Why Data Governance in Healthcare Is No Longer Optional

The healthcare industry is overflowing with data from various sources, including electronic health records, medical devices, wearable technology, and patient portals. This abundance of information presents significant opportunities to improve patient care and boost operational efficiency. However, without responsible management, these same data streams can also introduce substantial risks. This is why data governance is quickly becoming essential in healthcare.
The Rising Tide of Data and Its Implications
The sheer volume and diversity of healthcare data present inherent challenges. Consider the difficulty of compiling a complete patient history from various systems that may lack standardized formats or clear data ownership. Such inconsistencies can lead to misdiagnosis, delayed treatments, and administrative bottlenecks. Furthermore, the sensitive nature of healthcare data necessitates strict security measures to ensure patient privacy and regulatory compliance.
This demand for reliable data management is a key driver behind the increasing adoption of formal data governance programs. Projections indicate that by 2025, 71% of organizations will have a data governance program in place, up from 60% in 2023. This growth underscores the rising recognition of data governance as a strategic imperative, offering advantages such as improved data quality (58%) and better analytics capabilities (58%). More detailed statistics can be found here: 2025 Planning Insights: Data Governance Adoption Has Risen Dramatically. Despite this progress, challenges persist, with data governance remaining a top data integrity concern for 54% of organizations. Effective implementation is therefore critical for realizing the full benefits of data governance. For a strong foundation, consider a structured framework like the one offered by Kleene.ai: Data Governance Framework Template.
From Reactive Compliance to Proactive Strategy
Historically, healthcare data governance has often been a reactive measure, primarily driven by regulatory requirements. However, forward-thinking healthcare organizations are shifting toward a more proactive and strategic approach. They understand that effectively managed data is not just about avoiding penalties; it's a cornerstone of improved patient outcomes, optimized operations, and innovative research.
The Real Cost of Poor Data Practices
Ineffective data governance practices can lead to several serious consequences.
-
Financial Losses: Inaccurate data can result in billing errors, rejected claims, and overall operational inefficiencies.
-
Reputational Damage: Data breaches can severely erode patient trust and tarnish an organization's reputation.
-
Legal and Regulatory Penalties: Failure to comply with regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), can lead to significant fines.
-
Compromised Patient Safety: Incomplete or inaccurate data can negatively impact clinical decisions and jeopardize patient safety.
These risks highlight the importance of a comprehensive data governance framework that addresses data quality, security, accessibility, and compliance. This shift elevates data governance from a purely IT concern to a board-level priority, crucial for sustained organizational success in the dynamic healthcare landscape.
Building Your Healthcare Data Governance Dream Team

Successful data governance in healthcare relies heavily on the individuals driving the initiative. Technology plays a vital role, but without a dedicated and knowledgeable team, many projects struggle. A lack of clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and collaborative efforts can lead to failure. Constructing a strong team requires a diverse group of experts who understand the complexities of healthcare.
Key Players: More Than Just IT
IT professionals are critical to data governance success, but they represent only one part of the equation. A well-rounded team includes a wider range of stakeholders, each bringing unique skills and perspectives:
-
Chief Medical Information Officer (CMIO): The CMIO acts as a liaison between clinical practice and IT. This role ensures that data governance aligns with clinical workflows and, ultimately, supports better patient care.
-
Privacy and Security Officers: These individuals are essential for protecting patient data and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Their expertise is invaluable in safeguarding sensitive information.
-
Data Scientists: Data scientists bring analytical power to the team. They work with clinicians to extract meaningful insights from healthcare data, identifying patterns and trends that can inform critical decisions.
-
Frontline Clinicians: The input of frontline clinicians offers real-world perspectives on how data is used daily. Their feedback is critical to ensuring that data governance policies are practical and enhance, rather than hinder, patient care.
-
Data Stewards: These team members are responsible for the quality and consistency of specific data domains. They work to ensure data accuracy and completeness across the organization's systems.
To help illustrate the core components of a successful healthcare data governance framework, the following table outlines the key players, their purpose, healthcare-specific considerations, and common implementation challenges:
Core Elements of Healthcare Data Governance
This table outlines the essential components of a comprehensive data governance framework specifically tailored for healthcare organizations
| Component | Purpose | Healthcare-Specific Considerations | Implementation Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chief Medical Information Officer (CMIO) | Bridge the gap between clinical practice and IT | Aligning data governance with clinical workflows and patient care | Balancing clinical needs with technical requirements |
| Privacy and Security Officers | Safeguarding patient data and maintaining regulatory compliance | HIPAA, GDPR, and other relevant regulations | Staying up-to-date with evolving regulations and security threats |
| Data Scientists | Gleaning actionable insights from healthcare data | Identifying patterns and trends to inform decision-making | Ensuring data quality and accessibility for analysis |
| Frontline Clinicians | Providing real-world perspectives on data usage | Ensuring data governance policies are practical and enhance patient care | Resistance to new workflows and policies |
| Data Stewards | Ensuring data quality and integrity within specific domains | Maintaining data accuracy, completeness, and consistency | Lack of clear ownership and accountability for data |
This table highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in healthcare data governance. Addressing the implementation challenges requires ongoing communication and collaboration between all team members.
Establishing Clear Stewardship and Responsibilities
Once the team is assembled, it's crucial to define clear roles and responsibilities. A data governance steering committee can oversee strategy and policy development. This committee should represent all key stakeholders to ensure diverse perspectives are considered.
A data stewardship model is equally important. This model assigns ownership and accountability for individual datasets, promoting data quality and preventing ambiguity. It's similar to assigning nurses to specific patients, ensuring personalized attention and clear responsibility.
Practical Data Classification: From Genes to Claims
Healthcare data comes in various forms, each with unique handling requirements. A practical data classification framework is crucial. This framework should encompass all data types, from highly sensitive genomic sequences to general administrative data:
-
Genomic Data: This data demands strict security and anonymization measures to protect patient privacy.
-
Clinical Data: Accurate and accessible clinical data, including diagnoses, treatments, and lab results, is essential for informed patient care.
-
Claims Data: This data, used for billing and reimbursement, must be accurate and complete to avoid financial issues.
Effective classification allows for appropriate security measures and access controls, ensuring data integrity and compliance while facilitating its use in research and analysis.
Overcoming Resistance and Building a Data-Driven Culture
Implementing data governance in healthcare can encounter resistance. Clinicians may be hesitant to adopt new policies or workflows. Addressing these concerns proactively is key:
-
Demonstrating Value: Showing clinicians how data governance can positively impact their work and patient outcomes is crucial for buy-in.
-
Providing Training: Equipping clinicians with the necessary skills and knowledge to participate effectively will ease the transition.
-
Fostering Collaboration: Encouraging open communication between clinicians, IT, and data governance leaders will foster a collaborative environment.
Building a data-driven culture is an ongoing journey. Consistent communication, training, and showcasing the benefits of robust data governance are critical for long-term success.
Navigating The Regulatory Maze Without Losing Your Mind
Healthcare data is subject to a complex web of regulations. This makes robust data governance not just a best practice, but a necessity. This intricate landscape can seem overwhelming, ranging from HIPAA, GDPR, and the 21st Century Cures Act to various state privacy laws. However, compliance doesn't have to bring your organization to a standstill.
Understanding The Key Regulations
Effective data governance in healthcare begins with a deep understanding of the applicable regulations. This means going beyond simply knowing the names of the laws. It requires grasping their practical implications for data handling, storage, and sharing.
Healthcare Data Regulations Comparison
This table compares key healthcare data regulations across different jurisdictions and their specific requirements for data governance.
| Regulation | Jurisdiction | Key Requirements | Penalties for Non-Compliance | Impact on Data Governance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) | US Federal | Protecting sensitive patient data (data security, access control, breach notification) | Financial penalties, corrective action plans, criminal charges in cases of willful neglect | Sets baseline standards for data security and privacy in US healthcare |
| GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) | European Union | Individual rights regarding data privacy and control (data subject access requests, data portability, right to be forgotten) | Fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, reputational damage | Impacts any organization globally that handles data of EU citizens; requires stricter consent management and data subject rights protocols |
| 21st Century Cures Act | US Federal | Promoting interoperability and data sharing while maintaining patient privacy; information blocking prohibited | Disincentives for information blocking, potential civil monetary penalties | Encourages data sharing and standardization for improved patient care and research |
| State Privacy Laws (e.g., CCPA, CPRA) | US States (e.g., California, Virginia) | Varying requirements for data privacy, often stricter than federal regulations (consumer rights regarding data collection and use, data breach notification requirements) | Financial penalties, private right of action in some cases | Requires organizations to navigate a complex patchwork of regulations and adapt data governance strategies accordingly |
The table above highlights the diverse requirements and penalties associated with various healthcare data regulations. This complexity underscores the importance of a proactive and adaptable data governance strategy.
Implementing Practical Compliance Strategies
Effective compliance goes beyond just understanding the regulations. It involves implementing practical strategies that integrate seamlessly into existing workflows.
-
Consent Management: Implementing systems to obtain, track, and manage patient consent for data use. This is particularly crucial for research purposes.
-
Secure Data Sharing: Establishing protocols and technologies for secure data exchange between healthcare providers, researchers, and other authorized entities.
-
Breach Notification: Developing clear procedures for detecting, investigating, and reporting data breaches in compliance with regulations.
-
Patient Rights: Ensuring that patients can exercise their rights regarding data access, correction, and deletion as mandated by regulations like GDPR.
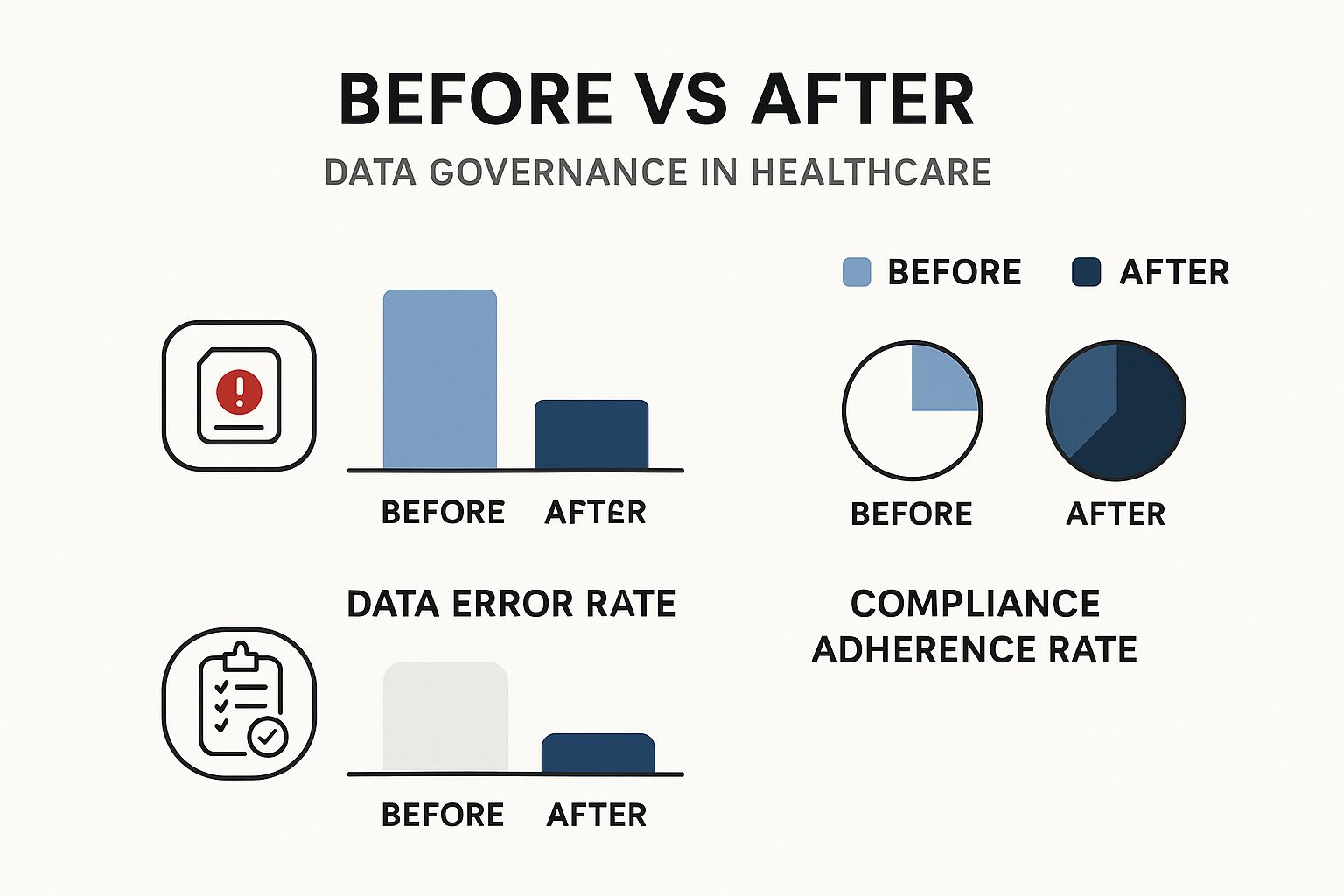
As the infographic illustrates, robust data governance strategies significantly decrease data error rates and increase compliance adherence. This reinforces the value of proactive data management in healthcare. Additionally, the evolving regulatory landscape itself adds complexity. For example, healthcare data in the European Union is predicted to reach 10,000 exabytes by 2025. This necessitates stringent governance. The EU Data Governance Act, effective since September 2023, introduces new data-sharing requirements. Simultaneously, GDPR constraints require organizations to adopt sophisticated compliance strategies. Find more detailed statistics here. This global trend toward stricter regulatory control over healthcare data emphasizes the need for adaptable governance frameworks.
Building Flexible Governance Frameworks
Forward-thinking healthcare systems are implementing adaptable governance frameworks. These frameworks emphasize key principles:
-
Scalability: The ability to handle increasing data volumes and complexity.
-
Interoperability: Enabling secure and compliant data exchange between different systems and organizations.
-
Transparency: Providing clear visibility into data lineage, access controls, and usage patterns for accountability.
-
Innovation: Supporting the development and implementation of new technologies and data-driven initiatives while maintaining compliance.
By embracing these principles, healthcare organizations can build robust and flexible governance frameworks. These frameworks not only ensure compliance today but also position organizations to leverage data's full potential to improve patient care and drive positive change.
Technology That Actually Makes Healthcare Data Governance Work

The healthcare industry faces a constant influx of new technology solutions, each promising streamlined data management. Choosing the right tools for effective data governance, however, requires careful planning and consideration. This section explores key technologies that truly support robust governance amidst the inherent complexities of clinical settings.
Master Data Management (MDM) for Consistent Patient Information
Maintaining consistent patient information across various systems is a significant challenge in healthcare. Master data management (MDM) solutions offer a centralized platform to consolidate and manage this crucial data. This creates a vital "single source of truth" for patient demographics, medical history, and other key identifiers. The result? Reduced errors and improved interoperability.
Consider a patient with multiple medical records scattered across different hospital departments. MDM can consolidate these fragmented records, ensuring clinicians have a complete and accurate view of the patient's health information. This comprehensive perspective supports better-informed clinical decisions.
Data Catalogs: Clarifying Ownership and Access
Data catalogs are another essential tool for effective healthcare data governance. These systems provide a detailed inventory of all available data assets, including location, ownership, and access permissions. This transparency is critical, clarifying who is responsible for specific data and streamlining data discovery for authorized personnel.
This streamlined access empowers researchers and clinicians to quickly find the data they need while ensuring appropriate security measures are maintained. Think of a data catalog as a roadmap to your organization's data landscape, guiding users to the precise information they require.
Metadata Management: Documenting Data Lineage for Insights
Metadata, often referred to as "data about data," provides critical context and characteristics about your data assets. Metadata management tools meticulously document data lineage, tracking the origin, transformations, and usage of data over time. This is essential for generating both clinical and operational insights.
For instance, understanding the origin and modifications of specific data is vital for ensuring reliability in research and informed decision-making. This meticulous tracking enables accurate analysis and validation of data quality, leading to more reliable results.
Selecting and Implementing the Right Technology
A strategic approach is essential when selecting and implementing data governance technologies. Here's a breakdown of key considerations:
-
Clearly Defined Needs: Begin by pinpointing specific data challenges and goals. What problems are you aiming to solve with new technology? Which aspects of your data governance framework require improvement?
-
Evaluation Criteria: Develop a tailored set of evaluation criteria based on your organization's unique requirements. Consider factors like cost, ease of integration with existing systems, scalability, and vendor reputation.
-
Phased Implementation: A phased approach to technology implementation allows for better control and minimizes disruptions to existing workflows. Start with a pilot project to assess effectiveness and gradually expand implementation as needed.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Integration challenges can hinder even the most promising technology implementations. Thoroughly plan how new tools will interact with your current infrastructure to ensure seamless operation.
Practical Considerations and Measurable ROI
Beyond the technical aspects, practical considerations are crucial for success:
-
User Adoption: Technology is only effective if staff members embrace and utilize it. Clinicians and other staff may be resistant to change if new tools disrupt familiar processes. Focus on user-friendly interfaces and intuitive design to encourage adoption.
-
Training and Support: Comprehensive training and ongoing support are essential for successful implementation. Users require clear guidance to effectively utilize new tools and maximize their potential.
-
Compliance: Ensure any new technology supports compliance with relevant industry regulations. Adhering to regulations like HIPAA is paramount for maintaining data security and patient privacy. You may find this guide helpful: Call Center Compliance Checklist This resource, while focused on call centers, offers insights applicable to other industries regarding compliance best practices.
By addressing these practical considerations, healthcare organizations can maximize their return on investment (ROI) in data governance technologies. This includes tangible benefits such as reduced data errors, improved regulatory compliance, and enhanced operational efficiency. This focus on measurable results justifies the investment and fosters a data-driven culture within the organization.
Turning Data Governance into a Healthcare Value Generator
Effective data governance is more than just ticking compliance boxes. It can significantly improve a healthcare organization's financial health. This involves moving from a reactive stance to a proactive strategy. The focus shifts to using data as a valuable asset.
Demonstrating ROI: Beyond Regulatory Compliance
The return on investment (ROI) of robust data governance goes beyond simply avoiding regulatory penalties. While avoiding fines is a plus, effective governance offers other major financial advantages. For instance, better data quality leads to more accurate billing and coding. This results in fewer rejected claims and increased revenue capture. Ultimately, this contributes to a healthier bottom line.
Furthermore, streamlined data management processes improve operational efficiency. This reduces administrative overhead and frees up resources. These resources can then be redirected toward crucial patient care.
Cost Reduction Through Data Quality and Efficiency
Data governance lowers costs in several key areas. Improved data quality minimizes errors, leading to fewer costly rework and corrections. Eliminating duplicate records, a frequent problem in healthcare systems, also streamlines operations and reduces storage costs. This increased efficiency directly benefits the bottom line.
Think of a well-organized warehouse versus one in disarray. The organized warehouse runs smoothly, retrieving items quickly and minimizing wasted time. Well-governed data operates similarly. It allows for smooth operations, reducing wasted resources and boosting productivity.
Empowering Value-Based Care Initiatives
Robust data governance is also essential for value-based care initiatives. Accurate performance metrics, based on reliable data, are crucial. They demonstrate the effectiveness of care provided and justify reimbursement under value-based models. In this model, providers are rewarded for the quality of care, not the quantity of services.
This data-driven approach ensures accurate reporting. It allows providers to receive appropriate compensation for their value-based services. Strong data governance enables organizations to demonstrate improved patient outcomes. This is a core component of value-based care, achieved by consistently and accurately tracking patient data.
Building a Business Case for Data Governance
Getting executive buy-in for data governance requires a compelling business case. Frame governance initiatives in terms that resonate with healthcare leadership. Emphasize financial benefits and demonstrate a clear ROI. Show how reduced costs, improved revenue, and enhanced value-based care reimbursement contribute to the organization’s financial success.
Presenting data governance as a driver of innovation can be especially persuasive. It appeals to executives seeking ways to improve patient outcomes and gain a competitive edge. The global data governance market is growing, fueled by increasing regulatory requirements and the need for data-driven decisions.
The market is expected to grow from $4.35 billion in 2024 to $5.11 billion in 2025. This growth shows rising investment in governance frameworks and expertise. Learn more about these investments: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/data-governance-global-market-report. Data governance is increasingly seen as a strategic investment, not a cost center. This investment not only addresses compliance but also positions healthcare organizations for future success in a rapidly evolving data landscape.
From Theory to Practice: Making Data Governance in Healthcare Stick
The healthcare industry has seen its share of failed data governance initiatives. How can your organization avoid this pitfall? This section offers a practical, step-by-step roadmap based on proven approaches in real healthcare settings.
Assessing Your Current State: Data Maturity and Governance Capabilities
Effective data governance begins with understanding your organization's current state. This involves a thorough assessment of your data maturity and existing governance capabilities. Ask key questions: Where is your data stored? Who can access it? How is data quality maintained? This process reveals strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, forming the basis for a tailored governance framework.
Securing Executive Buy-In: More Than Just Lip Service
Strong leadership support is crucial for data governance success. Securing executive buy-in means more than just obtaining a signature. It requires demonstrating the value of data governance through a compelling business case. Highlight the potential return on investment (ROI), showcasing cost reductions, improved revenue capture, and enhanced value-based care. When executives see tangible benefits, they become data governance champions, advocating for resources and fostering a data-driven culture.
Building Cross-Functional Collaboration: Blending Clinical and Technical Expertise
Data governance in healthcare isn't solely an IT responsibility. A successful program requires a cross-functional approach. Establish a data governance steering committee with representatives from various departments, including clinical staff, IT professionals, data scientists, privacy officers, and legal counsel. This diverse team can address the unique challenges of healthcare data, blending clinical and technical expertise to create practical, relevant policies that support both clinical workflows and organizational objectives.
Developing Healthcare-Specific Policies: Addressing Unique Requirements
Healthcare data has unique characteristics, demanding specialized governance policies. These policies must address requirements related to medical documentation standards, controlled medical terminologies, patient privacy regulations (like HIPAA), and evolving requirements like those within the 21st Century Cures Act. For instance, policies regarding patient consent are crucial for regulatory compliance. These tailored policies are fundamental for effective and compliant data management in healthcare.
Fostering a Data-Aware Culture: Making Governance Part of Everyday Workflows
Data governance should be seamlessly integrated into daily workflows, not an administrative burden. This requires implementing change management strategies designed for healthcare professionals. Targeted training, demonstrations of practical benefits, and user-friendly tools can encourage adoption and compliance. This cultivates a data-aware environment where governance becomes ingrained in daily practice.
Implementation Timelines and Success Metrics: Building Sustainable Governance
Realistic implementation timelines are essential. Break down the process into smaller, manageable milestones. Define clear success metrics to monitor progress and demonstrate program effectiveness. These metrics could include improvements in data quality, reductions in data errors, increased compliance rates, or enhanced operational efficiencies. Tracking these metrics ensures accountability and allows for ongoing adjustments, leading to a sustainable, adaptable data governance program.
Key Implementation Steps: A Practical Roadmap
Here's a summary of the key steps for successful data governance implementation in healthcare:
- Assessment: Evaluate your current data landscape, including systems, data quality, and existing governance practices.
- Planning: Create a detailed implementation plan with clear objectives, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Policy Development: Develop comprehensive data governance policies tailored to healthcare, addressing privacy, security, access, and quality.
- Communication and Training: Ensure clear communication and provide effective training to all stakeholders.
- Technology Implementation: Implement data governance technologies that align with your needs and integrate with existing systems.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor program effectiveness and evaluate performance against metrics.
- Refinement and Adaptation: Adjust policies, processes, and technologies based on monitoring and evaluation results.
Following these steps allows your organization to build a robust data governance program, resulting in improved data quality, enhanced compliance, and greater operational efficiency.
Ready to leverage your healthcare data as a strategic asset? PYCAD, with expertise in AI and medical imaging, can guide your organization toward effective data handling, model training, and deployment.