Introduction
We discussed the difference between Dicom and Nifti files in this article, and we stated that they are 3D representations of the patient. The Nifti files can also be used to represent the case’s segmentation (masks, annotations)!
What are STL files?
So, for segmentation files, we can find a variety of file types, including STL (Standard Triangle Language).
Install the dependencies
NumPy, Nibabel, scikit-image, and numpy-stl are the packages we’ll need for this project. Using pip, we can install them all:
pip install numpy pip install numpy-stl pip install scikit-image pip install nibabel
If you want to learn more about these libraries, you can do so by visiting their documentation:
Extract the NumPy array from the Nifti file
To convert the Nifti file to STL, we should first extract the NumPy array from the file so that we can use the numpy-stl library to do the conversion.
import nibabel as nib import numpy as np from stl import mesh from skimage import measure file_path = 'segmentation.nii' nifti_file = nib.load(file_path) np_array = nifti_file.get_fdata()
Preprocessing the Numpy array
We need to apply some processing after extracting the NumPy array from the Nifti file to create the 3D mesh from the NumPy array. From here, these operations are taken over from Mr. P Solver’s job.
verts, faces, normals, values = measure.marching_cubes(np_array, 0)
obj_3d = mesh.Mesh(np.zeros(faces.shape[0], dtype=mesh.Mesh.dtype))
for i, f in enumerate(faces):
obj_3d.vectors[i] = verts[f]Export the STL file
After completing the processing, you need just to save the 3D mesh as an STL file.
obj_3d.save('segmentation.stl')
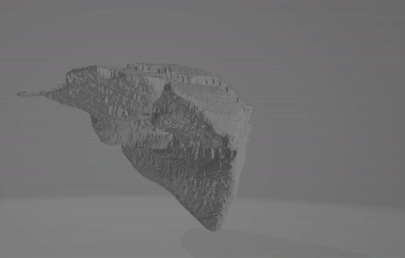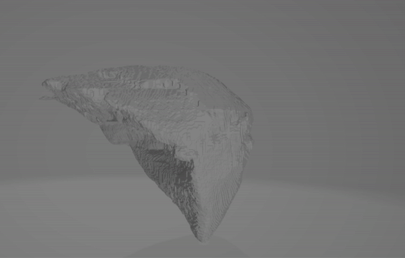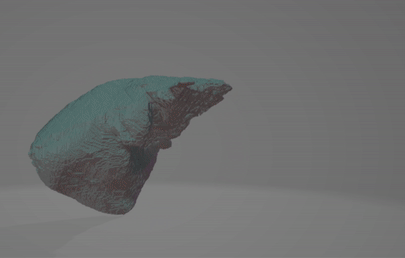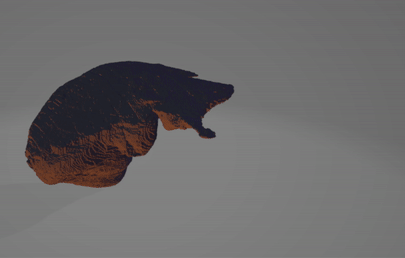
The code can be found here.
🆕 NEW
Learn how to effectively manage and process DICOM files in Python with our comprehensive course, designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge you need to succeed.






