The DICOM Difference: Why DCM Files Matter in Medicine
Navigating medical imaging can be confusing, especially when encountering DCM files. These files, crucial for modern medical image viewing, adhere to the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standard. DICOM isn't just a simple image format; it's a comprehensive record containing much more than what initially appears.
DCM files differ significantly from standard image formats like JPEGs or PNGs. While JPEGs and PNGs focus on pixel data, DCM files encapsulate vital patient metadata along with the image. This includes patient demographics, imaging parameters, and the equipment used during the scan. This is why opening a DCM file with a typical photo viewer won't work – it can't interpret the embedded information.
This combined image and metadata format revolutionized medical records. The DICOM standard, released in 1993, has been adopted by over 90% of global healthcare systems using DICOM-compatible devices for storing .dcm files. These files integrate pixel data (like X-rays and MRI scans) with metadata, adhering to a format used by over 100 medical equipment manufacturers. By 2023, cybersecurity research highlighted vulnerabilities in DICOM’s Store service, emphasizing the need for specialized software like OsiriX or 3D Slicer for secure access, while maintaining HIPAA and GDPR compliance. The standard's longevity, refined through 30 years of updates, ensures backward compatibility, allowing modern viewers to access legacy scans from the 1990s, provided the headers are intact. Learn more about DICOM's history here. This data integration facilitates smooth data transfer between healthcare providers and ensures accurate diagnoses.
Why DICOM Is the Gold Standard
DICOM's significance goes beyond simple record-keeping. It's essential for:
-
Interoperability: DICOM allows easy medical image sharing across different healthcare systems and software. This enables specialists in various locations to collaborate effectively.
-
Precise Diagnostics: The metadata in DCM files offers critical context for radiologists and specialists, ensuring accurate image interpretation.
-
Longitudinal Studies: DICOM's standardization allows comparisons of current and previous scans, facilitating patient progress tracking.
-
Research and Development: The rich data within DCM files makes them invaluable for research, enabling analysis of large datasets and the development of new diagnostic tools. Understanding file compression can aid in managing DCM files. For insights into file size reduction, see this resource on reducing file sizes.
This robust nature is why DICOM remains the gold standard for medical imaging, handling everything from basic X-rays to complex MRI and CT scans. This ensures medical professionals have the necessary information for optimal patient care.
Free Software Solutions: Opening DCM Files Without Cost
Accessing medical images shouldn't be a financial burden. Several robust free software options simplify opening DCM files, making medical data readily available to everyone, from patients to healthcare providers. This section explores some prominent freeware choices, focusing on installation, interfaces, and core viewing capabilities.
MicroDicom: A Versatile Windows Solution
MicroDicom (MicroDicom) is a widely-used free DICOM viewer for Windows. Its straightforward installation and intuitive interface make it ideal for users new to DICOM software.
MicroDicom offers several key features:
- Basic image manipulation: Adjust brightness, contrast, and zoom.
- Measurement tools: Perform distance and angle measurements.
- Multiple image viewing layouts: Compare images side-by-side or in grids.
- Patient demographics display: Access embedded patient information.
However, MicroDicom has some limitations:
- Windows only: It's unavailable for Mac or Linux.
- Limited advanced features: It lacks 3D reconstruction or specialized tools.
RadiAnt DICOM Viewer: Cross-Platform Simplicity
RadiAnt DICOM Viewer (RadiAnt) is another free option known for its user-friendly interface and cross-platform compatibility (Windows, Mac, and Linux). This makes it a versatile choice for users needing to access DCM files across different operating systems.
RadiAnt's highlights include:
- Intuitive image navigation: Scroll through image stacks and studies.
- Basic image processing tools: Adjust windowing, leveling, and apply presets.
- DICOM tag viewing and editing: Access and modify DICOM metadata.
- Report generation: Create reports with annotations and measurements.
The free version of RadiAnt does have some constraints:
- Limited advanced features: Access to advanced tools like MIP/MPR reconstructions is restricted.
- Performance with large datasets: Handling very large datasets can be challenging.
Horos: Mac-Focused Open-Source Powerhouse
Horos (Horos) is a powerful open-source DICOM viewer specifically designed for Mac users. Its open-source nature allows for community contributions and ongoing development. Horos offers a rich feature set often found in premium DICOM viewers.
These features include:
- Advanced image processing: Image fusion, filtering, and noise reduction.
- 3D reconstructions: Generate 3D models from image stacks.
- Measurement and annotation tools: Measure distances, angles, areas, and annotate images.
- Plugin support: Extend functionality with specialized plugins.
Despite its robust features, Horos has limitations:
- Mac only: Limited use for those on other operating systems.
- Steeper learning curve: Navigating its extensive features can be initially challenging.
Choosing the Right Free DCM Viewer
Choosing the best free DCM viewer depends on your individual needs. The data chart below visualizes key differences between the viewers, scoring them on ease of use and features to help inform your decision.
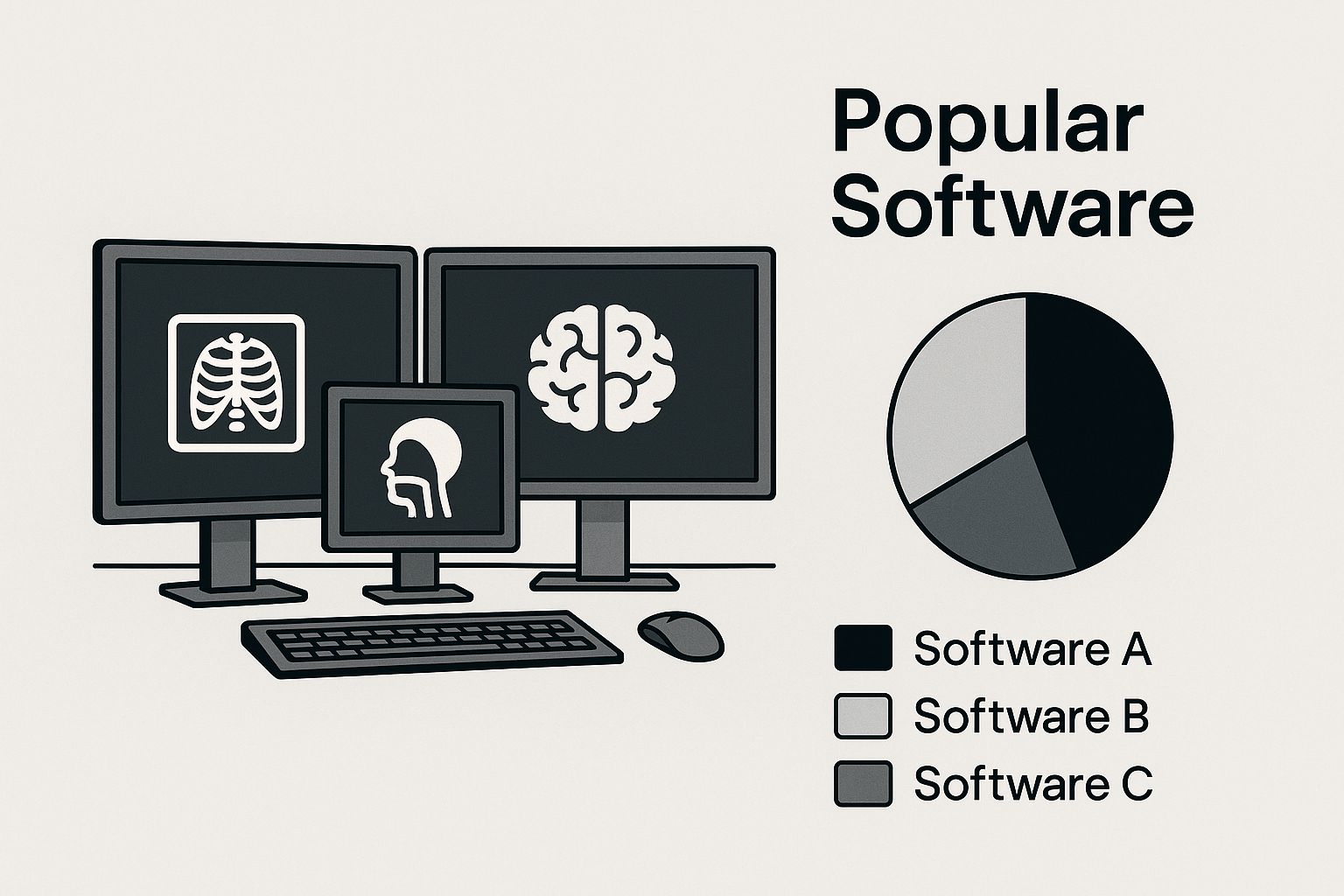
The chart highlights MicroDicom’s simplicity for beginners, scoring an 8/10 for ease of use. RadiAnt balances usability (7/10) and features (6/10). Horos excels in advanced functionality (9/10) but has a slightly lower ease of use score (6/10) due to its complexity. As the chart clearly depicts, Horos is better for advanced features and 3D reconstruction while MicroDicom and RadiAnt excel in simplicity for basic image viewing.
To help you make the best choice, we've compiled this comparison table:
| Software Name | Platforms | Key Features | Limitations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MicroDicom | Windows | Basic image manipulation, measurement tools, multiple image viewing layouts, patient demographics display | Windows only, limited advanced features | Beginners, basic image viewing on Windows |
| RadiAnt DICOM Viewer | Windows, Mac, Linux | Intuitive image navigation, basic image processing tools, DICOM tag viewing/editing, report generation | Limited advanced features, performance issues with large datasets | Cross-platform users, user-friendly interface, basic image processing |
| Horos | macOS | Advanced image processing, 3D reconstructions, measurement and annotation tools, plugin support | Mac only, steeper learning curve | Mac users, advanced features, 3D visualization |
Selecting the right viewer involves balancing simplicity with functionality. MicroDicom is excellent for basic viewing on Windows. RadiAnt is a strong contender for cross-platform compatibility and ease of use. Mac users needing advanced capabilities, like 3D reconstruction, should consider Horos. The best free DCM file opener ultimately depends on your specific needs, from simple viewing to in-depth analysis. This understanding provides a solid foundation when considering premium options if your requirements eventually exceed the capabilities of free software.
Premium DICOM Viewers: When Free Isn't Enough
Free DICOM viewers offer a convenient entry point for viewing .dcm files. However, their limitations become noticeable when handling complex medical cases, research projects, or specialized scenarios. Premium DICOM viewers address these limitations by providing advanced features and capabilities that enhance the interaction with medical images. For professionals requiring precise and detailed analysis, investing in premium software is often essential.
Advanced Features of Premium Viewers
Premium viewers, such as OsiriX Pro, Horos Pro, and ViewerLite, offer tools that extend beyond basic viewing functionality. Volumetric rendering, for instance, allows clinicians to visualize anatomical structures in 3D, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of complex pathologies. AI-assisted measurements automate time-consuming tasks, thus boosting workflow efficiency. This frees up medical professionals to concentrate on diagnosis and treatment planning instead of manual calculations.
-
Advanced 3D Visualization: Explore detailed 3D models using tools like MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) and VR (Virtual Reality) integration.
-
AI-Powered Analysis: Utilize artificial intelligence for automated segmentation, lesion detection, and quantitative image analysis.
-
Specialized Toolsets: Access tools tailored for specific medical disciplines, including cardiology, neurology, and oncology.
-
High-Performance Processing: Efficiently manage large datasets and complex image processing tasks.
-
Integration and Customization: Integrate seamlessly with existing PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) and customize workflows to suit specific needs.
If a DCM file contains embedded text or metadata, programmatic extraction might be necessary. A helpful guide on extracting text from PDF files can offer valuable insights, especially when working with research data or extracting specific information from patient records. This can be especially valuable in research and clinical settings.

Justification for the Investment
The cost of premium viewers is often justified by the value they bring to specialized clinical scenarios. Consider the interpretation of intricate neurological scans or research requiring precise tissue differentiation. In such cases, premium tools become crucial for diagnostic confidence and research accuracy. For routine viewing of standard medical images, however, free tools may suffice. Therefore, it's important to thoroughly evaluate your specific needs before investing in premium software.
Premium vs. Free: A Feature Comparison
To help you decide whether an upgrade is worthwhile, the following table compares the features of premium and free DICOM viewers.
| Feature Category | Free Viewer Capabilities | Premium Viewer Capabilities | Worth Upgrading? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Visualization | Limited or basic 3D rendering | Advanced 3D, MIP, VR, surface rendering | Often |
| Image Analysis | Basic measurements, annotations | AI-powered segmentation, quantification, advanced measurements | Sometimes |
| Specialized Tools | Few or none | Dedicated tools for specific medical specialties | Depends on need |
| Performance | Can struggle with large datasets | Optimized for large datasets, fast processing | Often |
| Integration & Customization | Limited | PACS integration, workflow customization | Sometimes |
This comparison highlights the areas where premium viewers excel. While free viewers handle basic tasks adequately, premium software offers substantial benefits for those requiring advanced capabilities. This ensures medical professionals have access to the most appropriate tools for their individual circumstances.
Understanding the premium DICOM viewer landscape facilitates informed decisions about whether the enhanced features justify the investment. Even if free solutions currently meet your requirements, awareness of premium viewer capabilities enables you to anticipate future needs and transition smoothly when necessary. This proactive approach prepares you for evolving demands in medical imaging and ensures access to the most effective tools.
Browser-Based Solutions: View DCM Files Without Installing
The need to access medical images swiftly and without cumbersome software installations is increasingly important in modern healthcare. This demand has fueled the development of browser-based DICOM viewers, effectively removing the hurdles associated with traditional software. This section explores several key online platforms, focusing on their accessibility, core functionality, and—most importantly—security considerations.
Online DICOM Viewing Platforms
Several online platforms provide convenient access to DCM file viewing:
-
DICOM Web Viewer: This platform presents a user-friendly interface for uploading and viewing .dcm files directly within your browser. Supporting basic image manipulation, it's ideal for quick reviews and remote consultations.
-
Postdicom: For users requiring more advanced functionality, Postdicom offers tools like 3D rendering and image annotation, all within a web browser environment. This makes it well-suited for professionals needing more in-depth image analysis capabilities.
-
OHIF Viewer (Open Health Imaging Foundation): The OHIF Viewer, an open-source, browser-based DICOM viewer, is known for its customizability. Developers can adapt the platform to meet specific requirements and integrate it seamlessly with existing healthcare systems.
Uploading and Viewing DCM Files Online
Using these viewers is generally straightforward:
-
Upload: Most platforms utilize a simple drag-and-drop interface or a standard file selection dialogue for uploading your .dcm files.
-
View: Once uploaded, images appear directly in the browser window. Typical features include navigating through image stacks, zooming, adjusting contrast, and using basic measurement tools.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Handling sensitive medical data online demands the highest levels of care. Patient privacy is paramount. When selecting a browser-based viewer, consider these critical factors:
-
Data encryption: Ensure the platform employs robust encryption methods for both data transmission and storage.
-
Compliance: Confirm the platform's compliance with all relevant healthcare regulations, including HIPAA and GDPR.
-
Data storage policies: Understand how the platform handles data storage, including retention periods and disposal procedures.
De-identification tools, such as DICOM Anonymizer, offer crucial safeguards for handling data online. These tools automatically remove over 50 PHI (Protected Health Information) tags from .dcm files while preserving vital diagnostic information. This process is critical for ensuring research compliance under GDPR and HIPAA. Studies indicate that improperly anonymized DICOM files contribute to 15-20% of healthcare data breaches, emphasizing the urgent need for secure viewers. Learn more about the DICOM standard here.
Browser Optimization for Seamless Viewing
Optimizing your browser can dramatically improve online viewing performance, particularly for large or complex datasets:
-
Close unnecessary tabs: Freeing up system resources can significantly enhance viewer responsiveness.
-
Clear browser cache: This simple step can resolve issues arising from outdated or corrupted files.
-
Update your browser: Using the most recent browser version ensures optimal performance and security.
-
Disable extensions: Browser extensions, while often helpful, can sometimes interfere with viewer functionality.
Browser-based DICOM viewers provide convenient and accessible ways to view medical images without requiring local software installations. Choosing the appropriate platform requires careful consideration of security, privacy, and the required functionality. Whether you need a quick image review or in-depth analysis, understanding the capabilities and limitations of these online tools empowers you to select the best solution for your specific needs.
Mobile DICOM Viewing: DCM Files in Your Pocket
The ability to access DCM files on mobile devices has revolutionized medical workflows. Physicians, specialists, and even patients can now view these critical images on smartphones and tablets, offering unprecedented flexibility. This section explores the practicalities of mobile DICOM viewing, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of popular apps, and addressing the challenges of working with medical images on smaller screens.

Top Mobile DICOM Viewers
Several mobile applications stand out for their effective handling of DICOM data:
-
Mobile MIM: This app offers a comprehensive suite of features, including advanced image manipulation tools and broad DICOM format support, making it a favorite among radiologists.
-
RadiAnt Mobile: A mobile counterpart to the popular desktop software, RadiAnt Mobile maintains a user-friendly interface optimized for touchscreens. Its intuitive design makes it ideal for quick image reviews.
-
DICOM Viewer by Sashidhar: This lightweight app prioritizes essential viewing functions, making it a good choice for older devices or when storage space is at a premium. Its simplified design ensures smooth operation even on less powerful hardware.
Practical Considerations for Mobile Viewing
Using mobile DICOM viewers effectively requires attention to some key practicalities:
-
Storage Management: Given the large size of DCM files, efficient storage management is essential. Consider using cloud storage services or external drives to supplement limited device storage.
-
Display Calibration: Accurate image interpretation depends on proper display calibration. While challenging on mobile, adjusting brightness and contrast is crucial for reliable diagnostic review.
-
Secure Image Transfer: Transferring sensitive medical information requires robust security measures. Employ encrypted transfer protocols like SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) and secure storage solutions to maintain patient confidentiality. For instance, when transferring files between devices, using SFTP is significantly more secure than sending unencrypted email attachments.
Interface and Interaction
Mobile DICOM viewers leverage touch-based interactions. Some apps attempt to replicate familiar desktop functions on a touchscreen, creating a hybrid approach. While potentially convenient, this can also lead to a learning curve for users accustomed to either a mouse-driven or purely touch-based interface. Choosing a viewer with an interface that aligns with your workflow is important.
Diagnostic Limitations
While mobile viewers offer valuable functionality, it's important to be aware of their inherent limitations:
-
Screen Size: Smaller screens restrict the level of detail visible, potentially impacting diagnostic accuracy in complex cases. Dedicated workstations with larger displays remain essential for thorough image analysis.
-
Processing Power: Mobile devices may struggle with demanding tasks like 3D rendering or advanced image processing, where desktop solutions maintain a significant advantage.
-
Connectivity: Reliable internet access is often needed for cloud-based image access and collaboration. Offline access capabilities become critical in areas with limited connectivity.
Despite these limitations, mobile DICOM viewers have become invaluable tools in modern healthcare. They enable remote consultations, facilitate quick image reviews during rounds, and empower patients to access their medical imaging data directly. By carefully selecting an appropriate viewer and understanding its capabilities and limitations, healthcare professionals can harness the power of mobile DICOM viewing to enhance their workflow and improve patient care.
Troubleshooting: Solving Common DCM File Problems
Working with DCM files, even with the right software, can sometimes present challenges. This guide addresses common issues users face when opening DCM files and offers practical solutions.
Common DCM File Opening Issues
Several factors can prevent a DCM file from opening as expected:
-
Corrupted DICOM Headers: The DICOM header contains crucial file information. If this header is damaged, the viewer may be unable to interpret the data, preventing the file from opening.
-
Incomplete File Transfers: Interrupted downloads or network issues can result in incomplete files. This is a frequent problem with large files or unstable connections.
-
Compatibility Issues: Older medical imaging equipment may use non-standard DICOM implementations. This can lead to compatibility problems with modern viewers, causing files to not open or display incorrectly.
Diagnosing the Problem
Pinpointing the specific problem is the first step to finding a solution:
-
File Doesn't Open: This might indicate a corrupted header or an incompatible file format. Try opening the file with different DICOM viewers to eliminate software-specific issues.
-
Incorrect Display: If the image displays with incorrect orientation, contrast, or resolution, it could suggest a header problem or viewer incompatibility. Check the viewer’s settings and try adjusting the display parameters.
-
Error Messages: Carefully review any error messages from the viewer. These messages can provide valuable clues about the underlying problem, such as missing tags or unsupported compression.
Recovery and Workarounds
Several techniques can help resolve DCM file issues:
-
Header Repair Tools: Specialized software can sometimes repair corrupted DICOM headers, allowing you to regain access to your data.
-
Re-transferring Files: If you suspect an incomplete transfer, try downloading the file again, ensuring a stable network connection.
-
Manufacturer-Specific Viewers: For compatibility issues with older equipment, using a viewer from the original manufacturer may be necessary to correctly interpret non-standard implementations.
Batch Processing and Validation
For multiple problematic files, consider these strategies:
-
Batch Processing: Some viewers offer batch processing, enabling you to apply fixes or conversions to numerous files at once, saving you significant time.
-
Validation Tools: DICOM validation software can check file integrity and identify potential errors, ensuring the quality and consistency of your medical imaging data.
Simplifying the Troubleshooting Process
These tips can streamline the troubleshooting process:
-
Start Simple: Before trying complex solutions, try restarting the viewer or updating the software.
-
Consult Resources: Online forums and documentation can offer valuable guidance and solutions for common DICOM problems.
-
Seek Expert Assistance: If you can't resolve the issue yourself, contact the software vendor or a DICOM specialist.
By understanding common problems and applying effective troubleshooting methods, you can efficiently access your medical imaging data. For advanced solutions and to improve your workflow, consider exploring AI-driven medical imaging services offered by PYCAD. Their expertise can enhance medical devices and improve healthcare outcomes.






