For decades, doctors were essentially asked to solve a three-dimensional puzzle using two-dimensional pieces. Imagine trying to understand the intricate workings of a clock by looking at a flat diagram—that’s the challenge they faced with traditional scans. Modern 3D imaging software completely changes the game by taking that flat data from CT and MRI scans and building it into a living, interactive model. It’s a quantum leap in what we can see and understand.
From Flat Scans to Dynamic Dimensions
The move from a simple 2D image to a full 3D model is one of the most significant shifts in modern medicine. A standard X-ray might show you that a bone is broken, but it can’t truly show you how the fragments are oriented in space. This is where 3D software becomes absolutely essential.
The software works by taking a whole stack of 2D images and computationally layering them to construct a complete, volumetric model. This process, which we dive into deeper in our guide to the https://pycad.co/acquisition-of-images/, turns a collection of static pictures into a dynamic digital twin of the patient's anatomy.
A New Perspective in Medicine
This jump in technology gives medical professionals a powerful new toolkit. Instead of having to mentally piece together a 3D structure from dozens of flat slices, they can now spin, dissect, and explore a fully realized digital model. The impact on patient care is immense.
- Smarter Surgical Planning: Surgeons can now rehearse procedures by rotating, slicing, and examining an organ from every possible angle—all before ever making an incision.
- Sharper Diagnostic Accuracy: Subtle or complex conditions that are easy to miss in 2D become immediately apparent when viewed in their true three-dimensional context.
- Better Patient Communication: It’s one thing to describe a condition; it’s another to show it. These vivid models help doctors walk patients through a diagnosis, building trust and understanding.
This isn't just a visual upgrade. Moving from static images to interactive models is a fundamental change that injects a new level of precision and insight into healthcare, paving the way for more personalized and effective treatments.
The Foundation of Modern Visualization
At its core, the power of this software is its ability to translate a massive amount of raw data into clear, actionable clinical insights. It’s a fantastic example of a broader trend, and it’s fascinating to see other examples of how technological innovation is revolutionizing various fields outside of just healthcare.
This is exactly where we at PYCAD live and breathe. Our focus is on making this complex data intuitive and accessible. We at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, making sure clinicians have these powerful visualizations right at their fingertips. This commitment to pushing medical technology forward is something you can see clearly in our work, which you can view on our portfolio page: https://pycad.co/portfolio. This evolution toward detailed, interactive models is opening the door to a more intuitive, data-driven era of medicine.
The Core Features of 3D Imaging Software
To get a real sense of what 3D imaging software can do, we need to pop the hood and look at the engine inside. It’s about more than just creating pretty pictures; these core features are the very tools that give doctors the power to see inside the human body with breathtaking clarity. Think of them as a set of digital instruments, each designed to turn raw scan data into a clear, understandable story.
This infographic breaks down how these fundamental tools and techniques work together.
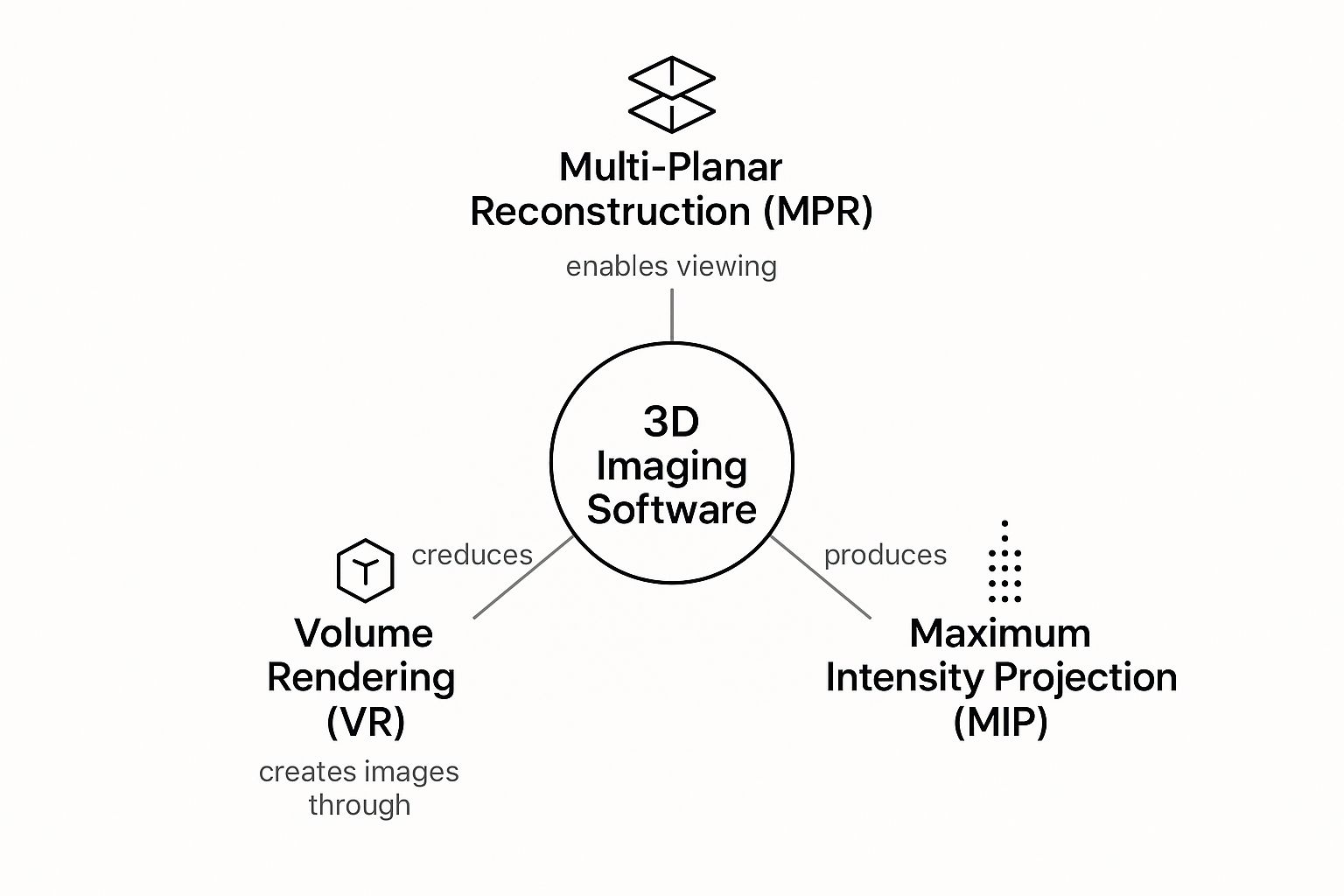
As you can see, features like reconstruction, rendering, and segmentation aren't standalone gimmicks. They're all interconnected pieces of a powerful diagnostic puzzle.
Bringing Digital Anatomy to Life
So, how does a flat, 2D scan become a dynamic 3D model? It starts with a few key techniques that act as the software's building blocks.
-
Multi-Planar Reconstruction (MPR): Imagine a CT scan as a loaf of sliced bread. MPR lets you look at the loaf from the top, the side, or the end—not just the way it was originally sliced. This gives clinicians the freedom to view anatomy from any angle, which is absolutely critical for pinpointing the exact location of a tumor or understanding the complexity of a bone fracture.
-
Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP): This one is fantastic for making specific things pop. MIP scans through all the layers of data and only shows the very brightest, densest points. It’s perfect for angiography, where it makes blood vessels filled with contrast dye light up like a road map, standing out clearly from the surrounding tissue.
-
Volume Rendering (VR): This is the magic that creates those stunning, photorealistic 3D models. The software assigns different colors and levels of transparency to tissues based on their density. The result is a lifelike digital twin of the patient’s anatomy that a surgeon can spin around, zoom into, and explore from every conceivable angle. It’s like having a dress rehearsal before a complex surgery.
-
Segmentation: Think of this as a high-tech digital scalpel. Segmentation allows a user to electronically "cut out" and isolate a single organ, a network of blood vessels, or a tumor from everything else in the scan. By removing all the visual noise, a specialist can get an unobstructed view, measure volumes with precision, and plan treatments with an incredible degree of confidence.
The technology that makes all of this possible is fascinating in its own right. Much of it stems from the fundamentals of computer vision, a field that has completely changed what’s possible in medical imaging.
Core 3D Visualization Techniques Explained
To really appreciate how these tools work in a clinical setting, it helps to see them side-by-side. Each technique offers a unique window into the patient's anatomy, and specialists choose the right one for the job at hand.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the heavy lifters in 3D visualization.
| Technique | What It Does | Primary Medical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Planar Reconstruction (MPR) | Re-slices 2D scan data into new planes (axial, sagittal, coronal). | Orthopedics (fracture assessment), neurology (brain tumor location). |
| Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) | Projects the brightest pixels from a 3D dataset onto a 2D image. | Vascular imaging (angiography), detecting pulmonary nodules. |
| Volume Rendering (VR) | Creates a 3D model by assigning color and opacity to different tissue densities. | Surgical planning, oncology (tumor visualization), patient education. |
| Segmentation | Digitally isolates specific anatomical structures or pathologies. | Organ volume measurement, creating models for 3D printing, radiation therapy planning. |
Ultimately, these core features—MPR, MIP, VR, and segmentation—aren't just code. They are the essential instruments that empower medical professionals to see, understand, and act on the complex stories hidden within every scan.
Where 3D Imaging is Changing Patient Lives
The real magic of 3D imaging software happens when you see it in action, directly improving patient outcomes in one specialty after another. This isn't some generic, one-size-fits-all tool. It's a remarkably adaptable platform that gives clinicians unprecedented clarity right where they need it most.
Whether in the operating room or the oncologist’s office, these dynamic digital models are completely reshaping how doctors and surgeons tackle their most complex cases. It's a fundamental shift from educated guesswork to true, data-driven precision.
The market numbers tell the same story. Medical image analysis software, a category that includes these powerful 3D tools, is already a $3.5 billion global industry. Forecasts show it rocketing to $7.5 billion by 2034. Hospitals make up over 56.8% of this market, signaling a deep, system-wide commitment to embedding this technology into everyday care. You can discover more insights about the medical image analysis market and see where it's heading.
Cardiology and Orthopedics
Take cardiology, for instance. Surgeons can now navigate the heart's incredibly complex structures using a patient-specific 3D model. Planning a delicate valve replacement becomes more like a dress rehearsal than a first performance. They can virtually explore the patient’s unique anatomy, spot potential roadblocks, and map out the safest surgical route long before making the first incision.
We see that same level of meticulous planning in orthopedics. For a joint replacement, surgeons use 3D reconstructions to select the absolute perfect implant size and position it with pinpoint accuracy. This means a better fit, faster recovery, and a device that lasts for years to come.
Oncology and Neurology
In the fight against cancer, 3D imaging has become an indispensable ally. Oncologists can map tumors with breathtaking accuracy, visualizing their exact size, shape, and relationship to nearby organs.
This precision is absolutely critical for radiation therapy. It allows doctors to focus intense energy directly on cancerous cells while carefully avoiding healthy tissue just millimeters away.
Neurosurgeons rely on this technology in a similar way. They use detailed 3D brain maps to plan incredibly delicate procedures, navigating around crucial areas that control speech, movement, and memory. The software lets them see the brain not just as a static organ, but as a living, complex network.
The list of applications just keeps growing. Dentistry uses it to design custom implants that fit perfectly from day one, and it’s become essential for complex maxillofacial surgeries.
At PYCAD, we live and breathe this work. We at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms. Our entire mission is to give specialists tools that feel like they were made just for them, for their specific challenges.
When you give clinicians this kind of clear, interactive view into the human body, you give them the confidence to make better, more informed decisions. To see what these custom solutions look like in the real world, we invite you to explore our portfolio. Every project reinforces a simple but powerful idea: better vision always leads to better care.
Choosing the Right 3D Imaging Platform

Picking the right 3D imaging software is one of the most significant decisions a healthcare practice or hospital can make. This isn't just about ticking boxes on a feature list; it's about finding a partner that will weave itself into the fabric of your clinical workflow, directly influencing patient outcomes and your team's day-to-day efficiency.
Think of it this way: the right platform should feel like an intuitive extension of your team’s own expertise, not another piece of technology to wrestle with. The first major fork in the road is deciding where this powerful tool will live.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Solutions
For a long time, the only real option was an on-premise solution. This meant installing the software directly onto a hospital's local servers, giving IT departments complete, hands-on control over sensitive patient data. It’s a model built on physical security, but it comes with a price—a hefty upfront investment in hardware and the constant demand for in-house maintenance.
Now, cloud-based platforms are changing the game. While on-premise has been the tradition, the tide is turning. Cloud-based 3D imaging software is set to grow at a staggering CAGR of 19.9%, leaving its on-premise counterparts far behind. Why? Because the cloud offers flexibility, easy scalability, and a much more predictable cost structure.
Choosing a platform isn't just a technical decision; it's a strategic one. The right software empowers clinicians by seamlessly fitting into their daily work, rather than forcing them to adapt to a rigid system.
Critical Factors for Evaluation
Looking beyond where the software is hosted, there are a few make-or-break factors to consider. A tool with amazing features is practically useless if it can’t talk to your other systems or doesn't meet critical industry standards.
Here are the non-negotiables to put at the top of your list:
- Seamless Integration: The software absolutely must play nicely with your existing Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Electronic Health Records (EHR). Clinicians need to pull up advanced visualizations from within a patient's chart without skipping a beat.
- Regulatory Compliance: Any platform that touches patient data has to be rock-solid on compliance, meeting regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. This isn’t just a good idea; it’s a legal and ethical necessity.
- Customization and Scalability: Your needs today won't be your needs in five years. The right solution should grow with your institution and be flexible enough to adapt to the unique workflows of different departments, whether it's cardiology or oncology.
This is exactly where we at PYCAD come in. We at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, creating solutions that are tailored to how your team actually works. As you weigh your choices, it’s worth exploring the wide world of 3-d visualization programs and seeing our work at https://pycad.co/portfolio.
In the end, the best platform is the one that gets out of the way and lets your team do what they do best: provide exceptional care for your patients.
The Future of Custom and AI-Powered Imaging
We're on the cusp of the next great leap in medical imaging, moving far beyond the one-size-fits-all software of the past. The future is all about specialization and the incredible power of artificial intelligence. Generic tools are giving way to solutions that feel like they were built just for a specific clinical need, fitting into a workflow as naturally as a surgeon's scalpel.
This is the very frontier where our work at PYCAD comes to life. We at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, creating systems that are genuinely intuitive and deeply connected to how medical professionals actually work. This push for tailored solutions is what’s fueling the industry’s incredible expansion. The global 3d imaging software market has already hit $5.57 billion and is projected to reach $6.35 billion next year, all thanks to this widespread investment in digital health. You can see examples of our work on our portfolio page: https://pycad.co/portfolio.
AI as an Intelligent Clinical Partner
If custom software is the vehicle, then artificial intelligence is the engine driving this new generation of imaging forward. AI algorithms can now automate incredibly complex tasks that once took clinicians precious hours to complete. It's like giving every radiologist a team of brilliant assistants who can instantly analyze scans, flag potential issues, and prepare data for review.
Here's how it's changing the game:
- Automated Image Segmentation: Imagine an AI that can identify and perfectly outline organs, tumors, or blood vessels in seconds. This frees up specialists to concentrate on what they do best: interpretation and diagnosis.
- Intelligent Anomaly Detection: These systems act as a vital second set of eyes, highlighting subtle abnormalities that might otherwise be missed. This boosts diagnostic confidence and catches problems earlier.
- Predictive Analytics: By learning from massive datasets, AI can help predict how a disease might progress or how a patient will respond to a specific treatment, paving the way for truly personalized medicine.
The goal was never to replace human experts, but to supercharge their abilities. AI handles the heavy lifting of data processing, allowing clinicians to focus their time and talent where it matters most—making critical decisions for their patients.
A Glimpse into Tomorrow's Clinic
This fusion of custom software and AI intelligence is painting a picture of a more proactive and precise future for healthcare. Of course, the transparency and trustworthiness of these systems are paramount, which is why understanding the principles of Explainable AI in Healthcare is so important.
Before long, a surgeon won't just see a 3D model of a heart; they'll be presented with an AI-generated surgical plan, optimized for that specific patient's unique anatomy. The possibilities are truly inspiring.
Have a Few Questions?
Diving into the world of 3D imaging software can feel a bit overwhelming at first. It's a field packed with innovation, and it’s completely natural to have questions as you explore how it can fit into your practice. Whether you're a clinician, an IT specialist, or a hospital administrator, getting clear answers is the first step.
Let's walk through some of the most common questions we hear. My goal here is to cut through the jargon and give you the straightforward, practical insights you need.
What’s the Real Difference Between 2D and 3D Medical Imaging?
This is the most fundamental question, and the answer is all about depth and perspective.
Think of a standard 2D scan, like a classic X-ray, as a single photograph. It’s a flat image that gives you one specific angle. It can absolutely tell you if a bone is broken, but it can't show you the full story of the surrounding anatomy.
Now, imagine taking hundreds of those flat pictures from every possible angle and digitally stacking them together. That's what 3D imaging software does. It takes a series of 2D slices from a CT or MRI scan and reconstructs them into a complete, interactive 3D model. Surgeons can virtually rotate it, look inside, and truly understand the spatial relationships between organs, blood vessels, and tumors. It’s the difference between looking at a map and exploring a living, breathing landscape.
Can 3D Imaging Software Actually Integrate with Our Hospital’s Systems?
Yes, and honestly, it has to. Any modern platform worth its salt is built with integration in mind. The whole point is to make life easier, not to add another complicated step to your day.
Quality software speaks the same language as your existing hospital infrastructure—your PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) and EHR (Electronic Health Records). It does this using a universal standard called DICOM, which ensures all your different medical imaging systems can communicate smoothly.
A great integration means a doctor can pull up a patient’s record and launch an advanced 3D model with a single click. This is exactly what we focus on at PYCAD. We at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, putting powerful visualization tools right at your fingertips. See our work at https://pycad.co/portfolio.
Is Cloud-Based 3D Imaging Software Secure Enough for Patient Data?
This is a big one, and the answer is a resounding yes. Protecting patient data isn't just a feature; it's the foundation of any reputable cloud-based medical software. Security and HIPAA compliance are non-negotiable.
Leading platforms use multiple layers of protection, like end-to-end data encryption (scrambling the data so only authorized users can read it), multi-factor authentication, and constant security monitoring by dedicated teams.
It's a common misconception that on-premise servers are always safer. While you have physical control, major cloud providers often have security teams and resources that far exceed what a single hospital can dedicate to the task. It's all about choosing a partner with a proven, transparent commitment to healthcare security.
How Does AI Make 3D Imaging Software Better?
Think of artificial intelligence as an incredibly smart and fast assistant for the clinician. AI doesn't replace human expertise; it amplifies it.
For instance, one of the most time-consuming tasks is segmentation—manually outlining an organ or a tumor slice by slice. AI algorithms can do this automatically in seconds, with remarkable precision. This frees up an enormous amount of time for clinicians to focus on diagnosis and treatment planning.
AI also acts as a second set of eyes, helping with anomaly detection by flagging subtle patterns in a scan that might otherwise be missed. This combination of speed and analytical power helps create more consistent, accurate, and rapid diagnoses, which ultimately leads to better outcomes for patients.
At PYCAD, we live and breathe this technology. Our passion is crafting custom solutions that don't just work, but feel intuitive and genuinely helpful in a clinical setting. If you'd like to see how we've helped others turn these ideas into reality, I'd encourage you to explore our portfolio.