Artificial intelligence is no longer a concept from science fiction; it's a powerful force actively transforming the healthcare landscape. From the diagnostic lab to the operating room and a patient's home, AI is introducing unprecedented levels of precision, efficiency, and personalization. The core promise of ai in healthcare benefits lies in its ability to analyze vast, complex datasets faster and more accurately than humanly possible, unlocking insights that lead to earlier diagnoses, more effective treatments, and streamlined operations. This shift is not just an incremental improvement but a fundamental revolution moving medicine towards a future that is more predictive, preventive, and patient-centric.
Successfully integrating these advanced tools requires a robust digital foundation. The broader IT services healthcare transformation is crucial for implementing and scaling the AI-driven solutions that deliver these benefits system-wide. Without a solid IT infrastructure, even the most innovative algorithms cannot reach their full potential.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the seven most significant benefits of AI in healthcare. We'll move beyond theory to provide practical examples, actionable insights, and a clear view of how these innovations are creating better outcomes for patients, providers, and researchers alike. Get ready to discover how AI is making modern medicine smarter, faster, and more effective.
1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy and Early Disease Detection
One of the most transformative AI in healthcare benefits is its ability to dramatically improve diagnostic accuracy and enable earlier detection of diseases. AI-powered systems can analyze vast quantities of medical data, including images, lab results, and genomic sequences, identifying subtle patterns that are often invisible to the human eye. This capability is not about replacing clinicians but augmenting their expertise with a powerful, data-driven second opinion.
Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning models, excel at this task. When trained on millions of annotated medical images, these models learn to recognize the earliest signs of conditions like cancer, diabetic retinopathy, or cardiovascular disease. For instance, Google's DeepMind algorithm has demonstrated a 94% accuracy rate in detecting over 50 eye diseases from OCT scans, matching or exceeding the performance of leading specialists. Similarly, PathAI's platform assists pathologists by highlighting suspicious regions in tissue samples, significantly reducing diagnostic errors and improving consistency in cancer grading.
Implementing AI for Diagnostics
For healthcare organizations, integrating these tools means faster, more reliable diagnoses, which directly translates to better patient outcomes and more efficient resource allocation. A key benefit lies in the system's ability to triage cases, flagging urgent findings for immediate review by a specialist. This ensures that critical cases receive prompt attention, reducing wait times and accelerating the start of treatment.
Adopting this technology effectively requires a strategic approach.
- Start with Pilot Programs: Begin with a focused pilot in a specific area, such as mammography or dermatology, to measure impact and refine workflows before a large-scale rollout.
- Ensure Robust Validation: AI models must be validated against diverse patient datasets to avoid bias and ensure they perform reliably across different demographics and populations.
- Maintain Human Oversight: The final diagnostic decision must always rest with a qualified clinician. AI should serve as a supportive tool, not an autonomous decision-maker.
- Invest in Staff Training: Provide comprehensive training for clinical and IT staff to ensure they understand how to use the AI tools, interpret their outputs, and integrate them into existing diagnostic pathways.
The following infographic highlights the quantifiable impact of AI on diagnostic precision.
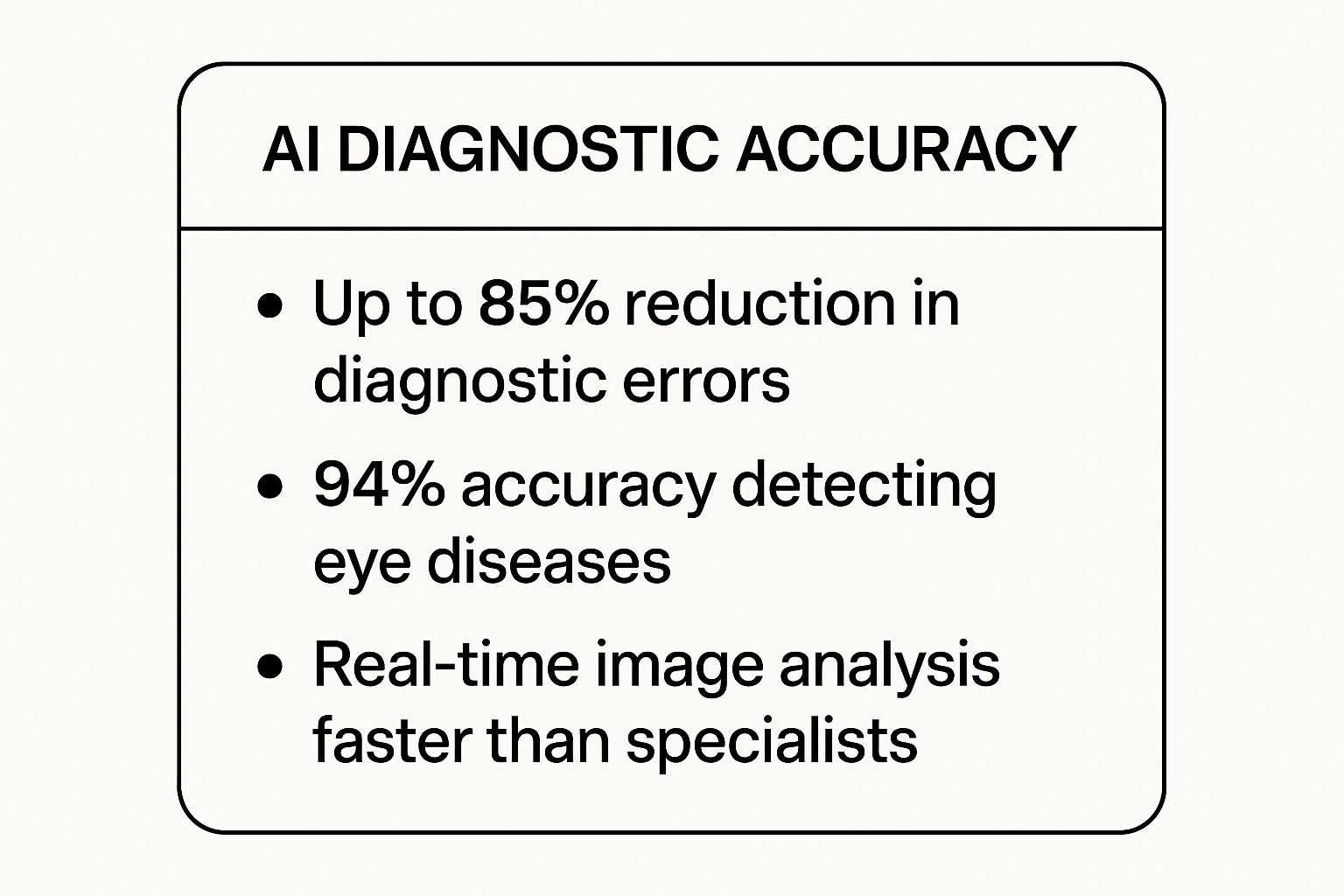
These metrics underscore how AI enhances clinical capabilities, achieving superhuman speed and accuracy in critical diagnostic tasks. Organizations like PYCAD are pivotal in this space, offering end-to-end services from data annotation to model deployment. They help medical device companies integrate sophisticated AI, turning standard equipment into intelligent diagnostic powerhouses that boost both confidence and speed.
2. Personalized Treatment Plans and Precision Medicine
A significant AI in healthcare benefit is the shift from one-size-fits-all treatments to hyper-personalized care. AI algorithms can synthesize vast and diverse patient datasets, including genetics, lifestyle factors, medical history, and real-time biometric data. This analysis allows clinicians to develop precision medicine strategies tailored to an individual’s unique biological and environmental profile, dramatically improving treatment efficacy and reducing adverse effects.

The power of AI in this domain lies in its ability to identify complex relationships between a patient’s genomic makeup and their likely response to specific therapies. In oncology, for example, platforms like Tempus and Foundation Medicine analyze tumor genomics to match patients with targeted therapies or clinical trials that are most likely to succeed. Similarly, AI can predict which patients are at higher risk for medication side effects, allowing doctors to adjust dosages or select alternative drugs proactively, as seen in pharmacogenomics reports from services like 23andMe.
Implementing AI for Personalized Medicine
For healthcare providers, integrating AI for personalized medicine means delivering more effective, safer, and cost-efficient care. It moves the focus from reactive treatment to proactive, individualized health management. By predicting treatment outcomes, AI helps avoid prescribing expensive drugs that are unlikely to work for a specific patient, optimizing both clinical results and resource use.
Adopting this technology requires careful planning and a phased approach.
- Start with Specific Disease Areas: Begin implementation in fields like oncology or cardiology, where the link between genetic markers and treatment outcomes is well-established and shows clear benefits.
- Establish Robust Data Governance: Create strict protocols for data privacy, security, and consent. Handling sensitive genetic and personal health information demands the highest level of data governance to maintain patient trust.
- Collaborate with Specialists: Work closely with genetic counselors, bioinformaticians, and other specialists to ensure the complex data outputs from AI platforms are interpreted correctly and translated into actionable clinical insights.
- Invest in Physician Training: Develop comprehensive training programs to help clinicians understand the principles of precision medicine, interpret AI-generated recommendations, and effectively communicate these complex treatment plans to patients.
These strategies enable organizations to harness the full potential of AI, making precision medicine a standard of care rather than a niche specialty.
3. Predictive Analytics for Preventive Care
Another of the key AI in healthcare benefits is the shift from reactive to proactive care through predictive analytics. AI models can sift through extensive electronic health records (EHRs), real-time monitoring data, and population health information to forecast individual and group health risks. By identifying patients who are on a trajectory toward a critical event like sepsis or hospital readmission, these systems allow clinical teams to intervene preemptively.
This approach is not about fortune-telling; it's about identifying subtle, data-driven signals of deterioration that often precede overt symptoms. For example, Johns Hopkins developed the Targeted Real-time Early Warning System (TREWS) which analyzes EHR data to alert clinicians to early signs of sepsis, often hours before a physician would recognize the condition. Other notable systems include Epic's deterioration index, which is integrated directly into EHR workflows, and Philips' eICU program, which uses predictive algorithms to help clinicians remotely monitor critically ill patients across multiple hospitals.

Implementing Predictive Analytics
For healthcare providers, the goal of implementing predictive analytics is to improve patient outcomes while simultaneously reducing costs associated with emergency interventions and lengthy hospital stays. It empowers care teams to manage high-risk populations more effectively, allocating resources to those who need them most. For a deeper dive into the broader applications, tools, and trends of predictive analytics, consider Exploring the Predictive Analytics World for comprehensive insights.
Successfully deploying these models requires careful planning and execution.
- Focus on High-Impact Outcomes: Start by targeting conditions with clear, measurable outcomes and established intervention protocols, such as sepsis, acute kidney injury, or 30-day readmissions.
- Tune Alert Thresholds Carefully: To prevent alert fatigue among clinicians, models must be fine-tuned to balance sensitivity with specificity, minimizing false positives while ensuring critical cases are not missed.
- Integrate into Clinical Workflows: Predictions are only valuable if they are actionable. The insights must be delivered seamlessly within existing EHRs or clinical communication platforms, not in a separate, siloed system.
- Provide Clear Action Protocols: When an alert is triggered, staff must have clear, evidence-based guidelines on the next steps to take, ensuring a consistent and effective response.
These strategic steps transform predictive models from academic exercises into powerful clinical tools. Companies in this space, such as Jvion, offer platforms that help organizations manage population health by identifying patients at risk and recommending specific, personalized interventions. This targeted approach is fundamental to making preventive care a scalable and impactful reality.
4. Streamlined Administrative Operations and Cost Reduction
Beyond clinical applications, another of the most impactful AI in healthcare benefits is its capacity to streamline administrative operations and drive significant cost reduction. Healthcare systems are burdened by a massive volume of routine tasks, from patient scheduling and billing to insurance claim processing and medical coding. AI-powered automation tackles these challenges head-on, freeing up administrative staff to focus on higher-value, patient-facing activities.
AI technologies, particularly Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), are central to this transformation. NLP models can accurately interpret unstructured clinical notes, automatically extracting relevant information for billing codes and medical records, which drastically reduces manual data entry and human error. For instance, platforms like Nuance's Dragon Medical use voice recognition and NLP to allow clinicians to dictate notes directly into electronic health records (EHRs), saving hours of documentation time per day. Similarly, Athenahealth uses AI to automate revenue cycle management, optimizing claim submissions and reducing denials.
Implementing AI for Administrative Efficiency
For healthcare organizations, automating administrative workflows leads to lower operational costs, improved revenue cycles, and enhanced staff satisfaction by reducing tedious, repetitive work. This efficiency allows resources to be reallocated toward direct patient care, improving the overall patient experience.
Adopting this technology effectively requires a focused strategy.
- Start with High-Volume Tasks: Begin by identifying and automating high-volume, rule-based processes like appointment reminders or initial insurance verification to achieve quick wins and demonstrate ROI.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: All AI tools handling patient data must be fully compliant with regulations like HIPAA. Vet vendors thoroughly to ensure their platforms meet stringent security and privacy standards.
- Provide Retraining Opportunities: As routine tasks are automated, offer retraining and upskilling programs for administrative staff, transitioning them into roles that require human empathy and complex problem-solving.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Continuously track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as claim denial rates, time-to-payment, and administrative overhead to validate cost savings and identify areas for further optimization.
5. Accelerated Drug Discovery and Development
Another of the most groundbreaking AI in healthcare benefits is the unprecedented acceleration of drug discovery and development. Traditionally a multi-billion dollar, decade-long process, bringing a new drug to market has been fraught with high failure rates. AI is rewriting this narrative by rapidly analyzing complex biological data to identify promising drug candidates, predict their efficacy, and optimize clinical trials, drastically reducing both time and cost.
Machine learning models are at the heart of this revolution. They can sift through immense libraries of molecular compounds, predict how they will interact with specific proteins, and identify novel therapeutic targets that human researchers might overlook. For example, DeepMind's AlphaFold has solved the protein folding problem, allowing scientists to predict the 3D structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence with incredible accuracy. This knowledge is crucial for designing drugs that can bind effectively to their targets. Similarly, companies like Atomwise and Recursion Pharmaceuticals use AI platforms to screen billions of molecules virtually, flagging only the most promising candidates for expensive lab testing.
Implementing AI for Drug Development
For pharmaceutical companies and research institutions, leveraging AI means identifying viable drug candidates faster and with a higher probability of success. A key advantage is the ability to repurpose existing drugs for new diseases by identifying previously unknown mechanisms of action, a strategy that BenevolentAI successfully used to identify a treatment for COVID-19. This approach significantly shortens the development timeline by building on established safety profiles.
Adopting AI in this domain requires a forward-thinking strategy.
- Partner with Academic Institutions: Collaborate with universities and research centers to gain access to cutting-edge research, diverse datasets, and novel AI algorithms.
- Focus on Specific Therapeutic Areas: Concentrate initial efforts on diseases with clear unmet needs and well-understood biological pathways to maximize the chances of a breakthrough.
- Invest in High-Quality Data Curation: The success of any AI model depends on the quality of the data it is trained on. Prioritize robust data collection, annotation, and management.
- Maintain Strong Regulatory Affairs Expertise: Ensure your team is well-versed in the evolving regulatory landscape for AI-driven drug development to navigate approvals efficiently.
The following video from Recursion Pharmaceuticals explains their AI-driven approach to decoding biology and industrializing drug discovery.
6. 24/7 Virtual Health Assistants and Telemedicine
A key AI in healthcare benefit is the expansion of patient access through 24/7 virtual health assistants and enhanced telemedicine platforms. These AI-driven tools provide round-the-clock support, answering health queries, managing medication reminders, and monitoring symptoms remotely. They serve as a first point of contact, helping patients navigate their health concerns and triaging cases to determine the appropriate level of care, which is crucial for improving healthcare accessibility, especially in remote or underserved regions.

AI chatbots and symptom checkers, like those developed by Ada Health and Buoy Health, use natural language processing to understand a patient's reported symptoms. The system then asks a series of intelligent, targeted questions to build a preliminary assessment. Based on this interaction, the AI can suggest self-care measures, recommend a consultation with a primary care physician, or flag the case for urgent attention. Platforms like Babylon Health take this further by integrating AI-powered triage directly into their virtual consultation services, seamlessly connecting patients with clinicians when human intervention is necessary.
Implementing AI for Patient Support
For healthcare providers, these virtual assistants reduce the burden on call centers and clinical staff by automating routine inquiries and initial assessments. This allows human personnel to focus on more complex patient needs, improving overall operational efficiency and ensuring timely care delivery. Integrating these systems effectively can transform patient engagement and satisfaction.
A successful deployment hinges on a patient-centric strategy.
- Communicate Limitations Clearly: It is vital to clearly inform users that the AI is a supportive tool, not a substitute for a doctor, and specify when they should seek direct medical attention.
- Ensure Data Privacy: Adherence to healthcare privacy regulations like HIPAA is non-negotiable. All patient data must be encrypted and handled with the highest security standards.
- Provide Multilingual Support: To serve diverse patient populations effectively, virtual assistants should be capable of communicating in multiple languages, improving accessibility and health equity.
- Update Algorithms Regularly: The AI models must be continuously refined based on user feedback, clinical outcomes, and the latest medical guidelines to ensure their accuracy and safety.
These AI tools are not just a convenience; they represent a fundamental shift in how healthcare is delivered. By providing immediate, accessible, and intelligent guidance, virtual health assistants empower patients to take a more active role in managing their health while ensuring healthcare systems operate more efficiently.
7. Remote Patient Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management
Another critical AI in healthcare benefit is the transformation of chronic disease management through intelligent remote patient monitoring (RPM). AI-powered systems leverage data from wearable devices, sensors, and mobile apps to continuously track patient health outside the hospital walls. This technology empowers clinicians to monitor vital signs, treatment adherence, and symptoms in real-time, shifting care from a reactive to a proactive model.
These systems analyze continuous data streams to detect subtle signs of deterioration before they become critical events. For example, AI algorithms can predict a hyperglycemic event in a diabetic patient based on glucose readings and lifestyle data, or flag an impending cardiac episode from ECG patterns. Companies like Dexcom and AliveCor have pioneered this space with continuous glucose monitors and mobile ECG devices, respectively. Platforms such as Philips' HealthSuite and Teladoc's Livongo integrate these data points, providing patients with personalized feedback and alerting care teams to intervene when necessary.
Implementing AI for Remote Monitoring
For healthcare providers, integrating AI-driven RPM reduces hospital readmissions, improves management of chronic conditions like hypertension and heart disease, and enhances patient engagement. It allows for more efficient allocation of clinical resources, focusing attention on patients who need it most. This proactive approach not only improves outcomes but also fosters greater patient autonomy in managing their health.
A successful RPM strategy requires careful planning and execution.
- Focus on Patient Engagement: Prioritize patient education and create simple, user-friendly interfaces to encourage consistent use, especially for elderly or less tech-savvy populations.
- Ensure Device Usability: Select devices that are easy to set up and use. The technology should reduce patient burden, not add to it.
- Establish Clear Alert Protocols: Define clear, actionable protocols for how clinical staff should respond to AI-generated alerts to ensure timely and appropriate interventions.
- Integrate Data into Workflows: Seamlessly integrate RPM data into the electronic health record (EHR) and clinical decision-making processes, making it a core part of the patient's care plan.
The following video from Livongo (now part of Teladoc Health) explains how their applied health signals platform works to empower people with chronic conditions.
AI in Healthcare Benefits Comparison Table
| AI Application | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy and Early Disease Detection | High: needs large datasets, validation, regulatory approval | High: advanced imaging, computing power, training | Significant reduction in diagnostic errors; earlier detection of diseases | Medical imaging analysis, cancer and cardiovascular diagnosis | Up to 85% error reduction; real-time faster processing; consistent analysis |
| Personalized Treatment Plans and Precision Medicine | High: requires comprehensive data integration and privacy safeguards | High: genomic data, real-time monitoring, specialized experts | Improved treatment efficacy by 20-30%; fewer adverse drug reactions | Oncology, pharmacogenomics, individualized therapy adjustments | Tailored treatments; optimized dosing; accelerates clinical trial matching |
| Predictive Analytics for Preventive Care | Medium-High: strong data standards, alert tuning needed | Medium: data integration, sensors, IoT devices | Reduces hospital readmissions by up to 30%; enables early interventions | Chronic disease management, early warning systems, population health | Shifts care from reactive to proactive; optimizes resources and staffing |
| Streamlined Administrative Operations and Cost Reduction | Medium: IT infrastructure and legacy integration challenges | Medium: automation software, compliance tools | Cuts administrative costs by 20-30%; faster claims and billing processes | Appointment scheduling, billing, medical coding, documentation | Reduces errors; frees staff time; accelerates revenue cycles |
| Accelerated Drug Discovery and Development | Very High: complex modeling, regulatory challenges | Very High: computational power, biological data | Drug development timelines halved; lower costs; higher success rates | Molecular design, clinical trial optimization, drug repurposing | Speeds discovery; improves safety monitoring; fast response to health threats |
| 24/7 Virtual Health Assistants and Telemedicine | Medium: NLP and integration with EHRs required | Medium: AI platforms, continuous updates | Immediate patient support; reduces non-urgent ER visits; improves adherence | Patient triage, symptom assessment, medication reminders | Extends access; multilingual support; enhances patient engagement |
| Remote Patient Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management | Medium: device integration, compliance issues | Medium: wearables, apps, data platforms | Reduces readmissions and costs; enables early intervention; improves QoL | Chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, hypertension | Continuous monitoring; proactive care; patient education tools |
Harnessing AI for a Healthier Tomorrow
The integration of artificial intelligence is fundamentally redefining the boundaries of what is possible in medicine. The ai in healthcare benefits we've explored, from enhancing diagnostic precision to personalizing treatment and streamlining complex workflows, are not isolated advancements. They represent a cohesive movement toward a healthcare system that is more intelligent, responsive, and centered on the patient.
This technological evolution is moving healthcare from a reactive model, which primarily treats sickness, to a proactive one focused on preserving wellness. We see this shift in AI's ability to power predictive analytics for preventive care and in its capacity to accelerate drug discovery, bringing novel therapies to patients faster than ever before. The journey from a promising algorithm to a life-saving clinical tool is complex, but the destination is a future where healthcare is more accessible, efficient, and effective for everyone.
Key Takeaways and Future Outlook
The core message is clear: AI is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day catalyst for transformation. The most critical takeaways from our exploration include:
- Precision at Scale: AI's capacity to analyze vast datasets allows for unparalleled precision, whether in identifying subtle anomalies in medical images or tailoring treatment protocols to an individual's unique genetic makeup.
- Operational Efficiency: By automating administrative tasks and optimizing resource allocation, AI directly combats clinician burnout and reduces operational costs, freeing up valuable human resources to focus on direct patient care.
- Empowered Patients: Technologies like virtual health assistants and remote monitoring tools place patients at the center of their own care, fostering greater engagement and improving management of chronic conditions.
Looking ahead, the continued collaboration between innovators, clinicians, and regulatory bodies will be paramount. As AI models become more sophisticated, ensuring their ethical implementation, data privacy, and unbiased performance will be the defining challenge. Companies specializing in this domain, like PYCAD, are crucial partners in this ecosystem. They provide the specialized expertise needed to navigate the complexities of AI development and deployment, turning powerful concepts into validated, clinical realities, particularly in demanding fields like medical imaging.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
For healthcare organizations and technology developers ready to embrace this future, the path forward requires strategic action.
- Identify High-Impact Areas: Start by targeting specific challenges within your operations. Is it diagnostic bottlenecks in radiology? Administrative overload? Begin with a defined problem where AI can deliver a measurable return on investment.
- Forge Strategic Partnerships: You don't have to build everything from scratch. Collaborate with AI specialists who understand the unique regulatory and technical demands of the healthcare sector. This accelerates development and mitigates risk.
- Prioritize Data Integrity: The success of any AI initiative hinges on the quality of your data. Invest in robust data governance and infrastructure to ensure your datasets are clean, secure, and representative of your patient population.
By embracing these technologies responsibly and strategically, we can address long-standing challenges in healthcare. The ai in healthcare benefits are not just theoretical; they are tangible advantages that lead to better patient outcomes on a global scale. This is our opportunity to build a truly healthier tomorrow for all.
Ready to unlock the full potential of AI in your medical imaging projects? Partner with PYCAD to leverage our world-class expertise in data annotation, model development, and validation. Visit PYCAD to discover how our specialized services can accelerate your innovation and bring your vision to life.






