Imagine a safety net for radiologists. A vigilant, second set of digital eyes scanning every single detail of a mammogram. That’s the real promise behind mammography with CAD (Computer-Aided Detection)—a technology built to support and enhance human expertise in the crucial fight against breast cancer. It’s not about replacing the skilled radiologist; it’s about giving them an indispensable co-pilot.
A New Era in Breast Cancer Screening
When you’re dealing with a disease that impacts millions, diagnostic accuracy isn't just a goal—it's everything. CAD has become an essential tool in this high-stakes environment, sharpening a radiologist’s ability to spot subtle abnormalities that the human eye might overlook. It transforms a demanding diagnostic process into one grounded in greater confidence and precision.
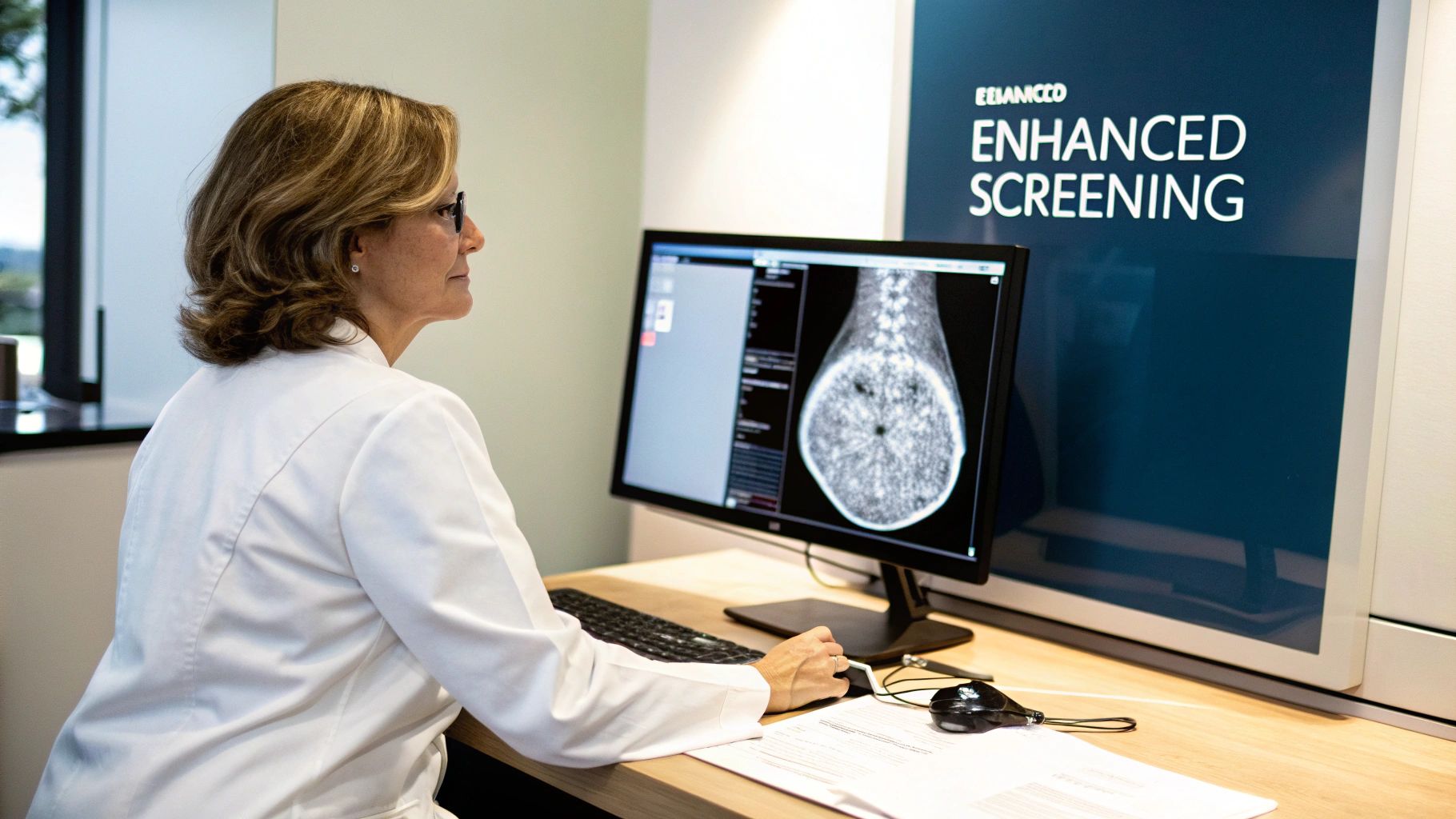
This guide is your journey from the early days of CAD to the powerful, AI-driven systems we see today. We’ll break down how this technology works, why it matters, and how it’s creating the foundation for better patient outcomes across modern breast imaging.
The Role of Technology in Modern Diagnostics
The idea behind mammography with CAD is brilliantly simple: let sophisticated algorithms analyze digital mammograms for the tell-tale signs of cancer. The system meticulously scans every pixel, flagging suspicious areas that demand a closer look from the radiologist.
Think of it as an assistant that has reviewed millions of scans, learning to recognize the incredibly subtle patterns associated with malignancies—things like microcalcifications, masses, or slight distortions in breast tissue.
- Highlighting Suspicious Areas: The software places digital markers directly on the image, drawing the radiologist's eye to areas that warrant a second opinion.
- Improving Detection Rates: Research has consistently shown that CAD can increase cancer detection rates, especially for those early-stage cancers that are most treatable. It acts as a systematic double-check.
- Standardizing Interpretation: By providing an objective, data-driven analysis, CAD helps reduce variability between different readers, leading to more consistent and reliable performance across an entire department.
CAD was never about creating a flawless, all-knowing machine. It’s about forging a powerful partnership between human intuition and artificial intelligence, where each one’s strengths make the other better. The end goal? Saving lives.
Here's a quick overview of what makes this technology so important.
Mammography with CAD at a Glance
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | To act as a "second reader" by automatically highlighting suspicious areas on a mammogram for the radiologist to review. |
| Key Technologies | Employs advanced image processing and pattern recognition algorithms, which have now evolved into machine learning and AI. |
| Main Benefit | Increases the cancer detection rate, particularly for early-stage and subtle cancers, without significantly impacting workflow. |
| How It Works | The system analyzes digital mammograms for specific features like microcalcifications, masses, and architectural distortions. |
| Clinical Impact | Helps reduce missed diagnoses and provides a consistent, objective analysis to supplement the radiologist's interpretation. |
This table captures the essence of CAD's role, but its true power is only unlocked when it’s integrated seamlessly into a clinician’s daily workflow.
At PYCAD, this is where our expertise comes in. We understand this ecosystem inside and out. That is why we build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms. Our work ensures that radiologists can access, view, and interact with these AI-driven insights effortlessly, without friction.
This deep dive into mammography with CAD will cover everything from clinical performance and evolution to the nitty-gritty of integration and validation. We'll lay out a clear roadmap for healthcare leaders and innovators looking to implement these systems.
To see how we bring these complex integrations to life, feel free to explore our work in our portfolio.
How AI-Powered CAD Is Changing the Game in Mammography
Think of an expert detective, one who’s spent a lifetime studying millions of cases, able to spot the tiniest, almost invisible clue that cracks the whole case open. That’s the role Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) plays in mammography. It’s not just a piece of software; it's a highly trained partner working right alongside the radiologist, dedicated to uncovering the earliest, most subtle signs of breast cancer. This blend of human insight and machine precision is making a real difference in diagnostics.
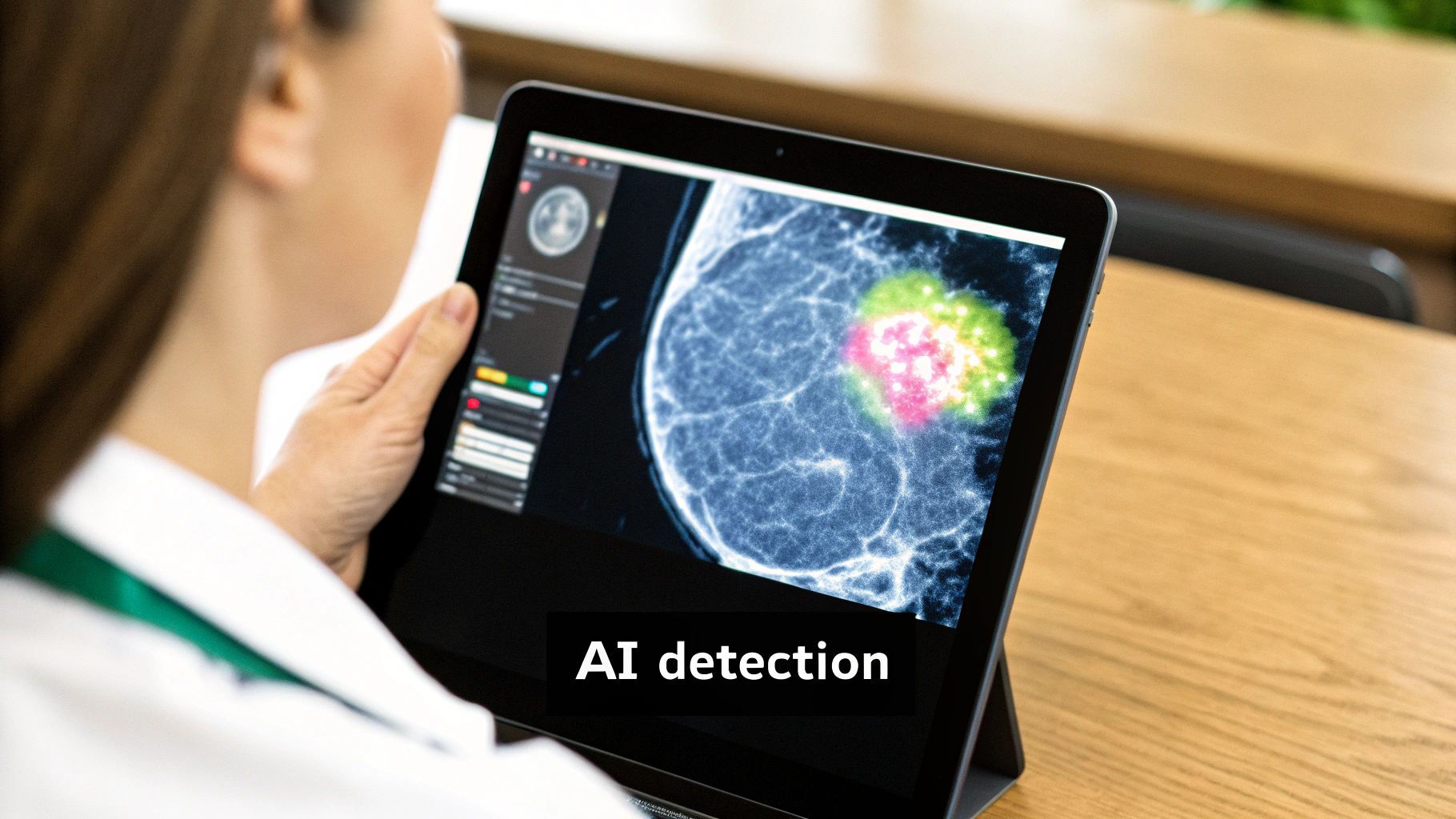
The moment a digital mammogram is taken, the AI gets to work. This complex map of breast tissue is instantly fed into the CAD system, where powerful algorithms begin their meticulous scan, combing through every single pixel for abnormalities that hint at potential malignancies.
The AI-Powered Analytical Process
First up, the system pre-processes the image. You can think of this as a digital darkroom, where a photo is carefully enhanced to bring hidden details into sharp focus. The AI adjusts contrast and removes digital "noise," giving the algorithms the clearest possible view of the tissue.
With a crystal-clear image, the real analysis begins. The AI is trained to hunt for specific biomarkers that are often tell-tale signs of cancer, including:
- Microcalcifications: These are tiny calcium deposits that show up as bright specks. While many are harmless, certain clusters or patterns can be an early red flag for cancer.
- Masses: The AI looks for dense tissue areas, paying close attention to those with irregular shapes or spiculated margins—the little tentacle-like projections that can indicate a problem.
- Architectural Distortion: This is one of the trickiest signs for the human eye to catch. It involves subtle shifts in the normal structure of the breast tissue, which the AI is specifically trained to identify.
When the system flags a region of interest, it places a digital marker on the image. It’s like a gentle tap on the radiologist’s shoulder, a quiet prompt saying, “You might want to take a closer look right here.”
At its core, mammography with CAD isn't about replacement; it's about augmentation. It gives radiologists a powerful tool to double-check their work, offering a data-driven second opinion in seconds and ensuring even the most minute details don't get missed.
We at PYCAD, build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, which is essential for visualizing these AI-driven findings effectively. For a deeper dive into the algorithms powering these technologies, our guide on machine learning for medical imaging is an excellent resource.
The Critical Difference: CADe vs. CADx
It's important to know that not all CAD systems are created equal. They fall into two main camps, each playing a distinct but complementary role in the clinic. Understanding this difference shows just how far we've come—from simply pointing things out to providing intelligent assessments.
The two main categories are CADe (Computer-Aided Detection) and CADx (Computer-Aided Diagnosis).
-
CADe (Detection): This is the classic "second reader." A CADe system's job is to find and highlight suspicious areas on a mammogram. It’s like a digital highlighter, drawing the radiologist’s eye to potential spots of concern without making a judgment call. The entire goal is to boost sensitivity and lower the odds of a missed cancer.
-
CADx (Diagnosis): This is where AI gets much more advanced. A CADx system goes beyond just finding a potential issue; it provides an assessment of how likely it is to be malignant. It might generate a risk score or a probability, helping the radiologist classify the finding and decide on next steps, like whether a biopsy is needed.
For a wider perspective on how AI is reshaping diagnostics across medicine, real-world examples can be incredibly insightful. The case study on AI in Imaging for Surgical Prediction at Mass General Brigham offers a fantastic look at the potential of integrating these intelligent systems into clinical workflows.
This foundational knowledge of how AI-powered CAD works—from the nuts and bolts of image analysis to the crucial distinction between detection and diagnosis—is essential for anyone in medtech or hospital IT. At PYCAD, this is our world. We specialize in building custom web DICOM viewers and integrating them into medical imaging web platforms, making sure these powerful AI insights are delivered to clinicians in a way that’s clear, intuitive, and ultimately, actionable. Explore our work on our portfolio page.
So, Does CAD Actually Help in the Real World?
In the whirlwind of a busy clinic, a new technology is only as good as its real-world results. For mammography with CAD, the bottom-line question has always been: does this tool genuinely help us find more cancers and, ultimately, save lives? To get to the truth, we have to dig into the clinical evidence and get comfortable with the metrics that really matter.
The entire value of a diagnostic tool like this hangs on two ideas: sensitivity and specificity. Let’s make this simple. Imagine you’re using a high-tech metal detector on a beach. Its sensitivity is how well it beeps every single time it finds metal—even a tiny coin. Its specificity is its skill at staying quiet when it passes over a plain old rock or seashell.
Bringing that back to mammography, a CAD system's sensitivity is its raw power to flag a cancer that's actually there. High sensitivity means we miss fewer cancers, which is everything. Specificity, on the other hand, is the system’s ability to correctly see healthy tissue and leave it alone. High specificity means fewer false alarms, which saves patients from a world of unnecessary stress and follow-up procedures.
The Constant Balancing Act
The entire journey of improving breast cancer screening has been a delicate dance between these two forces. Study after study has shown that bringing CAD into the reading room often gives sensitivity a real boost. We've seen it help radiologists catch subtle malignancies that might have otherwise slipped by on a first read. That means finding cancer earlier, when it’s most treatable.
But that extra sensitivity can come with a trade-off. Some of the earlier CAD systems, in particular, were known for having a lower specificity. What did that mean in practice? A higher number of false positives—more women being called back for extra scans or even biopsies, only to find out everything was benign.
The real art and science of modern mammography with CAD is hitting that sweet spot—cranking up the life-saving power of high sensitivity while taming the patient anxiety and healthcare costs that come from low specificity. It's a quest for harmony between detection and precision.
How We Measure Diagnostic Horsepower: The ROC Curve
So, how do clinicians and researchers actually compare different CAD systems to see which one gets this balance right? They turn to a powerful tool called Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. Think of it as the ultimate performance report card for any diagnostic test.
An ROC curve is a graph that plots a system’s sensitivity (the good stuff) against its false-positive rate (1 minus specificity) across a range of settings. A system that's just guessing would produce a useless diagonal line. A mythical, perfect system would draw a line straight up the left side and across the top—that’s 100% sensitivity with 0% false positives. The closer a CAD system's curve hugs that top-left corner, the more powerful and reliable it is.
This kind of analysis is absolutely essential. It gives hospitals and technology developers a clear, objective way to vet and choose the algorithms that will truly empower their radiologists to make confident, life-saving calls.
This relentless drive for better performance has lit a fire under the industry. The global mammography market, where CAD plays a huge role, was valued at around USD 2.6 billion and is now projected to hit an incredible USD 6.35 billion by 2032. This growth is fueled by the heartbreaking rise in breast cancer cases—2.3 million new diagnoses in 2022 alone—and the shift to digital systems that can seamlessly integrate these AI-powered tools. It’s no surprise that digital mammography, hand-in-hand with CAD, now commands a dominant 64.34% market share. To get the full picture, you can read a complete analysis on mammography trends.
At PYCAD, we live and breathe this stuff. We're the ones in the trenches, building the custom infrastructure that makes these tools work. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, making sure the crucial insights from CAD get to the radiologist, clear and simple. To see how we help medical innovators turn powerful ideas into clinical reality, check out our portfolio of completed projects.
Making CAD a Natural Part of Your Workflow
Even the most brilliant technology is worthless if it's stuck on an island. For mammography with CAD to make a real difference, it has to become a fluid, almost invisible part of a radiologist's day. The key to this kind of harmony is a shared language for medical imaging called DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine). This is where the digital magic happens, turning complex AI findings into clear, actionable insights right where they're needed most.
Think of the CAD system as an expert consultant who meticulously marks up a blueprint. DICOM is the universal courier service that ensures those notes are delivered and understood perfectly by anyone else looking at that blueprint. When CAD flags a potential area of concern, it doesn't just draw a circle; it packages its findings—location, size, and suspicion score—into a standardized DICOM object.
The flowchart below shows what this is all about in practice. It visualizes the critical performance metrics that these integrated systems are designed to master.
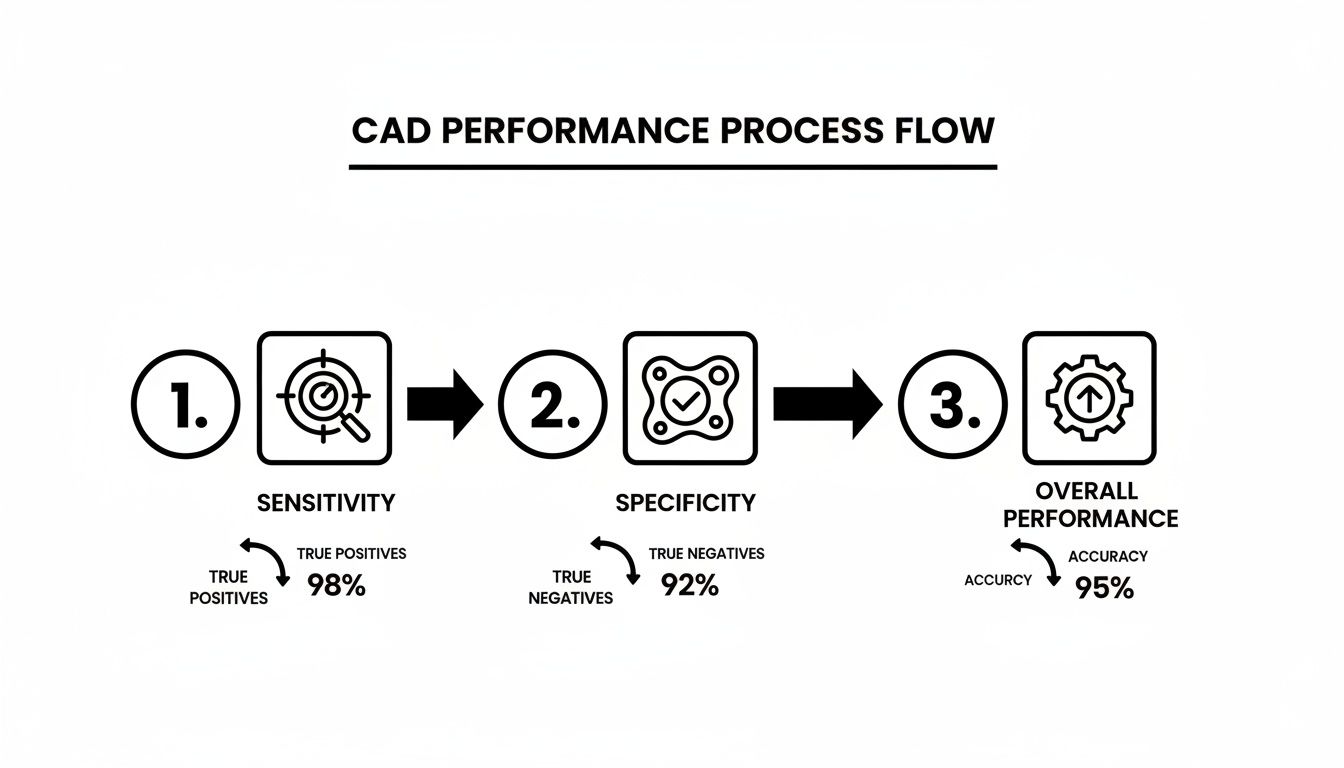
It’s a delicate balancing act. The system has to be sensitive enough to catch potential cancers while being specific enough to correctly identify healthy tissue. That's the tightrope walk to clinical effectiveness.
The Role of a Modern DICOM Viewer
These DICOM-packaged insights are sent to the radiologist's command center: the DICOM viewer. A basic viewer just shows the picture. An advanced, modern viewer, on the other hand, acts as an intelligent co-pilot. It seamlessly reads both the original mammogram and the separate CAD data, then perfectly overlays the AI-generated markers directly onto the scan.
This isn't just a static image with some circles on it. It’s a dynamic, interactive experience. Radiologists can toggle the markers on and off, zoom in on a flagged region, and instantly pull up the metadata from the CAD analysis—all within a single, unified workspace.
This is exactly where we live and breathe at PYCAD. Our specialty is building custom web DICOM viewers and integrating them into medical imaging web platforms. Our entire focus is on making sure this firehose of data is presented intuitively, quickly, and in a way that’s clinically meaningful. We stop the technology from becoming a frustrating roadblock.
An effective integration isn't just a technical handshake; it's a bridge between artificial intelligence and human cognition. It needs to be so seamless that the radiologist stops thinking about the software and focuses only on the patient.
Creating a Truly Unified Diagnostic Pipeline
Getting the full benefit of CAD requires thinking beyond just connecting it to a viewer. The goal is to build a unified pipeline that links every critical piece of the diagnostic journey.
This interconnected ecosystem usually includes:
- CAD Software: The AI engine doing the heavy lifting, analyzing mammograms and generating findings.
- PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System): The central library where all medical images and their associated CAD reports are stored, managed, and secured.
- RIS (Radiology Information System): The logistical hub that manages patient data, scheduling, and the final reporting process.
When these systems talk to each other fluently, the whole process just flows. A mammogram is taken, automatically sent to the CAD system, and then archived in the PACS with the AI results already attached. The moment a radiologist opens that case, both the image and the CAD insights are there, ready to go. You can learn more about how we make this happen in our deep dive on PACS integration strategies.
This level of deep integration is what turns a powerful algorithm from a novelty into a practical, life-saving tool that truly empowers clinicians.
Navigating the Path From Lab to Clinic
Bringing a new CAD system for mammography into a hospital isn't like installing a new piece of software. It’s a major strategic shift that changes the very rhythm of clinical practice. To get it right, you have to navigate a maze of regulatory approvals, data privacy laws, and very real-world implementation challenges. It's a journey, one that requires a solid plan to truly unlock the power of AI in diagnostics.
The first major hurdle is getting the green light from regulatory gatekeepers. In the United States, that means the Food and Drug Administration (FDA); in Europe, it’s the CE Mark. These aren't just rubber stamps. They represent an intense validation process, demanding undeniable proof that the CAD system is both safe and effective for real-world patient care.
Manufacturers have to build a rock-solid case with extensive clinical studies. This means showing how the algorithm performs on large, diverse datasets, proving it works reliably across different patient demographics and imaging machines. For anyone new to this world, the requirements can be daunting. We’ve actually broken down the whole journey in our guide to the FDA medical device approval process.
The Bedrock of AI: High-Quality Data
Deep down, every powerful AI is built on the data it learned from. For mammography CAD, this means getting your hands on massive, high-quality, and ethically sourced collections of breast images. It's not enough to just have the images; they need to be meticulously labeled by expert radiologists to teach the AI the difference between a suspicious mass and a benign shadow.
This entire process is wrapped in strict privacy laws like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. Protecting patient anonymity isn't optional—it's the law. This means rigorous de-identification protocols are essential before any data ever sees a training algorithm. When you're rolling out AI tools like CAD, solid sensitive data security is the foundation for both patient trust and regulatory peace of mind.
Best Practices for a Smooth Launch
Once a system has been validated and approved, the real work begins. A successful rollout is less about the technical setup and more about thoughtfully weaving the technology into the human workflow.
Here’s what truly makes a difference:
- Real-World Training: Radiologists, technologists, and IT staff all need deep training—not just on the "how-to," but on the "why." They need to understand the system's strengths and, just as importantly, its limitations.
- Smart Workflow Design: Nobody wants "alert fatigue," where clinicians start ignoring the AI's flags because there are just too many. You need clear protocols for triaging and interpreting CAD findings to keep the focus where it matters.
- Clear Rules of Engagement: What happens when the radiologist and the AI disagree? Establishing a standard procedure for handling these discrepancies is critical for consistent, reliable care.
A successful CAD implementation is a partnership between technology and people. The goal is to empower clinicians, not overwhelm them, by making the technology a natural and supportive extension of their expertise.
The excitement around these tools is backed by real numbers. The global market for mammography CAD has already hit USD 765 million, showing just how vital these systems have become. With North America leading the way, the broader mammography market is projected to skyrocket to USD 6.35 billion by 2032. This growth is fueled by technologies like CAD, which some studies show can boost detection accuracy by up to 20%.
At PYCAD, we specialize in closing the gap between a brilliant AI algorithm and its practical application in a busy clinic. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, making sure these life-saving tools are not just technically robust but also feel like a natural part of the diagnostic workflow. You can see examples of our work in our portfolio.
Where We're Headed: The Future of AI in Breast Imaging
The leap from early Computer-Aided Detection to the AI of today isn't just an incremental update; it’s a complete reimagining of what diagnostic intelligence can be. We're on the cusp of leaving behind an era where AI merely points out suspicious spots on an image. The future is about systems that see with greater depth, predict what comes next, and give clinicians a level of foresight that once felt like pure speculation.
This next generation of AI in breast imaging is shaping up to be more predictive, deeply personal, and woven into the very fabric of a patient's care journey. And that future isn't far off—it's already starting to unfold.
From Detection to True Prediction
Picture this: an AI that doesn't just identify a potential tumor but gives you a window into its likely behavior. That's the real game-changer. New AI models are being trained to recognize incredibly subtle patterns in imaging data—textures and features completely invisible to the human eye—and translate them into powerful predictions.
-
Personalized Risk Scoring: Instead of a one-size-fits-all screening schedule, AI will be able to analyze a patient’s mammogram, cross-reference it with their health history, and generate a highly accurate, personal risk score for developing breast cancer. This means screening becomes truly tailored to the individual.
-
Predicting Treatment Response: Imagine knowing, before the first dose, how a specific tumor will likely respond to chemotherapy versus radiation. AI is poised to make this a reality, helping oncologists choose the most effective path right from the start and avoiding a painful process of trial and error.
We are stepping into an age of proactive medicine. The goal is no longer just finding cancer but getting ahead of it, using AI to anticipate the disease and customize treatments with astonishing precision.
The Power of Smart Automation
Beyond its predictive might, AI is also set to tackle the repetitive, time-consuming tasks that can bog down a radiologist's day. The point isn't to replace human experts, but to empower them—to free them up to focus their expertise on the most challenging cases and the critical human element of patient care.
These future systems will help automate reporting, pre-fill findings based on image analysis, and smooth out clunky workflows, handing precious time back to clinicians.
For hospitals and medtech innovators ready to embrace this new reality, the journey begins with two key steps: building a solid, secure data foundation and collaborating with experts who live and breathe deep integration. This is exactly where we come in. At PYCAD, we build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, laying the essential groundwork for these next-generation AI tools to thrive.
Our solutions are designed to deliver these powerful insights directly and intuitively into the clinical workflow. Let's start building the future of medical imaging.
Take a look at what's possible by exploring our project portfolio.
Common Questions We Hear About CAD in Mammography
As more people explore the potential of CAD in mammography, it's natural for questions to pop up about how it all works in the real world. Let's clear up some of the most common ones to really grasp its impact.
Does CAD Actually Replace the Radiologist?
Not a chance. Think of CAD as an incredibly sharp-eyed assistant, a "second reader" that never gets tired. It’s a safety net designed to catch subtle details that might otherwise be missed during a long day of reading scans.
The final call always, and rightly, belongs to the radiologist. They bring years of experience and clinical judgment to the table, interpreting CAD’s flags in the full context of the patient’s history. It’s a tool that enhances human expertise, not a replacement for it.
What’s the Real Difference Between Old-School CAD and Modern AI?
This is a great question because while they’re related, their whole approach is different. The first generation of CAD systems were built on hand-coded rules. Engineers would literally tell the software what to look for—specific shapes, densities, and patterns that matched known signs of cancer, like microcalcifications.
Modern AI, especially deep learning, is a completely different ballgame. Instead of being told what to find, it learns what to find by analyzing hundreds of thousands of mammograms. This allows it to identify incredibly complex and subtle patterns that a rule-based system could never capture, leading to better accuracy and fewer false positives.
How Does This All Show Up on a Radiologist’s Screen?
Getting the AI's findings in front of the radiologist seamlessly is everything. The CAD software packages its results into a special DICOM object, separate from the original mammogram. A sophisticated DICOM viewer—like the kind we build at PYCAD—is smart enough to read both files at once.
This is where the magic happens. The viewer overlays the CAD markers, like circles or arrows, directly onto the mammogram. The radiologist gets a single, unified view where they can instantly see what the AI flagged without having to switch between screens or applications.
This integration is exactly what we specialize in at PYCAD. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms to make sure these powerful insights are presented clearly and intuitively. You can see examples of how we bring this to life for our clients on our portfolio page.






