A Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) and a Radiology Information System (RIS) are the two essential platforms that run the entire show behind the scenes in modern medical imaging. While they work together, they have very different jobs. The PACS is the massive digital vault for the medical images themselves, while the RIS is the air traffic controller, managing everything from patient scheduling to the final report and billing.
The Digital Heart of Modern Radiology
Not so long ago, radiology departments were a world of chemical smells, towering file cabinets, and radiologists squinting at physical films on a light box. It was a manual, cumbersome process where records could get lost and diagnoses were delayed.
Today, that scene has been completely replaced by the dynamic duo of PACS and RIS. These systems are the unsung heroes that create a seamless, digital workflow, profoundly impacting patient care every single day. The easiest way to understand their distinct roles is to think of a well-run library.
The Librarian and the Library
In this analogy, the Radiology Information System (RIS) is the meticulous, organized librarian. The librarian doesn't contain the actual stories but knows everything about them and where they are.
- Manages Patient Flow: Just like a librarian handles check-outs and reservations, the RIS manages patient appointments and scheduling.
- Tracks All Information: It's the central catalog, keeping track of patient histories, imaging orders, and radiologist reports.
- Coordinates the Workflow: The RIS orchestrates the entire process, ensuring every step, from the initial order to the final bill, is completed and documented.
The Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), on the other hand, is the library—the vast, secure archive containing the entire collection. Its job is to safely store every single X-ray, MRI, and CT scan and make them instantly available for viewing.
While the RIS manages the who, what, when, and why of a patient's imaging journey, the PACS securely holds the pictures that tell the clinical story. They are two sides of the same coin, indispensable to one another.
This powerful synergy shifted radiology from a film-based craft to a high-speed, data-driven science. Adopting PACS and RIS was a foundational step in the broader AI digital transformation that continues to reshape healthcare.
Here at PYCAD, we focus on a critical piece of this modern ecosystem. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, giving clinicians the power to access and analyze vital imaging data from anywhere, at any time. Feel free to explore our work on our portfolio page.
How PACS and RIS Work Together to Transform Patient Care
To really get a feel for the power of a modern pacs radiology information system, let’s walk through a patient's journey. This isn't just about bits and bytes; it's a beautifully coordinated dance of data that saves precious time, sidesteps mistakes, and ultimately, changes lives for the better. The whole process kicks off not with an image, but with a simple need—a doctor's order for a clearer look inside.
The moment a doctor orders an MRI, the Radiology Information System (RIS) wakes up. Think of the RIS as the air traffic controller for the entire radiology workflow. It manages the patient’s appointment, pulls in their demographic info, and tracks the specific scan the physician requested. This first step is all about administration, but it lays the foundation for everything that comes next.
The Seamless Handshake Between Systems
Once the appointment is on the books, a crucial data exchange happens behind the scenes. The RIS sends the order over to the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), typically using the HL7 (Health Level Seven) standard. This message automatically creates an entry on what’s called a DICOM Modality Worklist. Trust me, this is a game-changer for accuracy.
When the patient arrives for their scan, the technologist doesn't have to type in a single piece of information. They just select the patient's name from this worklist on the imaging machine's screen. With one click, the machine is populated with the correct patient ID, accession number, and procedure details. This simple action practically wipes out the risk of manual typos that could lead to a misidentified scan—a nightmare scenario for everyone involved.
This diagram shows you exactly how that digital process flows, from the administrative work in the RIS, to the image storage in the PACS, and finally to the radiologist's viewing workstation.
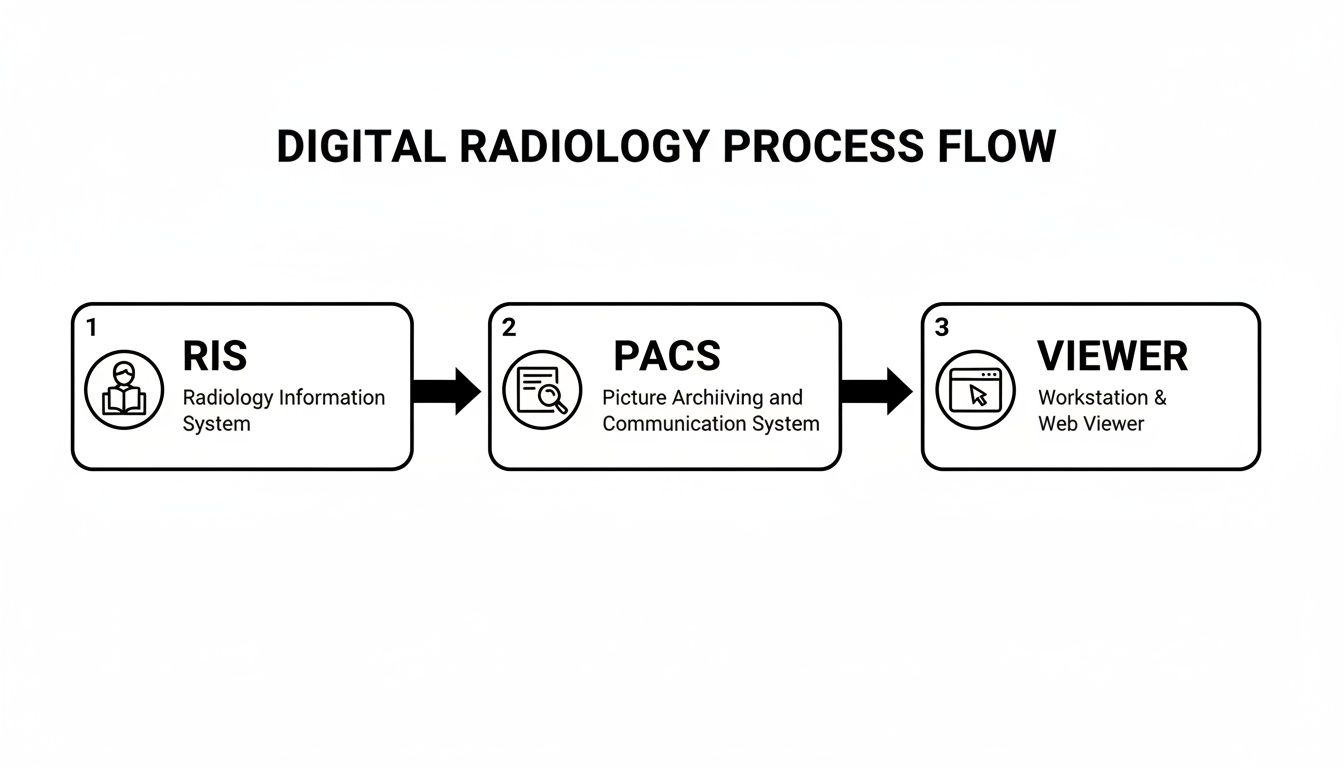
As you can see, each system has its own distinct job, but they work in perfect harmony to keep the data clean and the workflow moving smoothly from beginning to end.
As the MRI scanner captures the images—all in the universal DICOM format—they’re instantly sent across a secure network and stored in the PACS. The PACS is like a massive, highly organized digital library for medical images. It archives the scan and intelligently connects it back to the patient’s record in the RIS using that unique accession number. The exam status in the RIS updates automatically, letting everyone know the images are ready for the radiologist.
To better understand their distinct roles, let's break down their core responsibilities. While they work together, their functions are fundamentally different.
PACS vs RIS A Functional Comparison
| Function | Radiology Information System (RIS) | Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages the radiology workflow and patient data. The "brain" of the operation. | Stores, retrieves, and displays medical images. The "library" for visuals. |
| Core Tasks | Patient scheduling, registration, billing, and report generation. | Image archiving (long-term storage), image distribution, and viewing. |
| Data Handled | Text-based data: patient demographics, exam orders, clinical reports, billing codes. | Image-based data: DICOM files from MRI, CT, X-ray, Ultrasound, etc. |
| Key Users | Administrative staff, schedulers, technologists, and radiologists (for reporting). | Radiologists, referring physicians, and other clinicians who need to view images. |
| Integration Standard | Primarily uses HL7 to communicate with other hospital systems (like EMR/HIS). | Primarily uses DICOM to communicate with imaging modalities and viewers. |
This table clearly shows that RIS is the administrative engine, while PACS is the clinical image archive. Without both working in sync, the modern radiology department simply couldn't function.
Empowering Diagnosis Through Advanced Viewers
This is where the real diagnostic magic happens. A radiologist gets a notification and opens the case. They aren't looking at a piece of film; they're using a powerful DICOM viewer, a specialized software that lets them interact with the images in ways that were once impossible. They can zoom in on tiny details, pan across the anatomy, adjust brightness and contrast, and even use advanced tools to reconstruct 3D models.
The true leap forward is in accessibility and speed. What once took hours or even days—digging through film archives, waiting for new images to be developed, and manually dictating reports—now unfolds in minutes.
At PYCAD, we focus on building that critical viewing piece of the puzzle. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, giving radiologists and clinicians secure access to analyze these vital images from anywhere. This is absolutely essential for enabling teleradiology and fostering collaborative care. To see some of our work in action, feel free to explore our portfolio page.
Once the radiologist finishes their analysis, they create a report detailing their findings. This report is created and managed right inside the RIS, which then electronically sends it to the referring physician and links it permanently to the patient's health record. The entire loop, from the initial order to the final report, is now complete.
This tight integration is precisely why the global PACS and RIS market was valued at a staggering US$ 6,579.46 million in 2024 and is set to climb even higher. In North America alone, studies have shown these integrated systems can cut down on manual errors and reduce diagnostic turnaround times by up to 30-40%, proving just how deeply they impact both efficiency and patient care. Discover more market insights on global PACS and RIS systems.
Choosing Your System Architecture
Figuring out where your pacs radiology information system will live is one of the most fundamental choices you'll make. This isn't just an IT decision; it's a strategic move that dictates cost, security, and your ability to grow down the road. It directly impacts how your clinicians get the data they need and how well your institution can adapt to the future.
Think of it like deciding where to live. You could build a house on your own land, lease a high-tech apartment, or find a solution that gives you a bit of both. In the same way, your imaging infrastructure can be on-premise, in the cloud, or a hybrid of the two. Each path offers a different balance of control, flexibility, and investment, and the right one for you depends entirely on what you’re trying to achieve.
On-Premise: The Fortress of Control
The on-premise model is the classic approach. You buy, own, and manage all the servers, storage, and networking hardware right inside your own data center. This is the equivalent of owning your home—you have absolute control over everything, from the locks on the doors to the security system.
This setup gives you maximum command over your data security and system performance. Since the data never physically leaves your building, it can be simpler to navigate strict data sovereignty laws and compliance mandates. But that control comes with a hefty price tag.
- High Initial Cost: You’re looking at a significant upfront capital investment for hardware, software licenses, and the physical space to house it all.
- IT Overhead: It requires a skilled, in-house IT team to handle the daily grind of maintenance, updates, and security patches.
- Scalability Challenges: Need more storage or power? That means a manual, often expensive and time-consuming project to buy and install more hardware.
Cloud-Based: The Engine of Flexibility
A cloud-based architecture means partnering with a provider like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure to host your PACS and RIS. This is like leasing space in a state-of-the-art office building. You don't own the bricks and mortar, but you get access to world-class infrastructure, security, and amenities without the maintenance headaches.
This model is all about agility and scale. Need more storage? It’s available with a few clicks. The pay-as-you-go structure transforms a massive upfront investment into a predictable operational expense. You can explore the benefits of moving your PACS to the cloud in our deep-dive guide on the topic.
The true power of the cloud is how it democratizes access. It unlocks modern teleradiology and collaborative care by making images securely available from anywhere, which is absolutely critical for today’s distributed healthcare networks.
North America, which accounted for nearly 50% of the global market share for these systems in 2023, is quickly moving toward the cloud. A great example is the partnership between Konica Minolta and Apollo Enterprise Imaging. They created a platform that merges RIS and PACS into a single cloud database, a move shown to slash infrastructure costs by 20-30% while giving clinicians better, secure access. You can read the full analysis on this market trend for more details.
Hybrid: The Strategic Balance
For many, the hybrid model strikes the perfect balance. It blends the ironclad security of an on-premise system with the incredible flexibility of the cloud. In a typical hybrid setup, an organization might keep its newest, most frequently accessed imaging data on local servers for lightning-fast internal access. This is your "hot" storage.
At the same time, older studies that are accessed less often are automatically migrated to a secure, low-cost cloud archive for long-term retention. This "best of both worlds" approach optimizes both performance and cost. It allows you to protect sensitive data on-site while tapping into the cloud's infinite scale for archiving and disaster recovery. It's a smart, strategic choice for any organization that wants to modernize without having to rip and replace everything.
At PYCAD, we specialize in designing solutions that fit perfectly into any of these architectural models. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, ensuring your team has seamless and secure access whether your data lives down the hall, in the cloud, or both. To see examples of our work, please visit our portfolio page.
The Power of AI and Web DICOM Viewers
Having a solid PACS and RIS architecture is the starting point, but the real magic happens when you introduce technologies that bring that system to life. We’re moving past the days of just storing images and scheduling appointments. We’re entering an era where smart tools and go-anywhere access are completely changing the game in diagnostics.
This is where Artificial Intelligence and web-based DICOM viewers come in, turning what was once a passive digital filing cabinet into an active, life-saving partner in patient care.
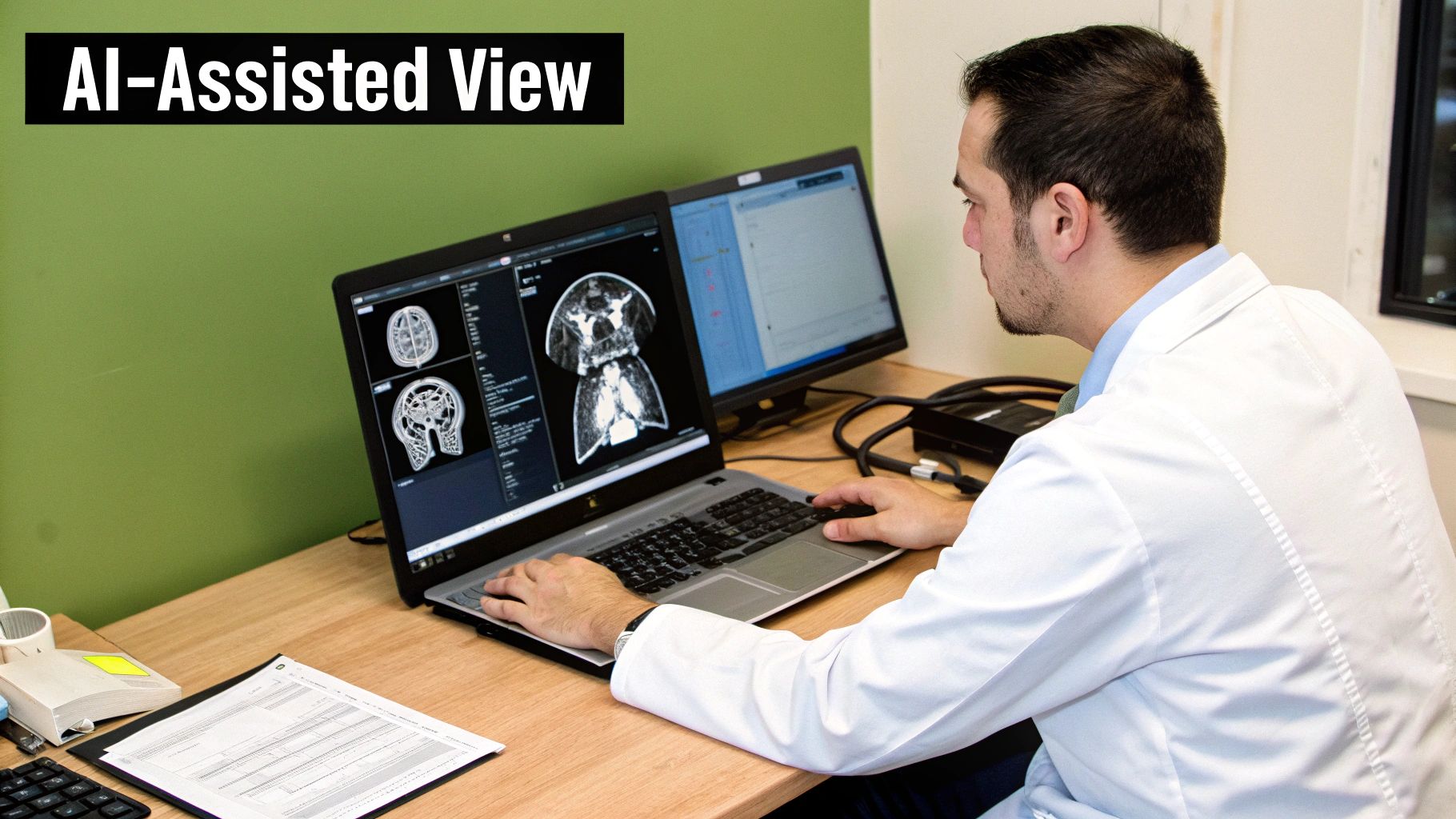
It’s a huge leap forward—one that puts incredible power directly into the hands of clinicians and raises the standard of care for everyone. We’re building a future where every image isn't just stored but truly understood, and every diagnosis is backed by the full power of intelligent data.
Unlocking Images with Web DICOM Viewers
For years, viewing medical images meant being physically tethered to a specific, high-powered workstation loaded with proprietary software. This created frustrating bottlenecks, restricting access to radiologists who were literally in the reading room. Web DICOM viewers completely shatter those walls.
These viewers are often called "zero-footprint" because they don't require any software installation—they just run in a modern web browser. That simple change has massive implications. A specialist can now review an urgent scan from home. A surgeon can pull up a patient’s MRI on a tablet right in the operating room. A team of doctors from different continents can collaborate on a complex case in real-time. It’s all about democratizing access to critical visual data.
The core idea behind web viewers is simple but profound: make life-saving images as accessible and collaborative as any other piece of digital information, all while keeping them secure and instantly available.
At PYCAD, this is exactly what we do. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging platforms, focusing on creating a seamless and intuitive experience. These viewers are the windows through which clinicians can finally see and interact with the rich data stored inside the PACS. To get a feel for how these tools work, you can explore an online DICOM viewer for free and see the technology firsthand.
The Rise of AI as a Radiologist's Assistant
If web viewers open the door, Artificial Intelligence provides the brilliant insight waiting on the other side. AI algorithms are now being woven directly into the PACS and RIS workflow, acting as a tireless and incredibly sharp assistant for the radiologist. Let's be clear: this isn't about replacing human experts. It’s about augmenting their expertise.
AI can analyze thousands of images in the time it takes a human to review just one. It truly shines at tasks that demand immense precision and pattern recognition, such as:
- Triage and Prioritization: AI can scan incoming studies and flag those with suspected critical findings—like a brain bleed or pulmonary embolism—pushing them straight to the top of the radiologist’s worklist.
- Automated Measurements: It can handle tedious but vital tasks like measuring a tumor or calculating cardiac output with perfect consistency, freeing up the radiologist to concentrate on the bigger picture.
- Abnormality Detection: Think of AI as a second set of eyes. It can highlight subtle abnormalities or hard-to-spot lesions that might otherwise be missed, giving a real boost to diagnostic accuracy.
The combination of these AI capabilities is supercharging the entire pacs radiology information system. This partnership between human and machine is quickly becoming the new standard of care, leading to faster diagnoses, lighter workloads, and most importantly, better patient outcomes.
The impact, both financially and clinically, is impossible to ignore. The market for radiology information systems is expected to climb to an incredible USD 3.92 billion by 2034, with AI-driven features being a major catalyst. In some cases, AI tools can spot abnormalities with over 95% accuracy and have been proven to reduce radiologist workloads by as much as 30%, unlocking massive efficiency gains. Learn more about the projected growth of the RIS market.
Here at PYCAD, we are right in the middle of this movement, integrating sophisticated AI solutions into the custom web platforms we build. We believe the future of radiology is collaborative, intelligent, and accessible to all. To see how we bring these powerful pieces together, we invite you to explore our portfolio page.
7. Navigating Security and Interoperability
When you're dealing with patient data, you're holding someone's life story in your hands. In the world of a pacs radiology information system, this is a profound responsibility. We're not just talking about best practices; protecting this data is a non-negotiable legal and ethical mandate. Every single piece of information, from a patient's name in the RIS to their MRI scan in the PACS, is considered protected health information (PHI) and demands Fort Knox-level security.
This is where crucial governance frameworks like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe come into play. Think of them less as rulebooks and more as the architectural blueprints for building trust. They are the foundation upon which secure, reliable systems are built—systems that give patients confidence that their most private information will remain just that: private.

Translating Compliance into Technical Safeguards
Bringing these regulations to life means translating dense legal text into hard-coded technical controls. These safeguards are the digital locks, virtual security guards, and unblinking access logs that protect the entire ecosystem.
- End-to-End Encryption: This is your first and most fundamental line of defense. Data has to be encrypted both "at rest" (while it's sitting in the PACS archive) and "in transit" (as it moves across the network to a DICOM viewer). It's simple: if data gets intercepted, it's just unreadable noise to anyone without the key.
- Granular Access Controls: Let’s be real—not everyone in a hospital needs to see every patient's scans. Role-based access control is all about granting permissions on a need-to-know basis. A radiologist gets full access to images, but the billing staff might only need to see the administrative data in the RIS.
- Immutable Audit Trails: Every single action—every click, every view, every edit—must be logged. These audit trails create a permanent, unchangeable record of who did what, and when. This isn't just for compliance; it's essential for accountability and for tracing any potential security incident back to its source.
Forging Connections with Interoperability
Security locks the data down, but interoperability is what allows it to be shared safely and effectively. A PACS or RIS that’s an island is useless in modern healthcare. For a system to be truly valuable, it must speak the same language as the other critical systems in the hospital, creating a complete and coherent patient story.
This communication is made possible by standards. If you want to get into the nuts and bolts of how medical images talk to each other, you can learn more about the crucial role of DICOM standards in our detailed guide.
The whole point of interoperability is to build a seamless digital environment. It's about letting data flow freely but securely between systems, giving clinicians the complete picture they need to make the best possible decisions for their patients.
A few key initiatives make this fluid exchange of information a reality:
- IHE (Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise): Think of IHE as the master translator. It provides detailed "profiles" that act as playbooks, showing vendors how to use standards like DICOM and HL7 to solve specific clinical problems. This ensures that a system from one company can reliably work with another.
- EHR (Electronic Health Record): The RIS must be deeply connected to the hospital's central EHR. It needs to pull patient demographics from the EHR and, just as importantly, push final radiology reports back, making them a permanent part of the official patient record.
- VNA (Vendor Neutral Archive): A VNA is a game-changer for long-term strategy. It decouples the image storage from the PACS application itself, creating a standards-based archive that prevents you from being locked into one vendor. This makes data migration and future system upgrades infinitely simpler.
When bringing powerful tools like AI into this sensitive environment, adhering to regulations is non-negotiable. For a closer look at what this entails, you can find great information on topics like GDPR Compliant AI Integration.
At PYCAD, we see the bigger picture. We don't just build software; we architect secure, connected ecosystems where data flows intelligently. We build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms, with security and interoperability woven into the very fabric of our design philosophy. You can see these principles in action by checking out our portfolio page.
Your Roadmap to a Successful PACS & RIS Implementation
Turning a vision for better imaging into a working reality isn't magic—it's about having a smart, practical plan. Choosing and implementing a new PACS and radiology information system is a massive undertaking, one that will define your clinical workflow for years. Think of this checklist as your roadmap, guiding you through the big decisions so you can choose a partner who’s truly aligned with your goals.
1. Start With Why: Defining Your Core Needs
Before you dive into product demos and sales pitches, you need to look inward. What specific problems are you actually trying to solve? Get everyone who will use the system in a room—radiologists, technologists, administrative staff, IT—and map out your current pain points.
Create two lists: "must-haves" and "nice-to-haves." Is your number one priority slashing report turnaround times? Do you need to build a robust teleradiology program from the ground up? Or is integrating new AI tools the main driver? Nailing down these objectives at the very beginning will act as your north star for the entire journey.
2. Putting Vendors Under the Microscope
With your needs clearly defined, it's time to find the right partner. This is where you need to look past the slick brochures and get into the nitty-gritty details that make or break a long-term relationship.
- Insist on True Interoperability: Don't just take their word for it. Confirm that their system is built on a rock-solid foundation of DICOM and HL7 standards. Ask them to show you real, live examples of how they’ve integrated with other EHRs and hospital systems.
- Think About Tomorrow's Growth: Your imaging volume isn't static; it's going to grow. Can their architecture—whether it's on-premise, cloud, or a hybrid model—scale with you without breaking the bank?
- Gauge Their Support and Training: A powerful system without great support is a recipe for frustration. What do their training programs look like? What are their guaranteed support response times and service level agreements (SLAs)?
The right vendor isn’t just selling you a piece of software. They are becoming a strategic partner in your patient care mission. Their expertise, reliability, and vision for the future are just as critical as any feature on a spec sheet.
3. Charting a Course for a Smooth Launch
Finally, you need a bulletproof plan for the transition itself. A detailed implementation and data migration strategy is what separates a seamless launch from a chaotic one. This means mapping out every single step, from the technical nuts and bolts of the setup to data cleansing and, most importantly, comprehensive training for your staff.
At PYCAD, we live and breathe this ecosystem. Our expertise lies in crafting the critical pieces that make these systems tick, as we build custom web DICOM viewers and integrate them into medical imaging web platforms. We're obsessed with security, interoperability, and creating tools that people actually love to use, ensuring our solutions slot perfectly into your bigger picture.
To see how we put all these principles into practice, take a look at our work on our portfolio page.
Answering Your Questions
When you start digging into the world of radiology technology, a few key questions almost always pop up. It's totally natural. Understanding how these powerful systems work together is the first step toward appreciating just how much they can improve patient care and make a clinic run smoothly. Let's tackle some of the most common ones.
What’s the real difference between a RIS and a PACS? Think of it this way: the Radiology Information System (RIS) is the front office and the brains of the operation. It manages the entire patient journey—from scheduling an appointment and tracking their visit to handling billing and creating the final report. It's all about the text-based data and the workflow.
The Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), on the other hand, is the massive, high-tech image library. Its sole focus is to store, retrieve, and display all the medical images—the X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. They're two different systems, but they have to work together perfectly to create a seamless experience.
Can a Web DICOM Viewer Work with Any PACS?
For the most part, yes—and that’s by design. Modern web DICOM viewers are built on universal standards, specifically DICOMweb (which includes protocols like WADO-RS, STOW-RS, and QIDO-RS). This common language allows them to communicate with just about any modern PACS or Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA) that also speaks it.
This is a huge win for healthcare providers. It means you're not locked into a single vendor's viewer. You can choose the best tool for your radiologists without worrying about compatibility issues. At PYCAD, we specialize in building custom web DICOM viewers and integrating them into medical imaging platforms, making sure they plug right into your existing setup.
How Does AI Fit into the PACS and RIS Workflow?
This is where things get really exciting. AI isn't just a buzzword; it’s a game-changer that weaves itself into the workflow at critical moments to boost both speed and diagnostic precision. As soon as a new set of images hits the PACS, an AI algorithm can automatically get to work.
Think of AI as a brilliant assistant for the radiologist. It’s not there to make the final call, but to provide incredibly insightful, data-backed suggestions that help the human expert make faster, more confident decisions for better patient outcomes.
For instance, an AI tool could instantly flag a study that looks critical, pushing it to the top of the radiologist's to-do list. It might perform complex measurements automatically or highlight a tiny, easy-to-miss anomaly right on the image. The radiologist sees these AI-powered insights directly in their DICOM viewer, and the findings can be seamlessly pulled into the final report in the RIS. The system transforms from a simple storage locker into an active partner in diagnosis.
At PYCAD, our passion is building the secure, smart, and connected platforms that are shaping the future of medical imaging. We build solutions that sharpen diagnostic abilities and simplify clinical workflows. To see what we've been working on, we invite you to explore our portfolio at https://pycad.co/portfolio.





