When you hear the term modalities in a medical setting, what comes to mind? It’s not just jargon. Think of it as a doctor's specialized toolkit, where each tool is a distinct modality designed for a very specific job, whether that's peering inside the body or actively treating a condition.
What Are Medical Modalities?

Let's dive deeper into that toolkit analogy. A master craftsperson doesn't use a hammer for every task, right? They have tools for measuring and inspecting, and other tools for building and repairing. Medicine works the same way.
This is the key to understanding how modern healthcare operates. One set of tools helps doctors see what's wrong, and the other helps them fix it.
The Two Core Categories of Modalities
At the highest level, every medical modality fits into one of two groups, each playing a crucial role in a patient's journey from diagnosis to recovery.
- Diagnostic Imaging Modalities: These are the incredible technologies that create pictures of the body's internal world. Their whole purpose is to give clinicians the visual evidence they need to identify, track, and understand an injury or disease. Common examples are X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
- Therapeutic Modalities: These technologies, on the other hand, are all about action. They actively treat a condition by delivering a form of energy or substance to heal tissues, destroy diseased cells, or manage symptoms. This includes everything from radiation therapy for cancer to the ultrasound used in physical therapy.
In the world of medical imaging, modalities are the powerful diagnostic tools—like CT scanners, MRI machines, and ultrasound devices—that generate incredibly detailed visuals of the body's interior, completely changing the game for healthcare diagnostics.
This isn't just a textbook classification; it defines the entire flow of patient care. The sheer volume of data produced by diagnostic modalities is staggering, driving the global medical imaging market to an estimated $40.6 billion in 2023.
This data is the lifeblood of modern diagnosis, and managing it is everything. These modalities are absolutely fundamental to patient care within the broader healthcare industry. At PYCAD, we live and breathe this data. We specialize in building the digital infrastructure needed to handle it—from custom web DICOM viewers to full-scale medical imaging platforms—ensuring the powerful insights from these machines are always accessible and actionable. You can see examples of our work on our portfolio page.
Imaging vs. Therapeutic Modalities Explained
To really get what medical professionals mean by modalities, we need to split them into two core groups. It helps to think of it this way: imaging modalities are the detectives, gathering visual clues to crack a medical case, while therapeutic modalities are the healers, stepping in to fix the problem once it's found. This one distinction shapes the entire journey of patient care.
The detectives—think MRI, CT scans, and X-rays—are brilliant at revealing what’s happening inside the body without a single incision. Their whole job is to capture information, to paint a picture for the diagnostician. They don’t treat the problem; they bring it into the light.
On the other side, you have the healers. These are the tools of direct intervention, from the focused energy of radiation therapy in oncology to the gentle sound waves of ultrasound in physical therapy. They actively apply energy or substances to the body to heal, to reduce inflammation, or to destroy diseased cells. They are all about action, treatment, and recovery.
The Role of Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging is truly the bedrock of modern medicine. It gives clinicians the non-invasive "eyes" they need to peer deep inside our incredibly complex anatomy. And each type of imaging offers a completely different vantage point.
- X-ray: Perfect for getting a sharp look at dense structures like bone.
- MRI: Unbeatable for its detailed views of soft tissues—the brain, muscles, and ligaments.
- CT Scan: Generates lightning-fast, cross-sectional images, making it a hero in emergency rooms and for complex anatomical mapping.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create real-time images of organs and blood flow, all without any radiation.
For those of us building the technology behind this, understanding the unique data each modality produces is everything. This is precisely the challenge we live and breathe at PYCAD. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, making sure that no matter where the data comes from, it's crystal clear, easy to access, and ready for a clinician’s expert eye. You can see some of the complex puzzles we've solved for our clients on our portfolio page.
The Power of Therapeutic Intervention
While imaging shows us the problem, therapeutic modalities deliver the solution. Their applications are incredibly broad, but they all share one focus: treatment and rehabilitation.
A therapeutic modality's purpose is not to see, but to act. It is the practical application of energy—be it sound, light, or radiation—to initiate a specific, positive biological response within the body.
This action-oriented approach is fundamental to getting patients better. And it’s a massive part of healthcare worldwide. These modalities cover a huge range of treatments, from physical agents like electrotherapy to biological game-changers like immunotherapy, all with the goal of healing.
In fact, physical therapy modalities are used in over 80% of rehabilitation programs around the globe, and the global physical therapy market was valued at an astounding $28.7 billion in 2022. You can dig deeper into the growth of therapeutic approaches to see just how significant this is. It underscores the incredible need for smart systems that can manage and track treatment, finally closing the loop between that initial diagnostic image and a patient’s full recovery.
A Closer Look at the Stars of Medical Imaging
Let's meet the all-stars of diagnostic imaging—the incredible technologies that give clinicians a window into the human body. Each one has a unique superpower, a distinct way of seeing that makes it the perfect tool for a specific job. Getting to grips with these core differences is the key to understanding how medical modalities truly shape patient care.
This concept map breaks down the fundamental split between imaging modalities, which focus on diagnosis, and therapeutic modalities, which center on treatment.
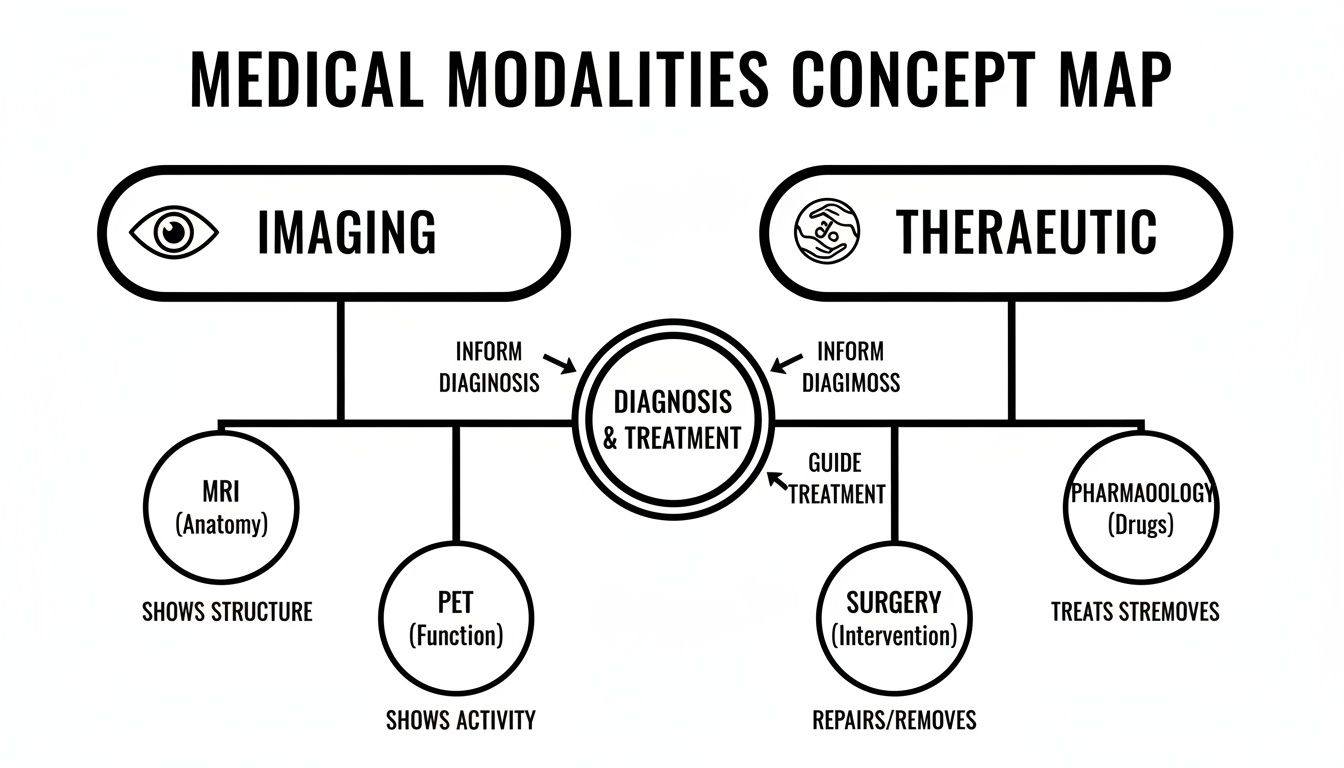
As you can see, the two paths are distinct yet deeply connected. What we discover through imaging directly guides the therapies that follow.
The Pioneers and The Powerhouses
Think of the classic X-ray as the original pioneer. It’s a master at visualizing dense structures, making it the undisputed go-to for identifying bone fractures or getting a quick look at the chest. Its speed and accessibility have made it a cornerstone of diagnostics for over 100 years.
Then you have Computed Tomography (CT), the swift architect. A CT scanner is like a supercharged X-ray, taking a rapid series of images from different angles to construct incredibly detailed 3D models of the body. Its breathtaking speed makes it invaluable in emergency rooms for assessing trauma, stroke, and internal bleeding.
Next is the meticulous artist of the group: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Instead of radiation, MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to paint exquisitely detailed pictures of soft tissues. It excels at visualizing the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and ligaments with a clarity no other modality can touch, making it indispensable in neurology and sports medicine.
Finally, we have Ultrasound, the real-time scout. It uses high-frequency sound waves to safely peek at organs as they function, track blood flow, and guide delicate procedures. Because it uses no ionizing radiation, it’s the gold standard for obstetrics and for examining sensitive organs like the heart and kidneys. To dive deeper into how these incredible images come to life, check out our guide on the acquisition of images and the technology behind it.
A Comparative Look at Core Technologies
To truly appreciate their distinct roles, it helps to see their strengths and weaknesses side-by-side. For developers and researchers, this information is vital for building effective software and tools that can handle the unique data each one produces.
This is exactly why we at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms. Each modality generates a different kind of data that demands specialized handling, and our systems are engineered to manage these specific visualization needs flawlessly.
To make things clearer, here’s a breakdown of the essential details for each primary imaging modality.
Comparison of Major Medical Imaging Modalities
This table provides a side-by-side comparison of the most common diagnostic imaging modalities, highlighting their core technology, primary uses, key advantages, and limitations.
| Modality | Core Technology | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | Ionizing radiation to create 2D images of dense structures. | Bones, chest imaging, detecting fractures. | Fast, widely available, and low cost. | Limited detail in soft tissues; uses ionizing radiation. |
| CT | Multiple X-ray projections to create 3D cross-sectional views. | Trauma, stroke, cancer staging, complex fractures. | Extremely fast and provides excellent anatomical detail. | Higher radiation dose than X-ray; less soft tissue contrast than MRI. |
| MRI | Strong magnetic fields and radio waves to image soft tissues. | Brain, spinal cord, joints, muscles, tumors. | Superior soft tissue contrast and no ionizing radiation. | Slower scan time, expensive, and not suitable for patients with certain metal implants. |
| Ultrasound | High-frequency sound waves to create real-time images. | Obstetrics, cardiology, abdominal organs, blood flow. | Safe (no radiation), real-time imaging, portable, and low cost. | Image quality is highly operator-dependent; cannot penetrate bone or air well. |
This comparison shows there's no single "best" modality—only the right one for the clinical question at hand.
Each imaging modality speaks a different visual language. An X-ray shows the body's scaffolding, an MRI reveals its intricate wiring and plumbing, and a CT scan provides a complete architectural blueprint.
Grasping this framework is the first step toward building the next generation of healthcare technology. The data from these machines is more than just pictures; it's the raw material for life-saving decisions.
The Critical Role of DICOM Modality Codes
If medical imaging has a universal language, its name is DICOM. And in that language, specific codes act as the core vocabulary—the essential nouns that give every image its context and identity. Without them, the entire digital imaging ecosystem we rely on would simply stop working.
These aren't complex, cryptic identifiers. They’re simple, powerful tags like ‘CT’ for Computed Tomography, ‘MR’ for Magnetic Resonance, and ‘US’ for Ultrasound. Tucked away in the metadata of every imaging file, these codes are the digital fingerprints telling any system, anywhere in the world, precisely what kind of image it’s looking at.
This might seem like a small technical detail, but it’s the absolute bedrock of interoperability in modern medicine. For anyone touching medical technology—from developers building next-gen viewing platforms to IT teams managing hospital networks—these codes are the key to a sane and functional workflow.
The Unseen Engine of Clinical Workflows
Think of a DICOM modality code as a smart routing slip on a critical package. When a CT scan hits the hospital's Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), that ‘CT’ tag instantly kicks off a domino effect.
The system knows exactly where to file it, which radiologist’s worklist to send it to, and which viewing protocols to fire up. This automation is what stops a radiologist from wasting precious time trying to open a complex 3D CT dataset with software built for a simple 2D X-ray. It’s an elegant system that works behind the scenes, millions of times a day.
This is the kind of precision we at PYCAD obsess over. When we build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, we engineer them to read these codes with absolute fidelity. It’s our guarantee that the right data reaches the right clinician with the right tools, every single time. You can see examples on our portfolio page.
Why Standardized Codes Are Non-Negotiable
The real magic of these codes is in their standardization. A ‘CT’ tag means the exact same thing in a Tokyo hospital as it does in a Toronto clinic. This global consistency is what makes true interoperability possible, allowing images to be shared and reviewed across different systems without ever losing their essential context.
A DICOM modality code is more than just a label; it's a promise of clarity. It ensures that no matter where an image travels, its origin and nature are understood instantly and accurately by any system that receives it.
Without this shared language, we’d have chaos. That’s why a deep understanding of the DICOM standard is a must for anyone creating healthcare technology. For a full breakdown of this vital framework, you can explore our in-depth guide that answers the question, what is DICOM?
This foundation of trust and reliability is what makes modern teleradiology and collaborative diagnostics a reality. It empowers specialists to consult on cases from anywhere in the world, completely confident they are seeing the image data exactly as intended.
The list of modality codes is vast, covering everything from the everyday to the highly specialized. Here are just a few examples that show their specificity:
- XA: X-Ray Angiography
- PET: Positron Emission Tomography
- MG: Mammography
- ES: Endoscopy
Each code tells a story. It speaks to how the image was created, and that story dictates how it’s handled from the moment of capture to its final archive. For any clinician or technologist, speaking this language isn’t just helpful—it’s fundamental to delivering safe, efficient, and accurate care.
How to Bring Diverse Medical Modalities Together
Knowing all the different medical imaging modalities is one thing. Actually making them all work together in one seamless system? That's where the real work begins. It’s a journey from theory to practice, and along the way, developers and healthcare IT pros will hit a ton of technical roadblocks. But getting this right isn't just a win for the tech team—it’s a massive leap forward for patient care and clinical efficiency.
The sheer volume of data is usually the first "uh-oh" moment. A single MRI study can spit out thousands of images, eating up storage like there's no tomorrow. Now, imagine that across an entire hospital, with CT scans, real-time ultrasound videos, and dozens of other modalities running all day. You need an incredibly robust and scalable architecture just to keep from drowning in data.
Beyond just storing it, you have to move that data securely and quickly. The network protocols that shuttle sensitive patient information from a scanner to a radiologist's screen have to be bulletproof. One little glitch can bring a whole clinical workflow to a grinding halt and put patient data in jeopardy.
Designing a Viewer That Actually Works for Everyone
One of the trickiest parts of the whole puzzle is building a user interface (UI) that doesn't make someone want to throw their computer out the window. A universal web DICOM viewer has to be a chameleon. It needs the muscle for a radiologist to dive deep into a 3D CT reconstruction, but it also has to be simple enough for a cardiologist to pull up an echocardiogram in seconds.
These are two completely different worlds, with completely different needs.
This means you can't just build a simple image display. You have to create an intelligent tool that adapts to the user. It’s all about smart design choices that put the right tools in front of the right specialist at the right time. The end goal is an experience so smooth that it feels like it was built just for them, no matter which modality they're looking at.
Clearing the Technical and Workflow Hurdles
Integrating a whole zoo of modalities means facing some very specific, very real challenges. Here’s a look at some of the biggest hurdles and how to get over them:
- Wrangling Proprietary Data Formats: DICOM is the gold standard, but you'll always find that one older machine or specialized piece of equipment that spits out its own weird file type. A truly integrated system needs a flexible front door—an ingestion engine that can grab those non-standard formats, make sense of them, and convert them into a clean, standardized structure.
- Syncing Up Different Views: Picture this: a patient has both a CT and an MRI of their brain. For a doctor to get the full story, they need to see those two scans perfectly aligned, one on top of the other. This takes some serious algorithmic magic, using sophisticated image registration to overlay different datasets for a side-by-side comparison.
- Making the Network Sing: Trying to stream massive imaging files through a web browser can be painfully slow if you're not smart about it. You have to use clever techniques like progressive loading (showing a low-res version first) and intelligent caching to make it feel instant. The goal is to get clinicians reviewing images right away, not staring at a loading bar while a multi-gigabyte study downloads.
Integrating medical modalities isn't about jamming different puzzle pieces together. It's about building a smarter puzzle board—one that understands the shape of every piece and helps them connect to reveal the complete picture of a patient's health.
This is exactly what we live and breathe at PYCAD. We don't just talk about these problems; we've been in the trenches solving them for years. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms that are designed from the ground up to unite all these different data streams. Our solutions create a natural, cohesive workflow that helps clinicians make better decisions, faster. You can check out how we tackle these complex projects on our portfolio page.
Of course, the heart of this entire ecosystem is the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS). Flawless PACS integration is absolutely essential—it's the central nervous system for all imaging data in a hospital. We design our systems to speak the same language as existing PACS infrastructure, making our custom viewers a powerful and intuitive extension of a hospital's proven workflow.
The Future of Integrated Modality Workflows
What happens when you connect the deep, rich data from every medical modality with the foresight of artificial intelligence and the organizational power of modern patient management systems? You get a glimpse into the future of intelligent, proactive healthcare. This isn’t some far-off science fiction; it’s the new reality taking shape in integrated workflows, where technology is always a step ahead, anticipating needs and making care flow effortlessly.
Think about a system where AI algorithms are constantly working behind the scenes. A CT scan from a busy emergency room is instantly triaged, and the system flags a suspected critical finding for the radiologist before they even open the file. This kind of automated prioritization ensures that the most urgent cases always jump to the front of the line, saving time that could literally save a life.
From Reaction to Prediction
The next leap forward is moving beyond simple alerts to genuine predictive analysis. Imagine an integrated platform that can analyze a patient’s entire imaging history—across MRI, X-ray, and ultrasound—to spot subtle changes over time that the human eye might miss. This creates a continuous, long-term view of a patient's health, turning diagnostic data into an incredible tool for early detection and preventative medicine.
The goal is to shift medical imaging from a reactive diagnostic tool into a proactive, predictive engine. We're moving from asking, "What's wrong right now?" to "What could go wrong, and how do we get ahead of it?"
This vision is the very heart of what we do at PYCAD. We don’t just build viewers; we engineer intelligent ecosystems. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms that become the central hub for this new era of patient care. You can see what these integrated systems look like in action on our portfolio page.
The Patient-Centric Ecosystem
This integration isn’t just about the radiology department. The real magic happens when imaging data flows seamlessly into a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. Suddenly, a complete patient story comes to life.
- A Truly Holistic View: A family doctor can instantly pull up the results from a specialist’s ultrasound, complete with notes and prior imaging, all in one unified record. No more chasing down files.
- Automated Patient Journeys: The system can automatically schedule follow-up appointments based on imaging results, making sure no patient ever falls through the cracks.
- Effortless Communication: Clinicians, administrators, and even patients themselves can communicate far more effectively when everyone is working from the same complete, up-to-the-minute information.
Grasping the bigger picture of digital transformation in the healthcare industry helps you see just how profoundly this level of integration will reshape medicine. It’s all about tearing down the walls between data silos to build a truly collaborative and patient-focused environment. Our platforms are designed to turn raw data from any medical modality into these kinds of powerful, actionable insights, delivering undeniable value to healthcare innovators ready to build the future of medicine.
Common Questions About Medical Modalities, Answered
Jumping into the world of medical imaging can feel like learning a new language. Let's clear up a few of the most common questions that come up when we talk about modalities.
What’s the Real Difference Between a Modality and a Medical Device?
It’s easy to get these two mixed up, but the distinction is pretty simple. Think of the medical device as the actual piece of equipment—the big, physical MRI machine in the room.
The modality, on the other hand, is the specific technique or method that machine uses to capture an image. In this case, it's Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). So, the device is the tool, and the modality is the process. Some advanced devices can even perform more than one modality.
Why Are DICOM Modality Codes Such a Big Deal for Hospital IT?
In a busy hospital, DICOM modality codes are the secret sauce that keeps everything running smoothly. These codes are like digital name tags that tell every system—from the PACS to the radiologist's viewer—exactly what kind of image it's looking at.
This little tag automates everything. It ensures a CT scan opens with the right viewing tools and an ultrasound study is routed to the correct specialist. Without these codes, a hospital's imaging workflow would grind to a halt, leading to delays and potential errors. They are the bedrock of modern clinical efficiency.
Can One Platform Really Handle Images From All Different Modalities?
Absolutely, and that's precisely what next-generation medical imaging platforms are built to do. A truly powerful, modality-agnostic system breaks down the walls between different imaging departments, creating one central hub for all patient data.
A great platform doesn't just show you pictures; it brings the entire patient story together. When you can seamlessly pull up an MRI, a PET scan, and an X-ray side-by-side, you're not just looking at data—you're seeing a complete clinical picture. That’s what empowers better, faster decisions.
At PYCAD, this is our specialty. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms that are designed from the ground up to handle everything—CT, MRI, X-ray, Ultrasound, and beyond. We build the unified ecosystems that clinicians need. To see this philosophy in action, take a look at our portfolio page.






