The Foundation of Medical Device Integration
Medical device integration is quickly becoming a cornerstone of modern healthcare. It signifies a move from isolated data points toward a connected ecosystem, where medical devices communicate with each other. This interconnectivity provides healthcare professionals with access to real-time data, enabling better decisions and improved patient care.
But what exactly does medical device integration entail? It's more than just plugging devices into a network. It’s about creating a cohesive system. This involves implementing standardized communication protocols, ensuring strong data security, and promoting interoperability among various systems.
Building Blocks of Integration
Successful medical device integration relies on several key elements. The most important is interoperability, the ability of different systems and devices to exchange and utilize information. This requires adherence to established standards such as HL7 and FHIR (Health Level Seven International) which act as a common language for medical devices.
A secure and dependable network infrastructure is also crucial. It must be capable of managing the growing amount of data generated by connected devices. This infrastructure needs to prioritize both performance and security to safeguard sensitive patient information. Finally, user-friendly interfaces are vital to ensure clinicians can easily access and understand the data.
The Power of Interoperability
Imagine a patient’s vital signs, collected from various bedside monitors, being automatically sent to their Electronic Health Record (EHR). This eliminates manual data entry, reducing errors and saving valuable clinical time.
Integrating medical devices with EHR systems also unlocks a treasure trove of data that can improve patient outcomes. This data can power clinical decision support systems, alerting physicians to potential problems or recommending personalized treatment plans.
The integration of medical devices with EHR systems is a key factor in the growth of the medical device connectivity market. This market is expected to reach $2.29 billion in 2025. It's projected to grow at a 23.5% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2025 to 2035. Learn more about this growing market here. The growing adoption of EHR systems is vital for modern healthcare, enabling real-time communication between medical devices and reducing administrative costs.
Organizational Structure and Strategic Planning
Effective medical device integration requires collaboration among different departments within a healthcare organization. IT departments, clinical engineering teams, and clinicians must work together. They need to define integration goals, choose the right technologies, and implement efficient training programs.
This collaborative approach ensures the integrated system meets everyone's needs and is seamlessly incorporated into clinical workflows. Careful strategic planning and this coordinated effort can transform separate devices into a unified patient care platform. This creates a foundation for a future of truly connected healthcare.
Tangible Benefits That Transform Patient Care
Medical device integration is more than just a technological advancement. It’s a catalyst for tangible improvements in patient care. By connecting separate devices into a unified system, hospitals see significant, measurable benefits that directly impact patient well-being and overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Clinical Efficiency and Reduced Errors
One of the most striking advantages is the reduction in manual documentation. Imagine nurses freed from manually recording vital signs from various machines. Integrated systems automatically send this data directly to the patient's Electronic Health Record (EHR), freeing up valuable time for direct patient care.
This automation not only saves time but also significantly minimizes the risk of transcription errors, which can have serious consequences for patient safety. For example, studies show that integrating smart pumps has led to a 63% reduction in medication errors in some hospitals.
Additionally, alarm management systems, enabled through medical device integration, allow clinicians to prioritize critical alerts. This minimizes alarm fatigue and ensures a quicker response to patients needing immediate attention. In some ICUs, this has dramatically reduced response times, directly improving patient outcomes.
Improved Treatment and Data-Driven Decisions
Real-time data flow, a key feature of medical device integration, enables better adherence to treatment protocols. Having instant access to patient data from multiple sources empowers healthcare providers to make more informed, data-driven decisions.
This translates to more effective treatment plans, improved patient compliance, and ultimately, better health outcomes. The seamless flow of information allows clinicians to adjust treatments promptly, based on the most up-to-date patient information.
To understand how these benefits affect various stakeholders, take a look at the table below:
Benefits of Medical Device Integration by Stakeholder
A comprehensive comparison of how different healthcare stakeholders benefit from medical device integration.
| Stakeholder | Clinical Benefits | Operational Benefits | Financial Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Improved safety, more personalized treatment, better outcomes | Reduced wait times, streamlined processes | Lower healthcare costs |
| Clinicians | Enhanced decision-making, reduced administrative burden, increased job satisfaction | Improved workflows, better communication | |
| Hospital Administrators | Enhanced quality of care, improved patient satisfaction | Increased efficiency, optimized resource allocation | Improved revenue cycle, cost savings |
The table above highlights how integrated systems positively impact everyone involved in patient care, from the patients themselves to the hospital administrators. Each stakeholder group experiences unique advantages that contribute to a more efficient and effective healthcare environment.
Financial Impacts and ROI
Integrating medical devices into broader healthcare systems is vital for the continued advancement of the medical device industry. The market is projected to grow to just under $800 billion soon, driven by the increasing importance of medical device connectivity. Find more detailed statistics here. This growth underscores the value and potential of integrating medical devices.
The benefits also extend to impactful financial outcomes. Reduced length of stay, a common result of more efficient and effective care, directly contributes to cost savings. Improved documentation through integration enhances reimbursement capture, ensuring hospitals receive appropriate compensation.
These financial benefits make medical device integration a compelling investment. While implementing such systems requires upfront costs, the resulting ROI can be surprisingly quick. It is often recouped within a few years due to efficiency gains, reduced errors, and improved revenue capture. These positive financial impacts make medical device integration not just a good clinical decision, but a sound financial one as well.
Breakthrough Technologies Powering Connected Care

The world of healthcare IT is always on the move, driven by the demand for more efficient, precise, and patient-focused services. As providers look to connect devices and data, certain solutions are standing out. This overview highlights the main advancements that are shaping more cohesive care networks.
FHIR: The Universal Language Of Healthcare
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is a standard developed by HL7 to unify data exchange across systems and devices. By acting as a common framework, FHIR allows medical equipment from different makers to “speak” the same data language. This interoperability is a cornerstone for building systems that can share vital patient information without manual intervention.
Edge Computing In Bedside Settings
Edge computing brings processing power directly to the patient’s location rather than sending every data point back to a central data center. This local analysis can trigger rapid alerts and reduce network delays—critical factors in intensive care and emergency units. For instance, an edge-powered alarm system can notify staff instantly when a patient’s vital signs cross a predefined threshold.
Cloud Integration Across The Enterprise
Cloud integration provides scalable storage and secure processing for medical data across departments and locations. Hospitals and clinics can hook devices into cloud platforms, granting care teams instant access to real-time patient metrics and historical records. This setup supports remote monitoring, centralized analytics, and coordinated workflows across multiple facilities.
The global medical device market is set to grow to $678.88 billion by 2025, driven by advances in AI, 3D printing, and robotics that enable more precise and personalized treatments. Explore these figures in more detail in the Medical Device Industry Statistics report. This growth underscores why integrating devices effectively is key to healthcare’s next phase.
Emerging Technologies Shaping The Future
Beyond these foundational systems, several newer solutions are poised to enhance device connectivity:
- AI-Powered Data Normalization to standardize outputs from diverse instruments
- Blockchain Technology for securing device logs and patient records
- API Architectures that allow flexible addition of new products and services
Together, these trends are building toward a healthcare environment where devices, data, and care teams operate in close coordination.
Overcoming Integration Roadblocks: Practical Solutions
Medical device integration offers significant benefits, but achieving a fully connected healthcare ecosystem presents several challenges. Understanding these potential roadblocks and implementing practical solutions is crucial for success.
Technical Hurdles and Their Solutions
One of the biggest technical challenges is legacy system compatibility. Older systems often rely on outdated communication protocols, making integration with modern devices difficult. This can be compared to connecting a vintage record player to a Bluetooth speaker – an adapter is needed to bridge the gap. Similarly, middleware solutions can translate data between legacy systems and newer devices, enabling effective communication.
Another hurdle is data standardization. Various medical devices often use different formats for recording and transmitting data. This inconsistency makes it challenging to aggregate and analyze data from multiple sources. Adopting standardized data formats, such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), can address this issue, enabling seamless data exchange.
Cybersecurity is another major concern. Connecting medical devices increases the potential vulnerabilities for hackers, putting sensitive patient data at risk. Robust security measures, including strong encryption and multi-factor authentication, are vital for protecting patient privacy and ensuring data integrity. Strong integrations are essential when implementing new technologies. Learn more about creating world-class integrations: World-Class Integrations.
Addressing the Human Element
Beyond technical challenges, medical device integration involves significant human factors. A key aspect is managing clinical workflow disruptions. Integrating new systems and devices can disrupt established workflows, potentially leading to frustration and resistance among clinicians. Thorough training and ongoing support are essential for helping clinicians adapt to new technologies and minimize disruptions.
Overcoming departmental silos is also crucial. Successful integration requires collaboration between IT, clinical engineering, and clinical staff. Establishing clear communication channels and fostering a culture of collaboration helps break down these silos and ensures everyone works towards a shared goal.
Furthermore, building cross-functional teams with representatives from all relevant departments streamlines decision-making. This inclusive approach ensures the integrated system meets the needs of all stakeholders.
A detailed table summarizing common integration challenges and solutions is provided below.
Introducing the table "Common Medical Device Integration Challenges and Solutions", this table provides a detailed breakdown of implementation challenges with proven solutions and mitigation strategies.
| Challenge Category | Specific Challenges | Solution Approaches | Success Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Compatibility | Legacy system integration, Data standardization | Middleware solutions, FHIR adoption | Thorough testing, Vendor collaboration |
| Security | Data breaches, Unauthorized access | Robust encryption, Multi-factor authentication | Regular security audits, Staff training |
| Clinical Workflow | Disruptions to existing processes, Clinician resistance | Training and support, Phased implementation | Change management strategies, Clinician involvement |
| Interdepartmental Collaboration | Siloed departments, Communication barriers | Cross-functional teams, Clear communication channels | Shared goals, Collaborative culture |
This table highlights the importance of addressing both technical and human factors for successful medical device integration. Solutions range from technical implementations like middleware and FHIR to strategic approaches like cross-functional teams and change management.
Practical Strategies for Success
A phased approach to medical device integration is often the most effective. Starting with a pilot project allows organizations to test the integration process and identify potential issues before a full-scale rollout. Regular assessments of organizational readiness and plan adjustments are essential for success.
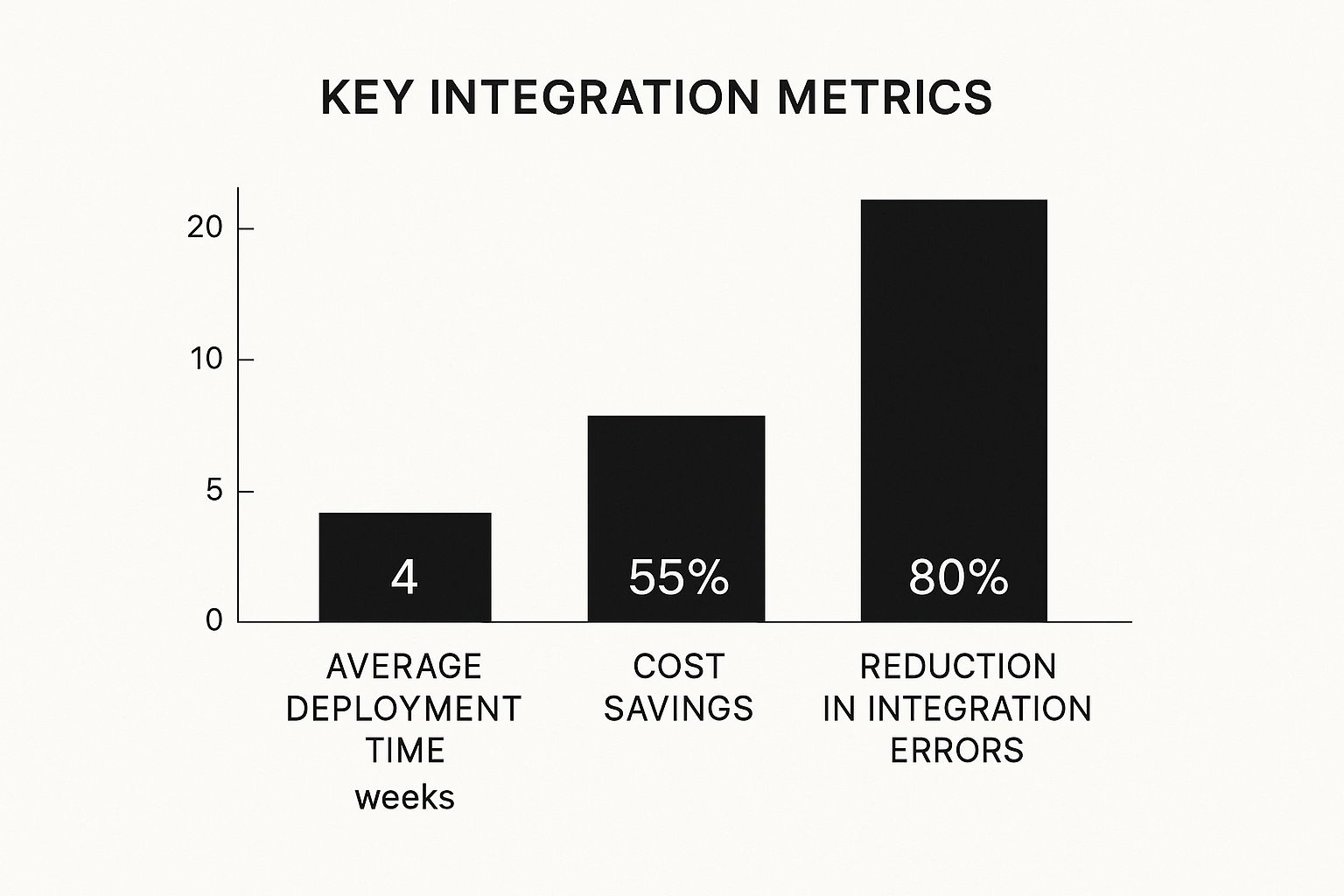
This infographic visually compares key integration metrics, demonstrating the benefits of a well-executed strategy. The data reveals significant improvements in deployment time, cost savings, and error reduction.
A phased rollout, combined with addressing both technical and human factors, enables healthcare organizations to realize the full potential of medical device integration while mitigating risks. This approach leads to improved patient care, enhanced efficiency, and a stronger, more connected healthcare ecosystem.
Medical Device Integration Across Clinical Settings

Medical device integration is changing how we deliver patient care. From busy critical care units to smaller outpatient clinics, the ability to connect various devices and systems gives healthcare providers a broader picture of patient health. This leads to better decisions and more efficient workflows. Examining how other industries address similar integration challenges can be insightful. For example, the HubSpot Jira integration demonstrates how improved collaboration and efficiency can be achieved.
Critical Care Units: Enhancing Patient Safety
In critical care environments, where time is of the essence, medical device integration is crucial for patient safety and quick interventions. For instance, connecting ventilators to patient monitoring systems allows clinicians to see ventilator settings and patient responses immediately. This readily available data enables faster adjustments to ventilation parameters, potentially minimizing the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia and other complications. Integrated alarm management systems also help to combat alarm fatigue and ensure that crucial alerts are addressed promptly.
Operating Rooms: Optimizing Surgical Precision
Precision and coordination are key in operating rooms, making medical device integration just as valuable in these settings. Integrating anesthesia devices allows for constant monitoring of vital signs, anesthetic delivery, and other important parameters throughout surgery. This real-time data allows anesthesiologists to make better-informed decisions regarding anesthetic adjustments, improving patient safety and optimizing surgical outcomes. Integration can also improve communication between surgical teams, guaranteeing everyone has the latest patient information.
Outpatient Settings: Empowering Patient Management
The advantages of medical device integration extend beyond hospitals, notably affecting outpatient care. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems, made possible through integration, allow patients to manage chronic conditions from home. Wearable devices and home-based monitoring equipment collect vital signs, activity levels, and other pertinent data, which is then sent to healthcare providers. This constant flow of patient information facilitates proactive intervention, medication adjustments, and personalized care plans, leading to improved patient outcomes and fewer hospital readmissions.
Emerging Care Models: Supporting Innovation
Medical device integration supports new care models like hospital-at-home programs and virtual consultations. These models heavily depend on remote monitoring and data sharing to provide quality care outside of traditional healthcare settings. Integration also supports the advancement of AI-driven early intervention systems. These systems analyze patient data from multiple sources to identify subtle shifts that may suggest deterioration, often hours before traditional methods. This early warning can be vital, allowing for timely interventions to prevent serious issues. These integrations are reshaping healthcare by enabling personalized, proactive, and data-driven care, regardless of the patient's location. This shift toward patient-centric models empowers both individuals and providers, supporting a collaborative approach to health management.
The Future of Medical Device Integration
Medical device integration is evolving at a rapid pace, constantly pushing the boundaries of connected healthcare. This naturally leads us to ask: what does the future hold and how can healthcare leaders adequately prepare? Let's explore the exciting possibilities and the strategies required to navigate this evolving terrain.
The Convergence of Consumer and Clinical Technology
The lines between consumer and clinical technology are blurring. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) expands medical device integration beyond the hospital, bringing it into patients' homes. This empowers individuals to actively participate in their own health management while giving clinicians access to continuous data streams for proactive interventions.
Wearable fitness trackers, for instance, can now gather physiological data that integrates directly with a patient's Electronic Health Record (EHR), painting a more complete picture of their health. This convergence is opening doors to personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring, significantly changing how we manage chronic diseases.
The Power of Predictive Insights
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming device data into predictive insights. By identifying subtle patterns, these technologies can predict potential adverse events before they happen. This predictive capability is particularly beneficial in critical care.
Imagine an AI algorithm analyzing data from numerous connected devices to detect early warning signs of sepsis. This would enable timely intervention, potentially saving lives. This proactive approach to patient care enhances patient safety and demonstrably improves outcomes.
Patient-Centered Integration Models
The future of medical device integration revolves around the patient. New models are providing individuals with unprecedented access to and control over their health data. Patients can access their medical records, monitor their progress, and connect with their care teams directly through secure portals.
This level of transparency cultivates trust and empowers patients to become active participants in their own care. Control over personal health information is a growing demand, and patient-centered integration models directly address this, ultimately strengthening the patient-provider relationship.
Navigating the Challenges of Next-Generation Integration
The future also brings new challenges. Successfully navigating regulatory requirements, guaranteeing data security, and managing increasingly complex integrated systems requires thorough planning. Healthcare organizations must embrace flexible and scalable architectures that readily accommodate new devices and technologies.
Investing in robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient information is equally vital. Addressing these challenges head-on is essential to realizing the full potential of next-generation integration.
A Roadmap for the Future
Forward-thinking healthcare organizations are already laying the groundwork for the future. They are adopting interoperability standards such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), investing in cloud-based platforms, and assembling cross-functional teams to manage integration projects. These organizations understand that medical device integration isn't just a technology upgrade; it's a strategic imperative.
PYCAD is at the forefront of this transformation, offering tailored AI solutions for medical imaging integration. From data handling and model training to deployment and ongoing support, PYCAD empowers healthcare organizations to optimize their medical devices, improve diagnostic accuracy, and enhance operational efficiency. Learn more about how PYCAD can help your organization embrace the future of medical device integration by visiting https://pycad.co.






