Understanding AI Regulatory Compliance Fundamentals

Artificial intelligence is rapidly changing how industries operate. But with this innovation comes a critical need for regulatory compliance. This means ensuring your AI systems follow established legal and ethical guidelines. Resources like Security Compliance Training can be valuable for building a strong foundation in this area. Compliance isn't simply about avoiding penalties; it's about building trust with users and promoting responsible AI development. This proactive approach is key for sustainable growth.
Key Principles of AI Regulation
Several core principles are driving AI regulations globally. These principles seek to address the unique challenges posed by AI technologies. They focus on areas like algorithmic transparency, data protection, and bias prevention. For example, regulations may require companies to explain how their algorithms make decisions, particularly in high-stakes situations like loan applications.
Robust data protection measures are also essential for safeguarding user information and preventing misuse. This is critical for maintaining public trust and preventing discriminatory outcomes. Furthermore, addressing potential biases in algorithms is paramount to ensuring fair and equitable results for everyone.
Compliance vs. Ethics: A Critical Distinction
It's important to understand the difference between ethics and compliance. While related, they are not the same. Ethical guidelines are often voluntary, representing best practices within an industry. Regulatory compliance, however, is mandatory and enforced by law.
Meeting ethical guidelines is a good starting point, but it's insufficient on its own. Businesses must prioritize adhering to legal requirements to avoid penalties and protect their reputations. Failure to comply can lead to substantial fines and significant reputational damage.
Real-World Compliance Examples
Many organizations are successfully integrating compliance into their AI development processes. These companies recognize that compliance is not an obstacle to innovation, but a vital part of responsible AI development. Some companies are implementing rigorous testing protocols to identify and mitigate bias within their algorithms.
Other organizations are establishing comprehensive data governance frameworks to comply with data protection laws. These real-world examples show that compliance and innovation can coexist effectively. By prioritizing both, companies can build AI systems that are both powerful and ethical.
The Role of Stakeholders in AI Governance
Various stakeholders, including government regulators and industry bodies, play a significant role in shaping the AI landscape. Regulators establish the legal framework and enforce compliance, while industry bodies often develop voluntary best practices and standards. Understanding the perspectives and actions of these stakeholders is crucial for any business working with AI.
This active engagement with the broader AI community helps companies anticipate regulatory changes and adapt their strategies. It also allows them to contribute to the ongoing conversation surrounding responsible AI development.
To help illustrate the varying requirements, let's take a look at the following table:
Core AI Compliance Requirements by Category
Comparison of key compliance requirements across different AI risk categories and applications
| Risk Level | Requirements | Documentation | Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Data minimization, transparency notices | Algorithm documentation, data processing records | Warnings, minor fines |
| Medium | Human oversight, impact assessments | Detailed algorithm audits, data protection impact assessments | Significant fines, operational restrictions |
| High | Pre-approval audits, independent ethical reviews | Comprehensive system documentation, independent audit reports | Substantial fines, license revocation, criminal charges |
This table summarizes some of the potential requirements and consequences related to AI compliance. As you can see, the specific requirements and penalties can vary significantly depending on the perceived risk level of the AI system.
Looking Ahead: The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The field of AI regulatory compliance is dynamic. New regulations are continually being developed, and existing ones are being updated to keep pace with technological advancements. This constant evolution necessitates that businesses stay informed and proactively adapt their compliance strategies. Failing to adapt can expose companies to substantial legal and reputational risks. By remaining vigilant and adaptable, organizations can ensure long-term success in the age of AI.
Navigating The US AI Regulatory Landscape

The United States' approach to AI regulation stands apart. Unlike the European Union's centralized AI Act, the US currently employs a combination of existing laws, frameworks, and emerging state regulations. This creates a complex landscape filled with both opportunities and challenges for businesses working with AI systems. Understanding the current regulatory environment and preparing for future changes are key to successful navigation.
Federal Guidance and Frameworks
Although comprehensive federal AI law is currently absent, several important initiatives are influencing AI compliance in the US. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework offers crucial guidance for organizations developing and using trustworthy AI. This framework promotes a risk-based approach, enabling businesses to identify and mitigate potential issues associated with their AI systems.
The AI Bill of Rights, introduced by the Biden administration, highlights key ethical considerations for AI. While not legally binding, it signals the government’s focus on areas like privacy, algorithmic discrimination, and transparency. These initiatives provide valuable insight into the future direction of AI regulation in the US and offer a foundation for potential federal legislation.
The Rise of State-Level AI Regulations
With no overarching federal legislation, individual states are leading the way in AI regulation. California, in particular, has been active, enacting laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which impacts AI systems handling personal data.
Other states are developing similar legislation, creating a complex and evolving regulatory web. This state-by-state approach presents a significant challenge for businesses operating across different jurisdictions. A flexible and adaptable compliance strategy is essential to navigate these varying requirements.
Currently, the US relies on existing frameworks and sector-specific laws for AI compliance. As of 2025, there is no single federal AI regulation. Frameworks like the NIST AI Risk Management Framework and sector-specific regulations play important roles. The Biden administration's 2022 AI Bill of Rights provides ethical guidelines, while industries like healthcare and finance face increasing regulatory scrutiny. State initiatives, such as California's CCPA, contribute to this complex regulatory environment. Learn more about this at White & Case's AI Watch.
Strategic Implications for Businesses
The fragmented nature of US AI regulation presents both challenges and opportunities. The absence of a single, overarching law allows for flexibility and innovation. Companies can adapt their compliance strategies to specific industry requirements and state regulations.
However, this also requires ongoing vigilance. Businesses must track regulatory developments at both federal and state levels and be prepared to adapt their AI systems and processes accordingly. This can be a substantial undertaking for companies operating nationwide.
Preparing for the Future of AI Compliance
The regulatory landscape will continue to evolve alongside AI technology. Businesses that proactively prepare for future regulations will be best positioned for success. This involves developing strong AI governance frameworks, emphasizing transparency and accountability in AI systems, and actively engaging with policymakers.
By taking these steps, companies can mitigate legal and reputational risks and build trust with customers and stakeholders, ensuring long-term success in the age of AI.
Mastering The EU AI Act Requirements

The European Union's AI Act is establishing a new global benchmark for AI regulation. Its impact stretches far beyond Europe, influencing AI development and deployment on a global scale. Recognizing this, proactive organizations are adopting the Act's risk-based framework to build their international compliance strategies. This forward-thinking approach allows them to turn regulatory hurdles into opportunities for competitive advantage.
Understanding the Risk-Based Approach
The EU AI Act classifies AI systems into four distinct risk categories: minimal, limited, high, and unacceptable. This classification system determines the specific compliance requirements for each type of AI system. Minimal risk AI, such as spam filters, faces limited regulatory oversight. Limited risk systems, like chatbots, have transparency obligations to ensure user understanding.
High-risk AI systems, including those used in healthcare, law enforcement, and critical infrastructure, are subject to stringent requirements. These include thorough testing, comprehensive documentation, and robust human oversight. Unacceptable risk AI systems, those considered to pose an inherent threat to fundamental rights, are prohibited entirely. This tiered approach ensures that regulatory scrutiny is proportionate to the potential societal impact of the AI system.
Practical Steps for Meeting EU AI Act Requirements
Compliance with the EU AI Act demands a comprehensive approach. For high-risk systems, companies must undertake thorough conformity assessments prior to market entry. This involves demonstrating adherence to the Act's stipulations through rigorous testing and meticulous documentation. Transparency is paramount, requiring clear and accessible communication with users regarding the AI system's functionality and potential risks.
Furthermore, organizations must implement robust bias detection and mitigation strategies. Regular audits of AI systems are essential to identify and rectify potential biases. Maintaining thorough documentation throughout the entire AI lifecycle, from development to deployment, is crucial for proving compliance.
The EU AI Act has significantly reshaped the regulatory landscape. Since its 2024 introduction and progressive enforcement, its oversight of high-risk AI systems has become a global standard. The Act's four-tiered risk categorization, with its stringent requirements for high-risk systems, has encouraged proactive compliance among European companies. A 2025 survey revealed that over 60% of European companies have already implemented comprehensive AI ethics policies. Penalties for non-compliance are substantial, reaching up to 7% of global annual turnover or €35 million, whichever is greater. For further insights, explore the Cloud Security Alliance Blog.
Building Scalable Compliance Processes
Long-term success requires building scalable compliance processes. This entails integrating AI governance throughout the AI development lifecycle, from initial design through ongoing monitoring and maintenance. By embedding compliance into each stage, organizations can meet regulatory requirements without stifling innovation.
Automating compliance tasks, where feasible, enhances efficiency and minimizes human error. Regular internal audits and reviews can identify potential compliance gaps and enable timely adjustments. Establishing robust internal policies and procedures clarifies roles and responsibilities, standardizing compliance practices across the organization.
The Global Impact of the EU AI Act
The EU AI Act's influence extends beyond the EU, shaping AI development globally. Its extraterritorial effects mean that companies operating outside the EU but offering AI services within its borders must also comply. This has far-reaching implications, impacting countless businesses worldwide.
Many organizations are now adopting the EU AI Act's framework as a global baseline, acknowledging its comprehensive approach to AI governance. This proactive strategy positions them well for navigating evolving AI regulations in other jurisdictions.
Tackling Asia-Pacific AI Compliance Complexity
The Asia-Pacific region presents unique challenges for companies navigating AI regulations. Each country's distinct approach to AI governance creates a complex web of requirements. Multinational corporations must therefore develop adaptable compliance strategies to thrive in this diverse market.
Navigating Data Protection and Algorithmic Transparency
India, China, and Singapore are key players in the APAC region, each with its own regulatory focus. India's Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) emphasizes user consent and data protection. China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) prioritizes data localization and algorithmic transparency. Singapore's Model AI Governance Framework, while voluntary, enjoys wide adoption and influences regional best practices.
These varied approaches mean companies must carefully consider data handling procedures, cross-border data transfers, and the transparency of their AI systems. Adapting to local nuances is crucial for avoiding penalties and maintaining efficient operations.
Adapting to Diverse Regulatory Requirements
Data localization requirements, mandating data storage within specific geographic areas, are a significant hurdle. Restrictions on cross-border data transfers further complicate data sharing and analysis across regions. These factors influence how companies structure their data infrastructure and manage international operations.
Differing consent mechanisms for data collection and use add another layer of complexity. Businesses must obtain valid consent according to each jurisdiction's regulations. This often requires implementing tailored consent processes and communicating clearly with users.
In the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, AI regulatory compliance is constantly shaped by legislative developments and diverse national approaches. For instance, India's DPDPA, enacted in 2023 and enforced by 2025, mandates robust user consent and imposes penalties up to 2.5 billion INR (approximately $30 million USD) for violations. China's PIPL, enforced since 2021, requires strict data localization and algorithmic transparency for domestic and international firms. In 2024–2025, multinational corporations in China reported a 40% increase in compliance costs to meet these requirements. Learn more at Cimplifi's AI Regulations Resource.
Building Adaptive Compliance Strategies
Successful companies are developing adaptive compliance strategies to address the region's varied legal landscape. These strategies prioritize flexibility and continuous monitoring of regulatory changes. They also integrate compliance into every stage of the AI lifecycle.
This proactive approach allows businesses to anticipate and respond to evolving requirements efficiently, minimizing non-compliance risks and associated penalties.
Balancing Compliance and Innovation
A key challenge is balancing AI regulatory compliance with the need for innovation. Overly strict compliance frameworks can hinder creativity and slow the development of new AI solutions.
However, integrating compliance into the innovation process, rather than treating it as an obstacle, can foster more robust and trustworthy AI systems. A proactive approach to compliance helps companies maintain a competitive edge while building trust with customers and regulators.
The Future of AI Compliance in the Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific regulatory environment is constantly evolving, with new regulations emerging and existing ones being refined. Businesses must stay informed about these changes and adapt their compliance strategies accordingly.
This requires constant vigilance and a commitment to ongoing learning. By staying ahead of the curve, businesses can minimize risks, maximize opportunities, and achieve long-term success in this dynamic market.
Building Effective AI Compliance Programs That Scale
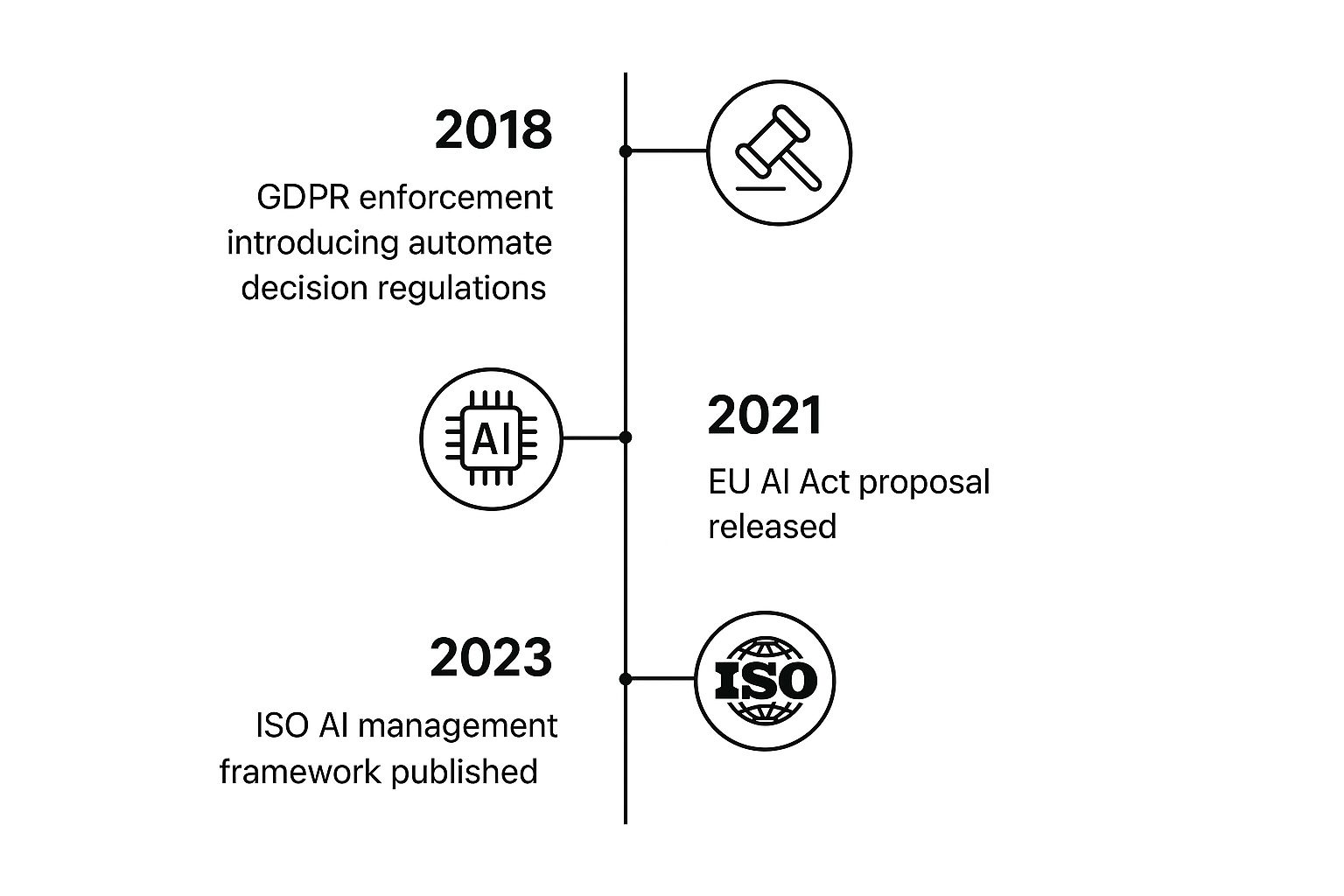
The timeline above highlights key milestones in the development of AI regulatory compliance. Starting with GDPR enforcement in 2018, followed by the EU AI Act proposal in 2021, and the ISO AI management framework in 2023, it's clear that AI governance is increasingly important. Regulations are developing rapidly, making a robust AI compliance program essential. This goes beyond simply checking boxes—it requires a strategic, scalable approach, integrating AI governance throughout the entire AI lifecycle.
Integrating AI Governance into the AI Lifecycle
Scaling AI initiatives successfully means considering compliance at every stage. This starts with defining clear AI usage policies outlining acceptable applications and risk parameters.
During the development phase, algorithmic audits help identify potential biases and ensure transparency. After deployment, continuous monitoring systems are vital for detecting and addressing emerging risks. This integrated approach fosters responsible AI development and minimizes costly non-compliance.
Establishing Effective Governance Structures
Robust governance structures are the foundation of effective AI compliance. One crucial step is establishing an AI ethics committee. This committee, comprising diverse stakeholders from legal, technical, and business backgrounds, oversees AI activities and guides ethical decision-making.
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are also key. Appointing a dedicated AI compliance officer with clear authority and accountability streamlines compliance efforts, ensuring oversight and fostering a culture of responsible AI use.
Mastering Continuous Monitoring and Documentation
Continuous monitoring is crucial for identifying and mitigating evolving AI risks. This involves tracking key metrics, such as algorithmic performance and data quality. Regular review of these metrics allows organizations to promptly address deviations from established standards.
Thorough documentation of all AI-related processes, from data collection and model training to testing and deployment, is also critical. This documentation provides evidence of due diligence and is invaluable during regulatory audits.
To help illustrate the timeline for implementing a comprehensive AI compliance program, the table below outlines the key phases, durations, activities, and deliverables:
AI Compliance Program Implementation Timeline
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment & Planning | 2-3 Months | – Gap analysis against existing regulations – Risk assessment – Define scope and objectives |
– Compliance roadmap – Resource allocation plan |
| Policy & Procedure Development | 3-4 Months | – Draft AI usage policies – Establish ethical guidelines – Develop monitoring procedures |
– Approved AI policies and procedures – Training materials |
| Implementation & Training | 4-6 Months | – Implement monitoring tools – Conduct employee training – Establish reporting mechanisms |
– Functional monitoring system – Trained workforce |
| Ongoing Monitoring & Review | Ongoing | – Regular audits – Performance tracking – Policy updates |
– Compliance reports – Continuous improvement plan |
This table provides a structured approach to building a successful AI compliance program, starting with initial assessment and planning, followed by policy development, implementation, and ongoing monitoring and review.
Training Teams and Maintaining Stakeholder Transparency
Investing in training programs equips teams with the knowledge and skills for responsible AI development and deployment. Training should encompass both technical aspects and ethical considerations, along with legal requirements.
Maintaining open communication with stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and employees, builds trust and promotes accountability. Regularly communicating AI policies, practices, and performance metrics fosters transparency and demonstrates a commitment to responsible AI.
Adapting to Evolving Regulatory Requirements
The AI regulatory landscape is constantly changing, with new regulations and guidelines frequently emerging. AI compliance programs must be adaptable to these changes without disrupting core business operations. This requires staying informed about regulatory developments and engaging with policymakers. A flexible compliance framework enables organizations to innovate while effectively managing evolving AI risks.
Future-Proofing Your AI Regulatory Strategy
AI technology is rapidly evolving, and regulatory frameworks are struggling to keep up. This presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses. This section explores emerging trends in AI regulation and offers practical strategies for maintaining compliance and a competitive edge.
Adapting to the Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment for AI is constantly changing. New regulations are being proposed and existing ones revised globally. This makes maintaining AI regulatory compliance an ongoing process. Organizations must actively monitor these changes and adapt their strategies.
For example, the EU's AI Act sets a precedent for global AI governance with its risk-based approach. While other regions may adopt different methods, they're still influenced by these developments. This emphasizes the need for adaptable and scalable compliance programs.
Building Adaptive Compliance Strategies
A future-proof AI compliance strategy requires a proactive and dynamic approach. Establishing robust internal governance structures is key. This includes clear AI usage policies, dedicated compliance teams, and regular audits. When building AI compliance programs, continuous monitoring and improvement are essential. For valuable insights into optimizing performance, consider exploring these form analytics strategies.
Another vital component is ongoing education and training. Keeping teams informed about the latest regulations and best practices helps identify and address potential compliance gaps before they escalate.
Transforming Compliance into Competitive Advantage
AI regulatory compliance shouldn't be seen as a burden. Instead, it's an opportunity to gain a competitive advantage. Demonstrating a commitment to responsible AI builds trust with users, investors, and regulators.
This trust can lead to increased customer loyalty, a stronger brand reputation, and a more favorable regulatory environment. It can also attract top talent seeking companies that prioritize ethical AI practices.
Monitoring Regulatory Developments and Engaging with Policymakers
Staying ahead of compliance involves actively monitoring regulatory changes. This can be done through various methods, like subscribing to industry newsletters, attending relevant conferences, and consulting with legal experts.
Directly engaging with policymakers is also beneficial. This allows organizations to provide input on developing regulations, ensuring practicality and effectiveness. It also enables companies to anticipate changes and adapt proactively.
Strategic Planning for Long-Term Success
A long-term AI regulatory strategy requires integrating compliance into the overall business strategy. AI governance should be a core component of an organization's values and operations, not an afterthought.
This means aligning AI development and deployment with regulatory requirements from the beginning. It also involves a commitment to continuous evaluation and improvement of compliance programs. A strategic approach to AI compliance positions organizations for long-term success in this evolving landscape.
Ready to improve your medical imaging capabilities while staying compliant with AI regulations? PYCAD offers comprehensive AI solutions tailored to the medical industry. From data handling and model training to deployment and support, we empower you to innovate responsibly. Visit PYCAD today to learn more about achieving your goals while maintaining full compliance.






