusting imaging protocols, providing additional training, or implementing new technologies. Tracking the effectiveness of these interventions is crucial. This iterative process of measurement, analysis, and adjustment is essential for continuous quality improvement.
Communicating Quality Data Effectively
Presenting quality data effectively demonstrates the value of QA initiatives. Different stakeholders have different needs. Department chairs might want an overview of key performance indicators, while hospital administrators might be more interested in the impact of QA on cost savings.
Creating tailored reports that address the specific interests of each audience is crucial. This means avoiding jargon and focusing on the key takeaways. For example, a report for hospital administrators might highlight how improved diagnostic accuracy through QA has reduced the need for repeat imaging, resulting in significant cost savings. Clear communication builds support for QA efforts.
Creating a Quality Culture That Radiologists Embrace
Effective quality assurance (QA) in radiology isn't an add-on; it's the foundation of a thriving department. It's about weaving QA into the very fabric of the culture, so radiologists see it as a vital part of patient care, not a chore. This section explores how leading radiology departments build this quality-focused culture.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Introducing new QA processes can be challenging. Radiologists, comfortable with familiar routines, may resist change. Open communication is essential. Explain the benefits clearly, emphasizing how improved QA leads to fewer errors, smoother workflows, and ultimately, better patient outcomes. This reinforces the message that QA is central to excellent care.
Engaging Radiologists as Quality Champions
Building a quality culture means finding and supporting quality champions within the department. These individuals are passionate about QA and inspire their colleagues to embrace quality improvement initiatives. They can lead training, share best practices, and encourage ownership of quality. This grassroots approach can dramatically shift departmental attitudes.
Transforming Error Detection into Learning Opportunities
Traditionally, finding errors might have been viewed negatively. A positive quality culture changes this. Errors become valuable lessons, helping radiologists identify areas for improvement and refine their skills. This requires a system where errors are discussed openly and constructively, without blame, creating a safe space for continuous growth.
Celebrating Quality Achievements
Recognizing and celebrating success reinforces the value of quality. Acknowledging improvements in metrics like reduced error rates or faster turnaround times builds pride and motivates continued effort. This can be done through departmental announcements, team meetings, or even small gestures of appreciation. The key is to celebrate achievements while maintaining a collaborative spirit.
Making Quality Visible in Daily Work
Integrating quality into daily routines makes it a constant focus. Visual reminders, like posters or dashboards displaying key quality metrics, can be effective. Regular discussions during team meetings also help. Integrating quality checks within a RIS system further reinforces its importance and promotes adherence to QA protocols.
Navigating Challenges and Changing Established Practices
Changing established routines isn't always easy. Resistance to new workflows or technologies is normal. Overcoming these challenges takes patience, persistence, and adaptability. Open communication and collaboration are essential, including seeking feedback from radiologists and incorporating their suggestions. This collaborative approach ensures buy-in and facilitates smoother transitions, ultimately leading to a robust quality culture that benefits both radiologists and their patients.
The Future of Quality Assurance in Radiology
The field of radiology is constantly evolving, and quality assurance (QA) needs to keep up. This means not only adapting to new technologies, but also anticipating future trends and building adaptable quality systems. Let's examine the emerging trends reshaping quality assurance in radiology, from AI-driven peer review to patient-centered metrics.
AI-Enhanced Peer Review
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming peer review processes. AI algorithms can analyze images, identify potential discrepancies, and flag them for radiologist review. This prioritizes cases needing closer scrutiny, making peer review more efficient and effective. This approach augments, not replaces, human judgment, allowing radiologists to focus their expertise where it’s most needed.
Patient-Centered Quality Metrics
The future of QA involves shifting toward metrics that directly reflect patient experience and outcomes. Instead of solely focusing on internal measures like turnaround time, future QA programs will incorporate metrics such as patient satisfaction with communication and their perception of care quality. This patient-centric approach aligns QA with improving patient well-being and involves gathering feedback directly from patients to inform QA initiatives.
Evolving Regulatory Requirements and Reimbursement Models
The regulatory landscape for radiology is dynamic. New regulations and evolving reimbursement models are increasingly linked to quality performance. QA programs must be flexible and adaptable to meet these changing requirements. Staying informed about updates to guidelines and incorporating them into QA processes is crucial. This proactive approach ensures compliance and positions radiology departments for success.
Increasing Transparency Expectations
Patients and payers are demanding greater transparency in healthcare. This involves making quality data accessible and understandable. Radiology departments need to develop clear and concise ways to communicate quality metrics to patients and other stakeholders, fostering trust and demonstrating a commitment to quality.
Building Adaptable Quality Systems
Rapid technological advancements require adaptable quality systems. Instead of overhauling QA programs with each new innovation, departments need frameworks that easily integrate new technologies. This might involve modular systems or platforms that allow for easy updates and integration with new tools. This forward-thinking approach ensures QA programs remain effective and relevant.
Maintaining Clinical Judgment in an Automated Environment
As AI and automation become more prevalent, maintaining the central role of clinical judgment is critical. While powerful tools, these technologies should augment, not replace, radiologist expertise. QA processes should ensure human oversight remains a core component, guaranteeing clinical decisions are based on both technological insights and professional experience.
Balancing Innovation with Proven Fundamentals
While embracing new technologies is essential, core QA principles remain crucial. Fundamentals like peer review, error analysis, and continuous improvement are still critical, even in an automated environment. Balancing innovation with proven QA fundamentals is key to building a successful and sustainable QA program.
Ready to enhance your radiology department's quality assurance? PYCAD offers AI solutions tailored to the needs of radiology departments. From AI-powered peer review assistance to advanced analytics for quality improvement, PYCAD helps build a more efficient, accurate, and patient-centered radiology practice. Visit PYCAD to learn more.






